Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Guide Pdf Chapter 23 Economic Biology Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 23 Economic Biology
9th Science Guide Economic Biology Text Book Back Questions and Answers
![]()
I. Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
The production and management of fish is called
(a) Pisciculture
(b) Sericulture
(c) Aquaculture
(d) Monoculture
Answer:
(a) Pisciculture
Question 2.
Which one of the following is not an exotic breed of cow?
(a) Jersey
(b) Holstein-Friesan
(c) Sahiwal
(d) Brown Swiss
Answer:
(c) Sahiwal
![]()
Question 3.
Which one of the following is an Italian species of honey bee?
(a) Apis mellifera
(b) Apis dorsata
(c) Apis florae
(d) Apis cerana
Answer:
(a) Apis mellifera
Question 4.
Which one of the following is not an Indian major carp?
(a) Rohu
(b) Catla
(c) Mrigal
(d) Singhara
Answer:
(d) Singhara
![]()
Question 5.
Drones in the honey bee colony are formed from
(a) unfertilized egg
(b) fertilized egg
(c) parthenogenesis
(d) both b and c
Answer:
(a) unfertilized egg
Question 6.
Which of the following is an high milk yielding variety of cow?
(a) Holstein-Friesan
(b) Dorset
(c) Sahiwal
(d) Red Sindhi
Answer:
(a) Holstein-Friesan
![]()
Question 7.
Which Indian variety of honeybee is commonly used for apiculture?
(a) Apis dorsata
(b) Apis florea
(c) Apis niellifera
(d) Apisindica
Answer:
(d) Apis indica
Question 8.
…………….. is the method of grafting plants without soil.
(a) Horticulture
(b) Hydroponics
(c) Pomology
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Hydroponics
Question 9.
The symbiotic association of fungi and vascular plants is
(a) Lichen
(b) Rhizobium
(c) Mycorrhizae
(d) Azotobacter
Answer:
(c) Mycorrhizae
![]()
Question 10.
The plant body of mushroom is
(a) Spawn
(b) Mycelium
(c) Leaf
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) Mycelium
II. Fill in the blanks :
1. Quinine drug is obtained from …………………
Answer:
Cinchona (cinjona maram)
2. Carica papaya leaf can cure disease.
Answer:
Dengue
3. Vermicompost is a type of soil made by …………… and microorganisms.
Answer:
Earthworm
![]()
4. …………… refers to the culture of prawns, pearl and edible oysters.
Answer:
Aquaculture
5. The largest member in a honey bee hive is is the ……………
Answer:
Queen Bee
6. …………… is a preservative in honey.
Answer:
Formic acid
7. …………… is the method of culturing different variety of fish in a water body.
Answer:
Polyculture
III. Say true or false. If false, correct Hie statement:
1. Mycorrhiza is an algae.
Answer:
Correct statement: Mycorrhiza is a tumgi
2. Milch animals are used in agriculture and transport.
Answer:
False
Correct statement: Milch animals are used in milk production
![]()
3. Apis florea is a rock bee.
Answer:
False
Correct statement: Apis florea is a rock bee.
4. Ongole is an exotic breed of cattle.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Ongole is an Indian breed of cattle.
5. Sheep manure contains high nutrients than farm yard manure.
Answer:
True.
IV. Differentiate the following :
(a) Exotic breed and Indigenous breed.
Answer:
| Exotic Breed | Indigenous Breed |
| The exotic breeds are imported from foreign countries. | Indigenous Breeds are native of India. |
| They include Jersey, Brown Swiss, Holstein – Friesian. | They include Sahiwal, Red Sindhi, Deoni and Gir. |
![]()
(b) Pollen and Nectar
Answer:
| Pollen | Nectar |
| It is fine powder of microscopic particles from the male flower. | It is a‘sweet sdbstance, produced by plants to attract pollinators such as bee, butterfly. |
| Pollen is produced by anther, male reproductive organ. | Nectar is converted into Honey. |
(c) Shrimp and Prawn
Answer:
| Shrimp | Prawn |
| Marine inhibited prawns are called Shrimps, which breed in deep sea. | Prawn are crustaceans inhibited in fresh water, marine water, estuaries, etc |
(d) Farmyard manure and Sheep manure
Answer:
| Farmyard manure | Sheep manure |
| It is a mixture of cattle dung, urine, litter material, and other dairy wastes. | This is the manure of sheep or Goat |
| 0.5% Nitrogen, 0.2% Phosphate, 0.5% potash. | 3% Nitrogen, 1% phosphorus pentoxide 2% potassium oxide. |
| Less compared to sheep manure | High nutrients. |
V. Match the following :
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Lobsters | Marine fish |
| 2. Catla | Pearl |
| 3. Sea bass | Shell fish |
| 4. Oysters | Paddy |
| 5. Pokkali | Fin fish |
| 6. Pleurotus sps | Psoriosis |
| 7. Sarpagandha | Oyster mushroom |
| 8. Olericulture | Reserpine |
| 9. Wrighta tinctoria | Vegetable farming |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Lobsters | Shell fish |
| 2. Catla | Fin fish Pearl |
| 3. Sea bass | Marine fish |
| 4. Oysters | Pearl |
| 5. Pokkali | Paddy |
| 6. Pleurotus sps | Oyster mushroom |
| 7. Sarpagandha | Reserpine |
| 8. Olericulture | Vegetable farming |
| 9. Wrighta tinctoria | Psoriosis |
![]()
VI. Answer briefly :
Question 1.
