Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Guide Pdf Chapter 14 Acids, Bases and Salts Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 14 Acids, Bases and Salts
9th Science Guide Acids, Bases and Salts Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer :
![]()
Question 1.
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + ….↑ (H2, O2, CO2)
Answer:
H2
Question 2.
Apple contains malic acid. Orange contains …………………(citric acid, ascorbic acid).
Answer:
ascorbic acid
Question 3.
Acids in plants and animals are organic acids. Whereas Acids in rocks and minerals are …………………. (Inorganic acids, Weak acids).
Answer:
Inorganic acids
![]()
Question 4.
Acids turn blue litmus paper to …………….. (green, red, orange).
Answer:
Red
Question 5.
Since metal carbonate and metal bicarbonate are basic, they react with acids to give salt and water with the liberation of ……………….. (NO2, SO2, CO2).
Answer:
CO2
Question 6.
The hydrated salt of copper sulphate has …………….colour (red, white, blue).
Answer:
Blue
![]()
II. Answer in briefly :
Question 1.
Classify the various types of Acids based on their sources.
Answer:
The acids are classified based on their sources and organic and inorganic acids.
Organic acids – acids present in plants and animals.
Inorganic acids – acids prepared from rocks and minerals.
Question 2.
Write any four uses of acids.
Answer:
- Sulphuric acid is called King of Chemicals because it is used in the preparation of many other compounds. It is used in car batteries also.
- Hydrochloric acid is used as a cleansing agent in toilets.
- Citric acid is used in the preparation of effervescent salts and as a food preservative.
- Nitric acid is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, dyes, paints and drugs.
- Oxalic acid is used to clean iron and manganese deposits from quartz crystals. It is also used as bleach for wood and removing black stains.
- Carbonic acid is used in aerated drinks.
- Tartaric acid is a constituent of baking powder.
![]()
Question 3.
Give the significance of pH of .soil in agriculture.
Answer:
In agriculture, the pH of soil is very important. Citrus fruits require slightly alkaline soil, while rice requires acidic soil and sugarcane requires neutral soil.
Question 4.
What are the various uses of Aquaregia.
Answer:
- It is used chiefly to dissolve metals such as gold and platinum.
- It is used for cleaning and refining gold.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the uses of Plaster of Paris?
Answer:
- It is used for plastering bones.
- It is used for making casts for statues.
Question 6.
Two acids ‘A’ and ‘B’ are given. Acid A gives one hydrogen ion per molecule of the acid in solution. Acid B gives two hydrogen ions per molecule of the acid in solution.
(i) Find out acid A and acid B.
(ii) Which acid is called the King of Chemicals?
Answer:
(i) Acid A – HCl – Hydrochloric acid. Acid B – H2SO4 – Sulphuric acid.
(ii)Sulphuric acid – H2SO4.
![]()
Question 7.
Define aquaregia.
Answer:
It is the mixture of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid prepared optimally in a molar ratio of 3 : 1.
Question 8.
Correct the mistakes :
(a) Washing soda is used for making cakes and bread soft, spongy.
(b) Calcium sulphate hemihydrate is used in textile industry.
Answer:
(a) Baking soda (Sodium bicarbonate – NaHCO3) is used for making cakes and bread soft spongy, (or) Washing soda is used for softening hard water.
(b) Calcium sulphate hemihydrate (CaSO4, 1/2 H2O)is used for plastering bones (or) Bleaching powder (Calcium oxy Chloride – CaOC12) is used in textile industry.
![]()
Question 9.
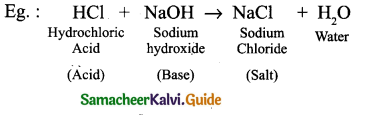
What is neutralization reaction? Give an example.
Answer:
Neutralization reaction is a reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water and H+ ion and OH– ion combines to generate water. The neutralization of a strong acid and strong base has a pHequal 7.
III. Answer in detail :
Question 1.
Differentiate hydrate and anhydrous salts with examples.
Answer:
| Hydrated | Anhydrous |
| 1. Hydrons is a term used to explain a substance that contains water as a constituent | Anhydrous is a term used to explain a substance that does not contain water as a constituent. |
| 2. Composed of water molecules. | Not composed of water molecules. |
| 3. These are known as hydrates. | Known as anhydrates |
| 4. Hydroscopic compounds can form hydrous compounds by Absorption of water from the air. | Anhydrous compounds can absorb water from the air. |
| Ex : CuSO4 5H2O – Blue vitrol. | Ex: NaCl |
![]()
Question 2.
Give the tests to identify Acids and Bases.
Answer:
- Acids turn blue litmus. Red bases turn red litmus blue.
- In acid phenolphthalein is colourless. In base Phenolphthalein is pink in colour.
- In acid methyl orange is pink. In bases methyl orange is yellow
Question 3.
Write any four uses of bases.
Answer:
- Sodium hydroxide is used in the manufacture of soap.
- Calcium hydroxide is used in the whitewashing of buildings.
- Magnesium hydroxide is used as a medicine for a stomach disorder.
- Ammonium hydroxide is used to remove grease stains from cloth.
![]()
Question 4.
Write any five uses of salts.
Answer:
Common Salt (NaCl) :
It is used in our daily food and used as a preservative
Washing Soda (Sodium Carbonate – Na2CO3) :
- It is used in softening hard water.
- It is used in glass, soap and paper industries.
Baking Soda (Sodium bicarbonate -NaHCO3):
- It is used in making of baking powder which is a mixture of baking soda and tartaric acid.
- It is used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
- Baking powder is used to make cakes and bread, soft and spongy.
- It neutralizes excess acid in the stomach and provides relief.
Bleaching powder (Calcium Oxychloride – CaOCl2):
- It is used as a disinfectant.
- It is used in textile industry for bleaching cotton and linen.
Plaster of Paris (Calcium Sulphate Hemihydrate – CaSO4 .1/2 H2O):
- It is used for plastering bones
- It is used for making casts for statues.
![]()
Question 5.
Sulphuric acid is called King of Chemicals. Why is it called so?
Answer:
Sulphuric acid is called King of Chemicals because it is used in the preparation of many other compounds
Intext Activities
ACTIVITY – 2
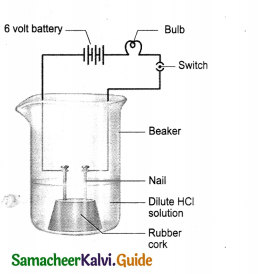
Take solutions of hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid. Fix two nails on a cork and place the cork in a 100 ml beaker.
Connect the nails to the two terminals of a 6 V battery through a bulb and a switch as shown in Figure. Now pour some dilute HCl in the beaker and switch on the current. Repeat the activity with dilute sulphuric acid, glucose and alcohol solutions. What do you observe now? Does the bulb glow in all cases?
Answer:
- The bulb glows when sulphuric acid and hydrochloric acid are used.
- The bulb does not glow when the activity is done with alcohol and glucose solution.
![]()
ACTIVITY – 3
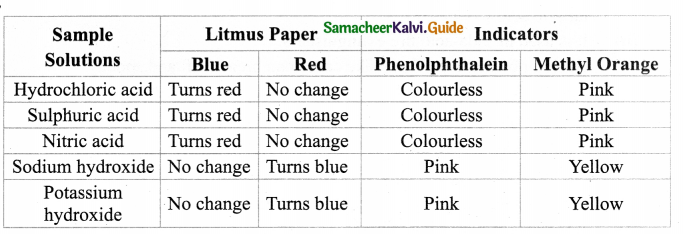
Collect the following samples from the science laboratory – Hydrochloric acid, Sulphuric acid and Nitric acid, Sodium hydroxide, Potassium hydroxide. Take 2 ml of each solution in a test tube and test with a litmus paper and indicators phenolphthalein and Methyl orange. Tabulate your observations.