What are the secondary metabolites?
Answer:
Most medicines are obtained either directly or indirectly from plants. All the major system of medicines such as Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, Homeopathy (AYUSH) use drugs obtained from plants and animals. These drugs from medicinal plants are called secondary metabolites.
Question 2.
What are the types of vegetable gardens?
Answer:
Types of vegetable gardens are
- Kitchen or Nutrition gardening
- Commercial gardening
- Vegetable forcing
- Greenhouse (or) Poly House
- Organic Vegetable Gardening.
![]()
Question 3.
Mention any two mushroom preservation methods.
Answer:
Drying and Vacuum Cooling are some methods used to preserve mushrooms.
Question 4.
Enumerate the advantages of vermicompost over chemical fertilizer.
Answer:
- Vermicompost is free from pathogens and toxic elements.
- It enhances the decomposition of organic matter in soil.
- It is rich in beneficial microflora.
- It contains valuable vitamins, enzymes and growth regulator substances.
Question 5.
What are the species of earthworm used for vermiculture?
Answer:
Among the vast community of earthworms, only very few species can be used for vermicompost production. They are Perionyx excavatus (Indian blue worm), Eisenia fetida (Red worms), Eudrilus eugeniae (African nightcrawler).
![]()
Question 6.
List the medicinal importance, of honey.
Answer:
- Honey has an antiseptic and antibacterial property.
- It is a blood purifier.
- It helps in building up hemoglobin content in the blood.
- It prevents cough, cold, fever, and relieves sore throat.
- It is a remedy for ulcers of the tongue, stomach, and intestine.
- It enhances digestion and appetite.
VII. Answer in detail :
Question 1.
Enumerate the advantage of hydroponics.
Answer:
Hydroponics was demonstrated by a German Botanist Julius Von Sachs in 1980.
Advantages:
- Crops can be grown in places where the land is limited, doesn’t exist, or is heavily contaminated.
- The climate – temperature, humidity, light intensification, the composition of the air can be monitored.
- Conservation of water and nutrients.
- Controlled plant growth.
- No intrusion by weeds.
- Fewer pests & diseases
- Minimal use of insecticide or herbicides
- In deserts and Arctic regions hydroponics can be an effective alternative method.
- Hydroponics is successfully employed for the commercial production of seedless cucumber and tomato.
Question 2.
Define Mushroom culture. Explain the mushroom cultivation methods.
Answer:
Mushroom is a fungus belonging to basidiomycetes. It is rich in proteins, fibres, vitamins and minerals. Mushroom culture is the process of producing food, medicine, and other products by the cultivation of mushrooms.
Mushrooms can be cultivated either on paddy straw or on the wood log.
Major stages of mushroom cultivation are;
- Composting: Compost is prepared by mixing paddy straw with a number of organic materials like cow dung and inorganic fertilizers. It is kept at about 50°C for one week.
- Spawning: Spawn is the mushroom seed. It is prepared by growing fungal mycelium in grains under sterile conditions. Spawn is sown on the compost.
- Casing: Compost is covered with a thin layer of soil. It gives support to the growing mushroom, provides humidity, and helps regulate the temperature.
- Pinning: Mycelium starts to form a little bud, which will develop into mushrooms. Those little white buds are called pins.
- Harvesting: Mushroom grows better in 15°C – 23°C. They grow 3 cm in a week which is the normal size for harvesting. In the third week, the first flush mushroom can be harvested.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the sources of organic resources for vermicomposting?
Answer:
Biologically degradable organic wastes are used as potential organic resources for vermicomposting.
They are :
- Agricultural wastes (Crop residue, Vegetable waste, Sugarcane trash).
- Crop residues (rice straw, tea wastes, cereal and pulse residues, rice husk, tobacco wastes, coir wastes).
- Leaf litter.
- Fruit and vegetable wastes.
- Animal wastes (cattle dung, poultry droppings, pig slurry, goat and sheep droppings).
- Biogas slurry.
Question 4.
Give an account of different types of fish ponds used for rearing fishes.
Answer:
Types of ponds for fish culture
The fish farm requires different types of the pond for the various developmental stages of fish growth. They are:
- Breeding pond: Healthy and sexually mature male and female fishes are collected and introduced in this pond for breeding. The eggs released by the female are fertilized by the sperm and fertilized eggs float in water as frothy mass.
- Hatchling pits: The fertilized eggs are transferred to hatching pits for hatching. Two types of hatching pits are hatcheries and hatching hapas.
- Nursery ponds: The hatchlings are transferred from hatching pits after 2 to 7 days. The hatchlings grow into fry and are cultured in these ponds for about 60 days with proper feeding till they reach 2 -2.5 cm in length.