Answer:
ACTIVITY-4
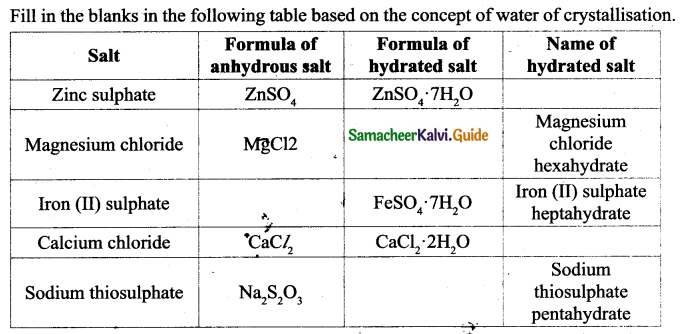
Answer:
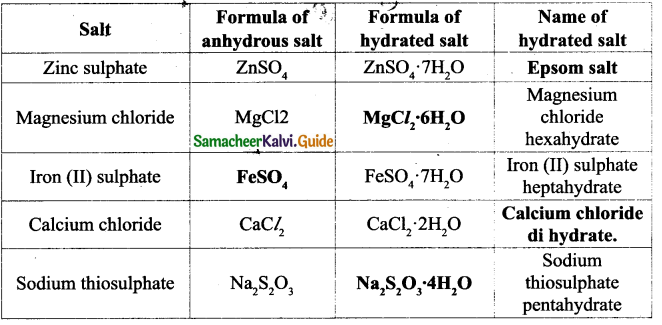
ACTIVITY – 5
Boil about 100 ml of groundwater in a vessel to dryness. After all the water get evaporated observe the inner wall of the vessel. Can you observe any deposits? This is the deposit of dissolved salts present in water.
Answer:
This is the deposit of dissolved salts present in water.
![]()
9th Science Guide Acids, Bases and Salts Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
Acid secreted in our stomach is ……………….
(a) hydrochloric acid
(b) sulphuric acid
(c) nitric acid
(d) carbonic acid
Answer:
(a) hydrochloric acid
Question 2.
Hydrochloric Acid reacts with metal bicarbonates to give ……………
(a) metal chloride
(b) water
(c) carbon di – oxide
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
![]()
Question 3.
…………… & ………….. metals do not react with HCl or HNO3.
(a) Gold & Magnesium
(b) Silver & Magnesium
(c) Gold & Silver
(d) Zinc & Silver
Answer:
(c) Gold & Silver
Question 4.
The molar ratio of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid in aquaregia is ………………..
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 6 : 3
(c) 2 : 3
(d) 3 : 1
Answer:
(d) 3 : 1
![]()
Question 5.
Bases ionise in water to form ……………………. ions.
(a) H+
(b) H3O+
(c) OH–
(d) O2-
Answer:
(c) OH –
Question 6.
Which of the following pairs are weak base?
(a) NH4OH & NaOH ‘
(b) Ca(OH)2 & KOH
(c) NH4OH & Ca(OH)2
(d) NaOH&KOH
Answer:
(c) NH4OH & Ca(OH)2
![]()
Question 7.
NaOH & KOH are …………….
(a) strong bases
(b) metal Oxides
(c) weak bases
(d) diacidic bases
Answer:
(a) strong bases
Question 8.
Which of the following solution is soapy to touch?
(a) Acidic
(b) Basic
(c) Salt
(a(d) Aquaregia
Answer:
(b) Basic
![]()
Question 9.
Which of the following solutions do not conduct electricity?
(a) alcohol
(b) glucose
(c) sulphuric acid
(d) both a & b
Answer:
(d) both a & b
Question 10.
The pH value of neutral solution is ………………
(a) = 7
(b) <7
(c) none of the above
(d) -7
Answer:
(a) = 7
![]()
Question 11.
The pH of stomach fluid is ……………….
(a) 4
(b) 2
(c) 6
(d) 7
Answer:
(b) 2
Question 12.
A salt which is formed by complete neutralization of an acid and a base is called ………………. salt.
(a) basic
(b) acid
(c) double
(d) normal
Answer:
(d) normal
![]()
Question 13.
The number of water molecules present in one molecule of copper sulphate is
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(d) 5
Question 14.
The molecular formula of copper sulphate pentahydrate is ………………..
(a) CuSO4. H2O
(b) CuSO4. 2H2O
(c) CuSO4. 5H2O
(d) CuSO4. 3H2O
Answer:
(c) CuSO4 . 5H2O
![]()
Question 15.
……………is the gas produced when HCl is added with carbonate salt.
(a) H2
(b) N2
(C) CO2
(d) O2
Answer:
(c)CO2
Question 16.
The formula of bleaching powder is ……………..
(a) CaCl2
(b) CaOCl2
(c) Ca(OH)2
(d) CaO
Answer:
(b) CaOCl2
![]()
Question 17.
The chemical name of plaster of paris is ……………………..
(a) Calcium sulphate hemihydrate
(b) Calcium sulphate monohydrate
(c) Calcium sulphate dihydrate
(d) Calcium sulphate trihydrate
Answer:
(a) Calcium sulphate hemihydrate
Question 18.
Which of the following metal does not react with sodium hydroxides?
(a) Cu
(b) Ag
(c) Cr
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
![]()
Question 19.
Curd contains …………….acid.
(a) malic ‘
(b) formic
(c) lactic
(d) ascorbic
Answer:
(c) lactic
Question 20.
Which one of the following acids undergoes complete ionisation?.
(a) HCl
(b) CH3COOH
(c) H2SO4
(d) all the above
Answer:
(a) HCl
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks :
1. Acid reacts with base to form a neutral product called ………………
Answer:
Salt
2. The taste of acid is ………………..
Answer:
Sour
3. …………….. contain one or more replaceable hydrogen atoms.
Answer:
Acids
![]()
4. ………………..acids have a relatively smaller amount of acids dissolved in a solvent.
Answer:
Dilute
5. Acids react with metallic oxides to produce ……………….
Answer:
salt and water
6. _________ acid is used in aerated drinks.
Answer:
Carbonic acid
![]()
7. Chemical formula of aquaregia is ________
Answer:
3HCl + HNO3
8. Water soluble bases are called ________
Answer:
alkali
9. Non-metallic oxides are ___________ in nature.
Answer:
acid
![]()
10. __________ are bitter in taste.
Answer:
Bases
11. __________ alkali has a relatively high percentage of alkali in its aqueous solution.
Answer:
Concentrated
12. Acids turn blue litmus to ………….
Answer:
red
![]()
13. Phenolphthalein and methyl Orange are ………………
Answer:
indicators
14. pH stands for …………….. in a solution.
Answer:
power of hydrogen ion concentration
15. The pH value of acids are …………….. than 7.
Answer:
lesser
![]()
16. White enamel coating of our teeth is…………….
Answer:
Calcium phosphate
17. Salt is ………….. in nature.
Answer:
hygroscopic
18. Salt which is formed by the partial replacement of hydrogen ions of an acid by a metal is called ………………………..
Answer:
acid salt
![]()
19 Salts contaíning water of crystallisation are called …………. salts.
Answer:
hydrated
20. Salts that do not contain water of crystallisation is called …………..
Answer:
anhydrous salt
21. pH value of human blood is ……………..(7.0, 7.4, 7.6).
Answer:
7.4
![]()
22. The nature of the toothpaste commonly used is ……………. in nature (acidic, basic, neutral)
Answer:
basic
23. You are given pure water to test the pH value using pH paper. It shows colour (White, black, green)
Answer:
green
III. To Match:
Question 1.
| Source | Acid present |
| 1) Apple | ? |
| 2) ? | Citric acid |
| 3) ? | tartaric acid |
| 4) Tomato | ? |
| 5) Vinegar | ? |
Answer:
| Source | Acid present |
| 1) Apple | Malic acid |
| 2) Lemon | Citric acid |
| 3) Grapes | tartaric acid |
| 4) Tomato | Oxalic acid |
| 5) Vinegar | Acetic acid |
![]()
Question 2.