- Rearing ponds: Rearing ponds are used to culture the fry. The fish fry are transferred from nursery pond to rearing ponds and are maintained for about three months till they reach 10 to 15 cm in length. In these rearing ponds the fry develops into fingerlings.
- Stocking pond: The stocking pond is also called a culture pond or production pond. These ponds are used to rear fingerlings upto the marketable size. Before releasing the fingerlings, the pond is manured with organic manure and inorganic fertilizers.
![]()
Question 5.
Classify the different breeds of the cattle with suitable examples.
Answer:
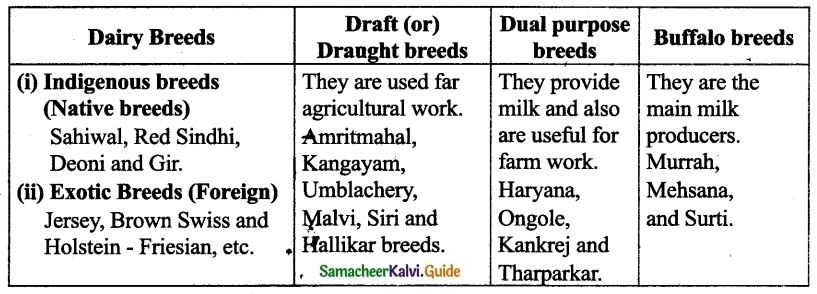
VIII. Higher Order Thinking Skills :
Question 1.
Biomanuring plays an important role in agriculture. Justify.
Answer:
- Biomanuring reduces soil pollution, water pollution and air pollution, etc.
- It protects soil health and promotes soil fertility.
- It provides healthy production of vegetables, fruits etc.
- It makes the soil fertile by adding nutrients like nitrogen.
Question 2.
Each bee hive consists of hexagonal cells. Name the material in which the cell is formed and mention the significance of the hexagonal cells.
Answer:
- The comb of the bees is formed mainly by the secretion of the wax glands present in the abdomen of the worker bee.
- A comb is a vertical sheet of wax with double layer of hexagonal / cells.
- Hexagonal cells serve as storage vessels for honey as well as homes to raise the young bees.
![]()
9th Science Guide Economic Biology Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
Olericulture refers to the farming of ………………..
(a) Vegetable
(b) Flowers
(c) Fruits
(d) All of these
Answer:
a) Vegetable
Question 2.
India is the ………………..largest producer of vegetables next to China.
(a) First
(b) Second
(c) Third
(d) Fourth
Answer:
(b) Second
![]()
Question 3.
Tuber rose is cultivated from ………………..
(a) Madurai zone
(b) Hill area zone
(c) Coimbatore zone
(d) Hosurzone
Answer:
(c) Coimbatore zone
Question 4.
Green manure also helps in reclamation of ……………….. soils.
(a) Acidic
(b) Alkaline
(c) neutral
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Alkaline
![]()
Question 5.
Azolla having a cyanobacterial symbiotic association with ………………..
(a) Azotobacter
(b) Azospirillum
(c) Mycorrhizae
(d) Anabaena
Answer:
(d) Anabaena
Question 6.
Quinine is a best drug for treatment of ………………..
(a) Dengue
(b) Psoriasis
(c) Malaria
(d) Leukemia
Answer:
(c) Malaria
Question 7.
Nilavembu kashayam is givep to patients/people to protect from . ………………..
(a) Dengue
(b) Chikungunya
(c) Diabetes
(d) All of these
Ans :
(d) All of these
![]()
Question 8.
Reserpine is derived from ………………
(a) Cathyranthusroseus
(b) Rauwolfia serpentina
(c) Hemidesmus indicus
(d) Aloe vera
Answer:
(b) Rauwolfia serpentina
Question 9.
Casing is done on the mushroom to ………………..
(a) support the growth of mushroom
(b) provide humidity to mushroom
(c) regulate the temperature
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 10.
The growth medium of Aeroponics is
(a) Nutrients
(b) Water
(c) air
(d) soil
Answer:
(c) air
![]()
Question 11.
The Indigenous Draught breed from Thanjavur district is ………………..
(a) Pulikulam
(b) Bargur
(c) Ongole
(d) Umblachery
Answer:
(d) Umblachery
Question 12.
………………..are low in fibre and contain a high level of carbohydrates, protein, and other
nutrients.
(a) Silage
(b) Concentrates
(c) Roughage
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Concentrates
![]()
Question 13.
Operation Flood is the programme for ………………..development.
(a) Dairy
(b) Cattle
(c) Marine
(d) Agriculture
Answer:
(a) Dairy
Question 14.
Air-breathing fishes are cultured in ………. water.
(a) Brackish
(b) Fresh
(c) Marine
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) Fresh
Question 15.
Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI) is situated at …………………
(a) Chennai
(b) Mumbai
(c) Cochin
(d) Vizag
Answer:
(c) Cochin
![]()
Question 16.