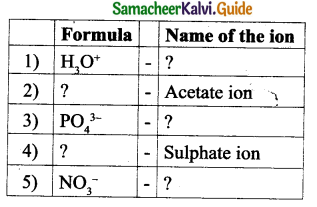
Answer:
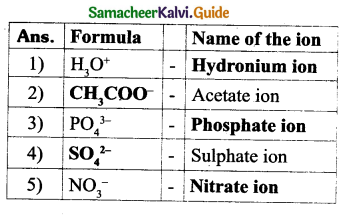
Question 3.
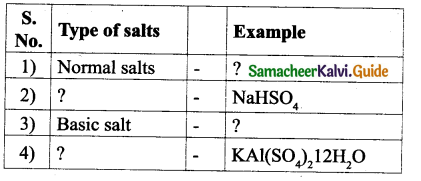
Answer:
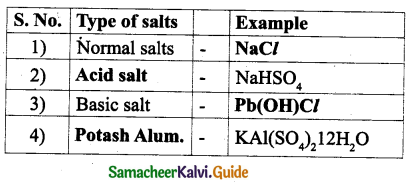
Question 4.
Answer:

IV. Complete the following equations.
Question 1.
HCl + H2O → ? + ?
Answer:
HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl–
![]()
Question 2.
H+ + H2O → ?
Answer:
H+ + H2O → H3O+
Question 3.
Mg+ ? → ? + H2
Answer:
Mg + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H2↑
Question 4.
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → ? + ? + CO2↑
Answer: Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2↑
![]()
Question 5.
ZnO + 2HCl → ? + ?
Answer:
ZnO + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2O↑
Question 6.
Zn + ? → Na2ZnO2 + H2 ↑
Answer:
Zn + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2+ H2↑
Question 7.
CaO + H2SO4 → ? + H2O
Answer:
CaO + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + H2O
![]()
Question 8.
HCl + ? → NaCl + H2O
Answer:
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
Question 9.
Ca(OH)2 + ? → ? + H2O
Answer:
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
Question 10.
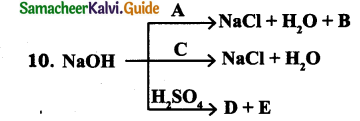
Answer:
A = NH4Cl, B = NH3↑
C = HCl
D = NaHSO4,E = H2O
V. Answer in briefly :
Question 1.
What are organic acids? Given examples.
Answer:
Acids present in plants and animals (living things) are organic acids.
Example: HCOOH, CH3COOH
![]()
Question 2.
How are acids classified based on ionisation? Give examples.
Answer:
Acids get ionise in water (produce H+ ions) completely or partially. Based on the extent of ionisation, acids are classified as follows:
Strong Acids:
These are acids that ionise completely in water.
Example: HCl
Weak Acids :
These are acids that ionise partially in the water.
Example: CH3COOH.
Question 3.
What is Aquaregia? Mention its uses.
Answer:
It is a mixture of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid prepared optimally in a molar ratio of 3:1. It is a yellow-orange fuming liquid. It is a highly corrosive liquid, able to attack gold and other resistant substances.
- Aquaregia is used tp dissolve noble metals such as gold, platinum, and palladium.
- It is used Tor cleaning and refining gold.
Question 4.
What does the acidity of base mean?
Answer:
It means the number of replaceable hydroxyl groups present in one molecule of a base.
![]()
Question 5.
What is Potash alum? Write its formula.
Answer:
Potash alum is a mixture of potassium sulphate and aluminium sulphate. KAl(SO4)2.12H2O.
Question 6.
What are double salts? Give an example?
Answer:
Double salts are the salts formed by the combination of the saturated solution of two simple salts in equimolar ratio followed by crystallization. For example : Potash alum.
Question 7.
What are basic salts? Give suitable reaction for this.
Answer:
Basic salts are the product formed by the partial replacement of hydroxide ions of a diacidic or triacidic base with an acid radical.