Culture of fishes along with Agricultural crops is known as ………………..
(a) Polyculture
(b) Extensive culture
(c) Integrated culture
(d) Intensive culture
Answer:
(c) Integrated culture
Question 17.
The longest marine water prawn is
(a) Penaeus Indicus
(b) Penaeus monodon
(c) Macro brachium rosenbergii
(d) Macro brachium malcoumsonii
Answer:
(b) Penaeus monodon
![]()
Question 18.
Earthworms are sacred – This statement was made by ………………..
(a) Aristotle
(b) Darwin
(c) Plato
(d) Cleopatra
Answer:
(d) Cleopatra
Question 19.
Vermicompost is similar to ……………….. in colour and appearance.
(a) sheep manure
(b) Farmyard manure
(c) Green manure
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) Farmyard manure
Question 20.
………………..is an enzyme present in Honey
(a) Sucrose
(b) Dextrose
(c) Invertase
(d) Maltase
Answer:
(c) Invertase
![]()
Question 21.
Fastest growing sector in Agriculture is ………………..
(a) Vegetable forcing
(b) Hydroponics
(c) Greenhouse
(d) Aqua ponies
Answer:
(c) Greenhouse
Question 22.
Which of the following are Indian cattle?
(i) Bos indicus
(ii) Bos domesticus
(iii) Bos bubalis
(iv) Bos vulgaris
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(b) (i) and (iii)
![]()
Question 23.
Which one of the following is referred as red worms?
(a) Eudrilus fetida
(b) Eudrilus eugieniae
(c) Eisenia fetida
(d) Lampito mauritii
Answer:
(c) Eisenia fetida
Question 24.
Mehsana is a breed of
(a) Cow
(b) Buffalo
(c) Goat
(d) Sheep
Answer:
(b) Buffalo
![]()
Question 25.
Binomial name of Nilavemubu is ………………..
(a) Leucas Aspera
(b) Andrographis paniculata
(c) Crotalaria juncea
(d) Cassia fistula
Answer:
(b) Andrographis paniculata
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. ………….. is the most intensive type of vegetable growing.
Answer:
Vegetable forcing
2. India stands first in the world in the production of…………………… and …………………….
Answer:
Potato, Lady’s finger
![]()
3. Compost is a …………………… as well as a fertilizer, which is rich in nutrients.
Answer:
Soil conditioner
4. Earthworms eat …………………… and excrete it in a digested form.
Answer:
biomass
5. Green manure is obtained from undecomposed green material derived from …………………… plants.
Answer:
Leguminous
6. …………………… is a type of Bio-fertilizers that are capable of producing antifungal and antibacterial compounds.
Answer:
Azotobacter
![]()
7. Mycorrhizae increase the uptake of …………………….
Answer:
Phosphorous
8. …………………… is the study of chemical substances derived from plants .
Answer:
Phytochemistry
9. …………………… is used as an antidote for snake bite.
Answer:
Chivan Amalpodi (Sarpagandha)
![]()
10. Alkaloids, Terpenoids, flavonoids etc are called …………………… metabolites.
Answer:
Secondary
11. India’s first anti-diabetic ayurvedic drug is …………………….
Answer:
BGR-34
12. Mushroom is a fungi belonging to …………………….
Answer:
Basidiomycetes
![]()
13. Hydroponics was first demonstrated by German botanist …………………….
Answer:
Julius Von Sachs
14. Milk production in cattle depends upon the duration of ……………………
Answer:
Lactation
15. Jallikattu madu belongs to …………………… breed.
Answer:
Indigenous Draught
16. Young female calf is called as……………………
Answer:
Heifer
![]()
17. Dr.Verghese Kurien is the Father of …………………….
Answer:
White revolution
18. Panchagavya is an…………………… Fertilizer .
Answer:
organic liquid
19. The Central Institute of Brackish Water Aquaculture (CIBA) was established in …………………….
Answer:
1987
20. India holds …………………… position in Marine fish production in the world.
Answer:
10th
![]()
21. The eggs released by the female fish are fertilized by the sperm and fertilized eggs float in water as …………………….
Answer:
frothy mass
22. Hatching period in Hatchling pits is …………………….
Answer:
2-7days
![]()
23. PUFA stands for ……………………
Answer:
Poly Unsaturated Fatty Acid
24. ………………….. culture is the oldest and traditional method of prawn culture practiced in Kerala.
Answer:
Pokkali
25. The nutrient rich materials that are excreted by earthworms knows as …………………….
Answer:
worm castings
26. The …………………… cells contain honey and pollen.
Answer:
Storage
![]()
27. …………………… and…………………… give sweet taste to the honey.
Answer:
Dextrose, Sucrose
28. One kilogram of honey contains …………………… calories.
Answer:
3200
29. …………………… is widely used in cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries.
Answer:
Bee wax
![]()
30. …………………… is a nodulating type of microorganism associating symbiotically with the root of legume plants.
Answer:
Rhizobium
31. …………………… is the maintenance of bee colonies in modem hives.
Answer:
Beekeeping
III. Match the following:
I.
| (1) Homeopathy | a) Hippocrates |
| (2) Siddha | b) Patanjali |
| (3) Unani | c) Charaka Samhita |
| (4) Ayurveda | d) Agasthya |
| (5) Yoga | e) Samuel Hahnemann |
Answer:
1-e, 2-d,3 -a,4-c,5-b
![]()
II.
| (1) Rhizobium | a) Crop plants |
| (2) Azolla | b) Antifungal and antibacterial compounds |
| (3) Azotobacter | c) vascular plants |
| (4) Mycorrhizae | d) leguminous plants |
| (5) Azospirillum | e) Floating nitrogen factory |
Answer:
1-d, 2-e, 3-b, 4-c, 5-a
III.
| (1) Paddy straw Mushroom | a) Volvariella volvacea |
| (2) Lingzhi Mushroom | b) Agaricus bisporus |
| (3) Oyster Mushroom | c) Pieurotussps |
| (4) Button Mushroom | d) Ganoderma lucidum |
Answer:
1-a, 2-d, 3-c, 4-b
![]()
IV.
| (1) Bargur | a) Indigenous dairy breeds |
| (2) Tharparkar | b) Buffalo breeds |
| (3) Murrah | c) Indigenous Draft breeds |
| (4) Gir | d) Dual-purpose breeds |
Answer:
1 – c, 2d, 3 – b, 4 – a
IV. Say true or false. If false, correct the statement:
1. Edible mushrooms are valuable source of supplementary lipids.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Edible mushrooms are valuable source of supplementary proteins.
2. The yield of greenhouse is very high compared to outdoor cultivation.
Answer:
True.
![]()
3. Rhizobium fix atmospheric nitrogen and convert them to nitrates.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Rhizobium fix atmospheric nitrogen and convert them to ammonia.
4. The roots in hydroponic plant absorb water and nutrients but do not perform the anchoring function.
Answer:
True.
5. Spawn is prepared by growing fungal mycelium in grains under fertile conditions.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Spawn is prepared by growing fungal mycelium in grains under sterile conditions.
6. Local breed animals show excellent resistance to diseases.
Answer:
True
![]()
7. Milk production of Buffaloes are less than that of cow.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Milk production of Buffaloes are more than that of cow.
8. The salinity of brackish water ranges from 30-35 ppt.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: The salinity of brackish water ranges from 1-32 ppt.
9. Fish meal is used as a feed for cattle and poultry farming animals.
Answer:
True.
10. Earthworm feeds on inorganic wastes and excrete it in digested form known as castings.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Earthworm feeds organic wastes and excrete it in a digested form known as castings.
![]()
11. Medicinal plants contain compounds that can be used for therapeutic purposes.
Answer:
True.
12. Anthraquinones is obtained from Ocimum sanctum.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Anthraquinones is obtained from Aloevera.
13. Aquaponics is a technique of growing plants with their root supplied with moisture present in the air.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Aeroponics is a technique of growing plants with their root supplied with moisture present in the air.
![]()
V. Assertion and Reason :
(a) Direction: In each of the following questions, a statement of Assertion is given and a corresponding statement of Reason is given just below it. Of statements, given below, mark the correct answer as
a. If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
b. If both Assertion and Reason are true that Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
c. If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
d. If Assertion is false but Reason is true.
Question 1.
Assertion : Apiculture, vermiculture are gaining more importance.
Reason : They have economical and commercial values.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion : Foreign dairy breeds are preferred over local breeds.
Reason: The foreign breeds have shorter lactation periods.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true but Reason is false
Reason : The foreign breeds have longer lactation periods.
Question 3.
Assertion : Bullocks are good draft animals in draft breeds.
Reason : Cows are poor milk yielders in draft (or) Draught breeds.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true that Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
Question 4.
Assertion : Porous soil permits both aeration and quick absorption of water.
Reason : The burrowing and soil feeding habits of earthworm make the soil
porous.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
![]()
Question 5.
Assertion : Hydroponics can be defined as a soilless growing system in which plants grow in water.
Reason : If a plant is provided with water, minerals and required nutrients, it will grow well and yield more even in the absence of soil.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
Question 6.
Assertion : Fish and other varieties of aquatic animals are used as food.
Reason : Fish and other varieties of sea food constitute good source of nutrition
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
Question 7.
Assertion : The production of food from animal sources has increased greatly in the last few decades.
Reason : Operation flood and blue revolution production has increased in recent years.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
Blue revolution is the concept of rapid increase in the production of fish and marine product.
![]()
VI. Define the following.
a. Pisciculture
Answer:
Pisciculture or Fish culture is the process of breeding and rearing of fishes in ponds, reservoirs (dams), lakes, rivers, and paddy fields.
b. Apiculture
Answer:
Apiculture is the rearing of honey bee for honey. It is called Beekeeping
![]()
c. Vermiculture
Answer:
Vermiculture involves the artificial rearing or cultivation of earthworms and using them for the production of compost from natural organic wastes.
d. Maricuiture (or) Marine water aquaculture
Answer:
The cultivation of aquatic organisms in seawater is referred as Mariculture (or) Sea farming.
e. Floriculture (or) Flower Farming
Answer:
Floriculture is the art of cultivation of flowering and ornamental plants in garden for beauty or floristry.
f. Compost
Answer:
Compost is a soil conditioner as well as a fertilizer, which is rich in nutrients.