Pb(OH)2 + HCl → Pb(OH)Cl + H2O
![]()
Question 8.
Why are tooth pastes basic?
Answer:
Toothpastes which are generally basic and used for cleaning the teeth can neutralise the excess acid and prevent tooth decay.
Question 9.
What is water of crystallisation?
Answer:
Many salts are found as crystals with water molecules they contain. These water molecules are known as water of crystallisation.
![]()
Question 10.
Why do blue colour copper sulphate becomes white on heating?
Answer:
On heating, blue colour copper sulphate loses its water molecules and becomes white.
Question 11.
Acidic or basic solutions are good conductors of electricity. Justify your answer.
Answer:
Acidic and basic solutions in water conduct electricity because they produce hydrogen and hydroxide ions respectively.
![]()
Question 12.
What are hygroscopic substances?
Answer:
Substance which absorbs water from the surroundings are called hygroscopic substances.
Question 13.
Define indicator. Give examples
Answer:
Chemical substances used to find out whether the given solution is acid or base are called indicators. Eg: Phenolphthalein, methyl orange.
![]()
Question 14.
Define ionisation.
Answer:
Ionisation is the condition of being dissociated into ions by heat or radiation or chemical reactions or electrical discharge.
Question 15.
How is normal salt obtained? Give a suitable reaction.
Answer:
A normal salt is obtained by complete neutralization of an acid by a base.
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
Question 16.
How are bases classified based on ionisation?
Answer:
Based on Ionisation
(a) Strong Bases :
These are bases which ionise completely in aqueous solution.
Example: NaOH, KOH
(b) Weak Bases:
These are bases that ionise partially in aqueous solution.
Example: NH4OH, Ca(OH)2
![]()
VI. To Interpret:
Question 1.
CH4 and NH3, are not acids.
Answer:
CH4 and NH3 do not produce hydrogen ion (H+) in its aqueous solution.
Question 2.
Acetic acid (CH3COOH) is a mono basic acid.
Answer:
Though acetic acid contains four hydrogen atoms only one hydrogen can be replaced in its aqueous solution. So CH3COOH is a mono basic acid.
CH3COOH → H++ + CH3COO–
![]()
Question 3.
Al(OH)3 & Zn(OH)2 are not alkalis.
Answer:
Al(OH)3 & Zn(OH)2 are water insoluble bases. So they are bases not alkalies.
Question 4.
NaOH & KOH are strong bases.
Answer:
These are bases which ionise completely in aqueous solution.
Question 5.
NaHSO4 is an acid salt.
Answer:
It is formed by the partial replacement of hydrogen ion of sulphuric acid (H2 SO4 ) by a metal present in sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
NaOH + H2 SO4 → NaHSO4 + H2O
![]()
Question 6.
Non-metallic oxides are acidic is nature.
Answer:
When non – metallic oxides react with bases, they can form a salt and water similar to the reaction of base with acids. So non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature.
VII. Complete the following table:
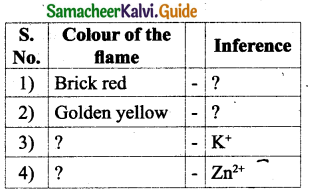
Question 1.
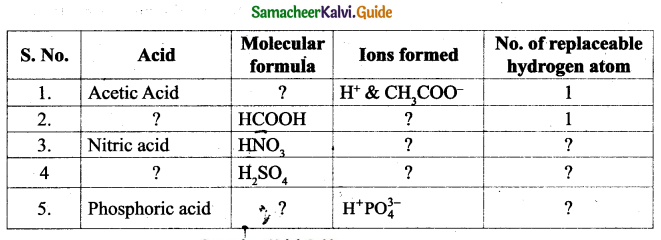
Answer:
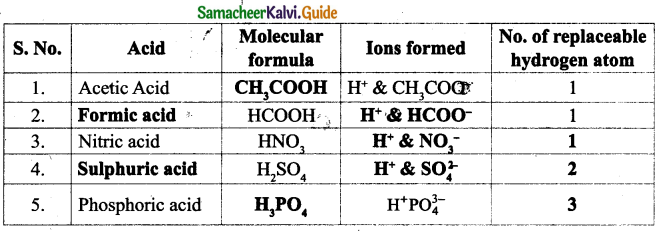
Question 2.