![]()
g. Pomiculture
Answer:
Pomiculture is cultivation, development, entrancement of Fruits.
h. Pinning
Answer:
Pinning is the development of little white buds from mycelium.
VII. Very Short Answer questions :
Question 1.
Name the main classes of Horticulture.
Answer:
They are four main classes of Horticulture
- Pomology (fruit farming),
- Olericulture (vegetable farming),
- Floriculture (flowers farming),
- Landscape gardening.
![]()
Question 2.
What is Floriculture?
Answer:
Floriculture is the art of cultivation of flowering and ornamental plants in garden for beauty (or) floristry.
Question 3.
What is spawning?
Answer:
Spawn is the mushroom seed. It is prepared by growing fungal mycelium in grains under sterile conditions. Spawning is the sowing or planting of spawn on the compost.
![]()
Question 4.
What is Vermicompost?
Answer:
Vermicompost is a method of making compost with the use of earthworms, which ^ generally live in soil.
Question 5.
List the leguminous plants providing green manure.
Answer:
- Sunhemp (Crotolariajuncea)
- Dhaincha (Sesbania aculeata)
- Sesbania (Sesbania speciosa)
Question 6.
Define: phytochemistry.
Answer:
Phytochemistry is the study of phytochemicals which are chemical substances derived from various parts of the plant.
![]()
Question 7.
Name any three edible mushrooms.
Answer:
- Button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus)
- Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus sps),
- Paddy straw mushroom (Volvariella volvacea).
Question 8.
Mention the main problems of harvesting mushrooms.
Answer:
- Discolouration
- Weight and flavour loss.
![]()
Question 9.
Name any three methods to increase mushroom life.
Answer:
- Freezing
- Vacuum Cooling
- Gamma radiation and storing at 15°C.
Question 10.
Write classification of cattle breeds.
Answer:
Cattle breeds are classified into three types:
- Dairy breeds
- Drought (or) Draft breeds
- Dual-purpose breeds.
Question 11.
How is the Fish Meal prepared?
Answer:
Fish meal is prepared from the wastes of fish oil (or) from whole fish.
Question 12.
List the methods employed in Prawn Culture,
Answer:
- Seed collection and hatchery method.
- Paddy cum prawn culture method.
Question 13.
What is Bee wax?
Answer:
Bee wax is the natural by-product secreted by the wax glands of worker bee to construct the combs of a beehive.
![]()
Question 14.
Mention the aim of operation Flood.
Answer:
Operation Flood is based on dairy commodity aid to increase milk supply in urban y areas.
Question 15.
What does NDDB stand for?
Answer:
NDDB – National Dairy Development Board.
VIII. Short Answer questions :
Question 1.
How is compost prepared?
Answer:
Compost is produced by the decomposition of organic matter such as crop residues,
animal wastes, food wastes, industrial and municipal wastes by microorganisms under controlled conditions.
Question 2.
Mention the advantages of Green Manure.
Answer:
- Green Manure improves soil structure.
- It increases water holding capacity and decreases soil loss by erosion.
- It also helps in reclamation of alkaline soils and reduces weed proliferation.
![]()
Question 3.
Write short notes on Mushrooms;
Answer:
- Mushroom is a fungi belonging to basidiomycetes.
- It is rich in proteins, fibres, vitamins and minerals.
- Cultivation of Mushroom takes one to three months.
Question 4.
Explain briefly about Aquaponics.
Answer:
- Aquaponics is a system of a combination of conventional aquaculture with hydroponics in a symbiotic environment.
- Two main parts are (i) Aquaculture – for raising aquatic animals like fish (ii) hydroponics – for raising plants.
Question 5.
Write short notes on Intensive Cattle Development Programme.
Answer:
- Intensive Cattle Development Programme is based on cross-breeding of indigenous cows with exotic European breeds to increase milk production.
- New methods and modem equipments are made available for machine – milking of cows.
![]()
Question 6.
Differentiate Extensive and Intensive Fish culture.
Answer:
Extensive Fish culture
- Culture of fishes in large areas.
- Low stocking density
- Natural feeding
Intensive Fish culture
- Culture of fishes in small areas.
- High stocking density
- Artificial feeding
Question 7.
What is green manure? How is it beneficial?
Answer:
Green manure is obtained by collection and decomposition of green leaves, twigs of trees, shrubs, and herbs growing in wastelands, field bunds etc. Green manure improves soil structure, increases water-holding capacity, and decreases soil loss by erosion. It also helps in the reclamation of alkaline soils and reduces weed proliferation. It is manure obtained from undecomposed green material derived from leguminous plants e.g. Sunhemp, Dhaincha, etc.
![]()
Question 8.
Enumerate the nutritional values of prawns.
Answer:
- Prawns are a rich nutritive source of protein, vitamin A & D, Glycogen and Amino acids.
- They contain less amount of fat.
- Cultured prawns provide Poly Unsaturated Fatty Acid (PUFA).
Question 9.
List the important methods of vermicomposting.
Answer:
- Bin or Container method.
- Vermicomposting of organic wastes in field pits.
- Vermicomposting of organic wastes on ground heaps.
![]()
Question 10.
What do you know about AYUSH?
Answer:
- AYUSH is the ministry of Government of India for Indian (or) Alternative Medicine. ‘
- AYUSH refers to Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha and Homeopathy.
Question 11.
Why do we call Haryana and Kankrej breed of cattle as dual-purpose breeds?
Answer:
Haryana, Kankraj breeds
- provide milk ,
- also useful for farm work.
So, they are called Dual-purpose breeds.
Question 12.
How is the division of labour observed in honey bees?
Answer:
Division of labour by Honey bees :
Queen Bee: Responsible for laying eggs in a colony.
Drones: They fertilize the eggs, produced by Queen Bee.
Worker Bee :
Functions
- Collect Honey
- Look after the young ones
- Clean the comb
- Defend the hive
- Maintain the temperature of beehive.
![]()
Question 13.
What is the nutritional importance of fish liver oils? Name any two marine fishes which yield these oils.
Answer:
Nutritional Importance of Fish liver oil:
- Great medicinal value
- They are rich in Vitamin A, D, and E.
Two marine fishes: Shark, Tuna.
IX. Long Answer questions :
Question 1.
Compare types of Bio fertilisers with their functions.
Answer:
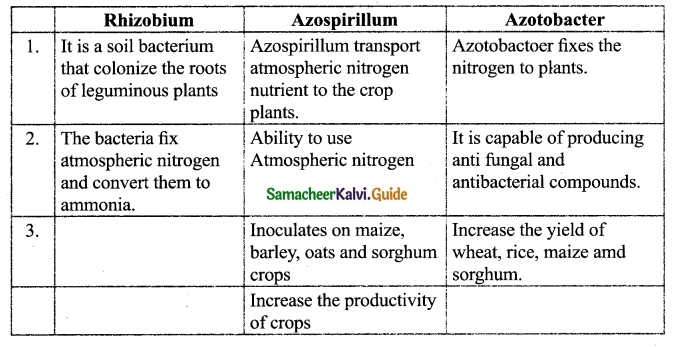
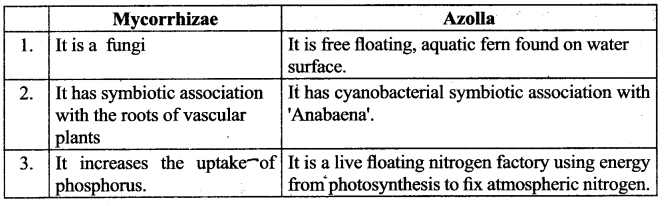
![]()
Question 2.
What are the types of honey bees found in a colony?
Answer:
There are three types of individuals in a colony namely the Queen bee, the drones and the worker bees.
- Queen Bee: The queen is the largest member and the fertile female of the colony. They are formed from fertile eggs. The queen is responsible for laying eggs in a colony. The life span of the queen bee is 3-4 years.
- Drones: They are fertile males. They develop from unfertilized eggs. They are larger than the workers and smaller than the queens. Their main function is to fertilize the eggs produced by the queen.
- Worker Bees: They are sterile female bees and are the smallest members of the colony. Their function is to collect honey, look after the young ones, clean the comb, defend the hive and maintain the temperature of the beehive.
Question 3.
Discuss various types of Honey bees with their functions.
Answer:
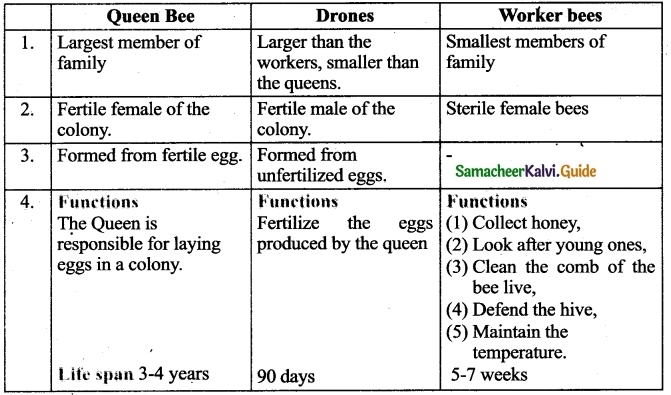
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the structure of Honey Bee Comb.
Answer:
The comb of the bees is formed mainly by the secretion of the wax glands present in the abdomen of the worker bee.
Comb : It is a vertical sheet of wax with double layer of hexagonal cells.
Types of Cells:
(i) Storage cell:
- They are built in the margin and at the top of the comb.
- It contains honey and pollen.