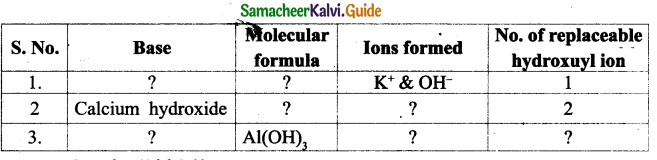
Answer:
Question 3.
| 1) Hydrochloric acid | a) Fertilizer |
| 2) Citric acid | b) Baking powder |
| 3) Nitric acid | c) Car batteries |
| 4) Oxalic acid | d) Cleansing agent in toilets |
| 5) Sulphuric acid | e) Removing black stains |
| f) Effervescent salts |
Answer:
1. – d, 2. – f, 3. – a, 4. – e, 5. – c
Question 4.
| 1) Hardest substance in our body | a) Aluminium phosphate |
| 2) Citrus fruits | b) Potash alum |
| 3) Rice plant | c) Insoluble in water |
| 4) Double salts | d) Acidic soil |
| 5) Silver chloride | e) Calcium phophate |
| f) Alkaline soil |
Answer:
l.-e,2.-f,3.-d,4-b,5.-c
VIII. Find odd one out & give reason :
Question 1.
HCl, HNO3, HCOOH, H3PO4
Answer:
H3PO4,
It is a tribasic acid whereas other three are monobasic acids.
Question 2.
Acetic acid, formic acid, tartaric acid, sulphuric acid.
Answer:
Sulphuric acid.
It is a mineral acid whereas other three are organic acids.
![]()
Question 3.
CaO, Na2O, ZnO, NaOH
Answer:
NaOH.
It is a base containing replaceable hydroxyl ion. whereas other three bases contain replaceable oxide ions.
Question 4.
Bitter taste, soupy to touch, turns red litmus to blue, produce pink colour with methyl orange.
Answer:
Produce pink colour with methyl orange.
It is the property of acids whereas other three are properties of bases.
![]()
Question 5.
Litmus paper, phenolphthalein, methyl orange, Aquaregia.
Answer:
Aquaregia.
It is a mixture of two acids namely, hydrochloric acid and nitric acid, used to dissolve metals such as gold and platinum whereas other three are indicators used to identify the nature of the solution.
IX. Spot the error / Correct the wrong statement given below :
Question 1.
An acid is the compound which are capable of forming hydroxyl ions (OH– ) in aqueous solution. .
Answer:
An acid is the compound which are capable of forming hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous , solution, (or) A base is the compound which are capable of forming hydroxyl ion (OH-) in aqueous solution.
![]()
Question 2.
Nitric Acid is a constituent of baking powder.
Answer:
Tartaric acid is a constituent of baking powder.
Question 3.
The pH value of the base in lesser than 7.
Answer:
The pH value of the base is greater than 7. (or) pH value of an acid is lesser than 7.
Question 4.
Ca(OH)2 is a triacidic base.
Answer:
Ca(OH)2 is a diacidic base (or) Al(OH)3 is a triacidic base.
![]()
Question 5.
Magnesium hydroxide is used in whitewashing of buildings.
Answer:
Magnesium hydroxide is used as an antacid. (or) Calcium hydroxide is used in whitewashing of buildings.
X. Answer in detail :
Question 1.
Explain the classification of acids based on their basicity.
Answer:
Monobasic Acid :
Acid that contain only one replaceable hydrogen atom per molecule is called monobasic acid. It gives one hydrogen ion per molecule of the acid in solutions.
Example: HCl, HNO3
.
Dibasic Acid :
An acid which gives two hydrogen ions per molecule of the acid in solution.
Example : H2SO4, H2CO3
‘
Tribasic Acid :
An acid which gives three hydrogen ions per molecule of the acid in solution.