(ii) Brood cells : They are built in the centre and the lower part of the comb. They
are dividecf into three cells such as
- Worker chamber
- Drone chamber
- Queen chamber
Where the larvae developing into worker, drone and queen aye reared.
Question 5.
How is honey formed?
Answer:
- The honey bees suck the nectar from various flowers.
- The nectar passes to the honey sac, where sucrose mixes with nectar.
- By enzymatic action, Nector along with sucrose is converted into Honey.
- Honey is stored in the special chambers of the hive.
![]()
Question 6.
Discuss the various nutrients present in Honey.
Answer:
Honey is a sweet viscous, edible natural food product. ‘
- Sweet taste : Dextrose and sucrose give sweet taste to the honey.
- Honey contains protein, free amino acids, vitamins like ascorbic acid etc.
- Acids such as citric acid, gluconic acid and formic acid are found in honey.
- Minerals such as calcium, Iron, Phosphorous and manganese are present.
- Invertase is the enzyme present in honey.
Question 7.
Give an account on medicinal plants.
Answer:
(1) Katralai (Aloe vera)
It is herbal leaves.
The drug derived from it, is Anthraquinones.
This is best treatment for skin problems and cancer. It heal wounds.
(2) Tulsi (Octimum sanctum)
It is an important herb.
Leaves have medicinal value.
Uses :
- Best medicine for cold and fever.
- It is also useful for cardiac diseases, gynecological disorder.
- Skin disorders and respiratory problems can also be treated.
Sura’s o Science – 9th Std o Unit 23 o Economic Biology
(3) Nilavembu (Andrograhis paniculata)
It is a herbal plant with roots and leaves have medicinal values.
Uses :
- It is the best tonic for dengue fever.
- It is also used to treat diabetes and malaria.
- It is best remedy for ulcer, Influenza, Chikungunya etc.,
(4) Vepalai (Neem) – (Wrightia tinctoria)
It is a medicinal plant with eVtry part has medicinal values.
Uses:
- It has antipyretic, antibacterial and antitumour.
- It gives best immunity power.
- It is used to treat 4rin infections (or) diseases such as Psoriasis.
- It is also good for respiratory disorders, diarrhoea and Swellings.
(5) Pappali (Carica papaya)
Like neem, every part of papaya has medicinal benefits.
Uses:
- Best medicine for Dengue.
- It reduces risk of heart diseases, diabetes arid cancer.
- It lowers blood pressure and heals wounds.
![]()
Question 8.
What are biofertilisers? Give examples. Why are biofertilisers better than other fertilisers?
Answer:
Biofertilisers are substances that contain living microorganisms, when applied to plant promote growth by increasing primary nutrients to host plant.
Examples: (1) Rhizobium (2) Azospirillum (3) Azotobacter (4) Mycorrhizae (5) Azolla
Advantages of Biofertiser over chemical fertilisers :
- Biofertilizers are environmental friendly fertilizers.
- They enrich the nutrient quality of soil.
- They sustain soil health.
- They improve texture, structure and water-holding capacity of soil.
- No adverse effect on plant growth and soil fertility.
Question 9.
Write short notes on
a) Importance of greenhouses
b) Uzahavan mobile Application
c) Major floriculture zones
d) Azospirillum
Answer:
(a) Importance of Greenhouses
- Continuous production of disease-free plants.
- Very less water requirement and less pesticide usage.
- Very high yield and protection from uncertain weather.
(b) Uzhavan App:
- Launched by the Government of Tamilnadu.
- It provides information to farmers about subsidies, crop insurance, and stock of seeds and fertilizer.
(c) Major Floriculture zones :
- Hosurzone
- Chennai zone
- Madurai zone
- Trichy zone
- Coimbatore zone
- Kanyakumari zone
- Hill area zone
(d) Azospirillum :
- It has the ability to use Atmospheric Nitrogen and transport to this nutrient crop plants
- It increases grain productivity, (e.g.) cereals 5-20%, millets 30% and Fodders 50%.
![]()
Question 10.
Explain the feeding management of dairy cattle.
Answer:
- Dairy cattle need balanced rations containing all nutrients in a proportional amount.
- Food additives should contain minerals, vitamins, antibiotics and hormones to
promote the growth of animals, good yield of milk, and protect from diseases. - The daily average feed ratio of milking cow is:
- 15 – 25 kg of roughage (dry grass and green fodder)
- 4 – 5 kg of green mixture.
- 100- 150 litres of water.
X. Thinking Skills.
Question 1.
Arun and Akash were given fertilisers and earthworm compost both to be used in the fields. Akash preferred to use earthworm compost. Why did not select the fertilizers?
Answer:
- Inorganic fertilizers pollute the soil.
- Inorganic fertilizers contain chemicals that are toxic in nature and will result in health problems.
![]()
Question 2.
What is pasturage and how is it related to honey production?
Answer:
- Pasturage is land with herbaceous vegetation cover used for unregulated livestock ; as a part of farms in arid regions.
- Better pasturage provides better habitat for honey bee and honey production.