Example: H3PO4.
![]()
Question 2.
Write notes on the properties of acids.
Answer:
(a) They have sour taste.
(b) Their aqueous solutions conduct electricity since they contain ions
(c) Acids turns blue litmus red.
(d) Acids react with active metals to give hydrogen gas.
Mg + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H 2↑
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2↑
(e) Acids react with metal carbonate and metal hydrogen carbonate to give carbon dioxide.
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2↑
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2↑
(f) Acids react with metallic oxides to give salt and water.
CaO + H2SO4 → CaSO4+ H2O
(g) Acids react with bases to give salt and water.
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O.
Question 3.
Write notes on the properties of bases. .
Answer:
(a) They have bitter taste.
(b) Their aqueous solutions have soapy touch.
(c) They turn red litmus blue.
(d)Their aqueous solutions conduct electricity.
(e) Bases react with metals to form salt with the liberation of hydrogen gas.
Zn + 2 NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2↑
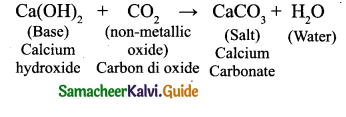
(f) Bases react with non-metallic oxides to produce salt and water. Since this is similar to the reaction between a base and an acid, we can conclude that non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature,
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3+ H2O
(g) Bases react with acids to form salt and water.
KOH + HCl → KCl + H2O
The above reaction between a base and an acid is known as Neutralisation reaction.
(h) On heating with ammonium salts, bases give ammonia gas.
NaOH + NH4Cl → NaCl + H2O+ NH3↑
![]()
Question 4.
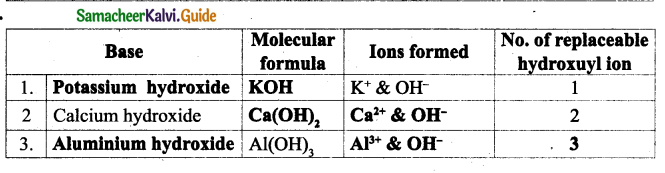
Describe the classification of bases based on their acidity.
Answer:
(a) Monoacidic Base :
It is a base that ionises in water to give one hydroxide ion per molecule.
Example: NaOH, KOH
(b) Diacidic Base:
It is a base that ionises in water to give two hydroxide ions per molecule.
Example: Ca(OH)2, Mg(OH)2
(c) Triacidic Base :
It is a base that ionises in water to give three hydroxide ions per molecule.
Example: Al(OH)3, Fe(OH)3
Question 5.
Write notes on importance of pH in everyday life.
Answer:
pH in our digestive system :
Hydrochloric acid produced in our stomach helps in the digestion of food without harming the stomach. During indigestion, the stomach produces too much acid and this causes pain and irritation. pH of stomach fluid is approximately 2.0
pH changes is the cause of tooth decay :
White enamel coating of our teeth is calcium phosphate, the hardest substance in our body. Toothpaste which are generally basic and used for cleaning the teeth can neutralise the excess acid and prevent tooth decay.
pH of soil:
In agriculture, the pH of soil is very important. Citrus fruits require slightly alkaline soil, while rice requires acidic soil and sugarcane requires neutral soil.
pH of rain water:
The pH of rainwater is approximately 7 which means that it is neutral and also represents its high purity. If the atmospheric air is polluted with oxides of sulphur and nitrogen, they get dissolved in rainwater and make its pH less than 7. Thus, if the pH of rainwater is less than 7, then it is called acid rain. When acid rain flows into the rivers it lowers the pH of the river water. The survival of aquatic life in such rivers becomes difficult.
![]()
Question 6.
List the properties of salts.
Answer:
- Salts are mostly solids which melt as well as boil at high temperature.
- Most of the salts are soluble in water.
For example, chloride salts of potassium and sodium are soluble in water. But silver chloride is insoluble in water. - They are odourless, mostly white, cubic crystals or crystalline powder with a salty taste.
- Salt is hygroscopic in nature.