Students can download Maths Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.15 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.15
Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
If x3 + 6x2 + kx + 6 is exactly divisible by x + 2, then k = 2
(a) 6
(b) -7
(c) -8
(d) 11
Solution:
(d) 11
Hint:
p(x) = x3 + 6x2 + kx + 6
Given p(-2) = 0
(-2)3 + 6(-2)2 + k(-2) + 6 = 0
-8 + 24 – 2k + 6 = 0
22 – 2k = 0
k = \(\frac{22}{2}\)
= 11
Question 2.
The root of the polynomial equation 2x + 3 = 0 is…….
(a) \(\frac{1}{3}\)
(b) –\(\frac{1}{3}\)
(c) –\(\frac{3}{2}\)
(d) –\(\frac{2}{3}\)
Solution:
(c) –\(\frac{3}{2}\)
Hint:
2x + 3 = 0
2x = – 3 ⇒ x = –\(\frac{3}{2}\)
![]()
Question 3.
The type of the polynomial 4 – 3x3 is ……..
(a) constant polynomial
(b) linear polynomial
(c) quadratic polynomial
(d) cubic polynomial
Solution:
(d) cubic polynomial
Question 4.
If x51 + 51 is divided by x + 1, then the remainder is …….
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 49
(d) 50
Solution:
(d) 50
Hint:
p(x) = x51 + 51
p(-1)= (-1)51 + 51
= -1 + 51
= 50
Question 5.
The zero of the polynomial 2x + 5 is ……..
(a) \(\frac{5}{2}\)
(b) –\(\frac{5}{2}\)
(c) \(\frac{2}{5}\)
(d) –\(\frac{2}{5}\)
Solution:
(b) –\(\frac{5}{2}\)
Hint:
2x + 5 = 0 ⇒ 2x = -5 ⇒ x = –\(\frac{5}{2}\)
![]()
Question 6.
The sum of the polynomials p(x) = x3 – x2 – 2, q(x) = x2 – 3x + 1
(a) x3 – 3x – 1
(b) x3 + 2x2 – 1
(c) x3 – 2x2 – 3x
(d) x3 – 2x2 + 3x – 1
Solution:
(a) x3 – 3x – 1
Hint:
p(x) + q(x) = (x3 – x2 – 2) + (x2 – 3x + 1) = x3 – x2 – 2 + x² – 3x + 1
= x³ – 3x – 1
Question 7.
Degree of the polynomial (y³ – 2) (y³ + 1) is
(a) 9
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 6
Solution:
(d) 6
(y³ – 2) (y³ + 1) = y6 + y³ – 2y³ – 2
= y6 – y³ – 2
Question 8.
Let the polynomials be
(A) -13q5 + 4q² + 12q
(B) (x² + 4)(x² + 9)
(C) 4q8 – q6 + q²
(D) –\(\frac{5}{7}\) y12 + y³ + y5.
Then ascending order of their degree is
(a) A, B, D, C
(b) A, B, C, D
(c) B, C, D, A
(d) B, A, C, D
Solution:
(d) B, A, C, D
![]()
Question 9.
If p(a) = 0 then (x – a) is a …….. of p(x)
(a) divisor
(b) quotient
(c) remainder
(d) factor
Solution:
(d) factor
Question 10.
Zeros of (2 – 3x) is ……..
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) \(\frac{2}{3}\)
(d) \(\frac{3}{2}\)
Solution:
(c) \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 11.
Which of the following has x -1 as a factor?
(a) 2x – 1
(b) 3x – 3
(c) 4x – 3
(d) 3x – 4
Solution:
(b) 3x – 3
![]()
Question 12.
If x – 3 is a factor of p(x), then the remainder is ……..
(a) 3
(b) -3
(c) p(3)
(d) p(-3)
Solution:
(c) p(3)
Question 13.
(x +y)(x² – xy + y²) is equal to ……..
(a) (x + y)³
(b) (x – y)³
(c) x³ + y³
(d) x³ – y³
Solution:
(c) x³ + y³
Question 14.
(a + b – c)² is equal to ……..
(a) (a – b + c)²
(b) (-a – b + c)²
(c) (a + b + c)²
(d) (a – b – c)²
Solution:
(b) (-a – b + c)²
Hint:
(a + b – c)² = a² + b² + c² + 2ab – 2bc – 2ac
(- a – b + c)² = a² + b² + c² + 2ab – 2bc – 2ac
(OR)
(- a – b + c)² = (-1)² (a + b + c)² (taking – 1 as common)
= (a + b – c)²
![]()
Question 15.
In an expression ax² + bx + c the sum and product of the factors respectively ……..
(a) a, bc
(b) b, ac
(c) ac, b
(d) bc, a
Solution:
(b) b, ac
Question 16.
If (x + 5) and (x – 3) are the factors of ax² + bx + c, then values of a, b and c are ………
(a) 1, 2, 3
(b) 1, 2, 15
(c) 1, 2, -15
(d) 1, -2, 15
Solution:
(c) 1, 2, -15
Hint:
(x + 5) (x – 3) = x² + (5 – 3) x + (5) (-3)
= x² + 2x – 15
compare with ax² + bx + c
a = 1, b = 2 and c = -15
Question 17.
Cubic polynomial may have maximum of ……… linear factors.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Solution:
(c) 3
![]()
Question 18.
Degree of the constant polynomial is ……..
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 1
(d) 0
Solution:
(d) 0
Question 19.
Find the value of m from the equation 2x + 3y = m. If its one solution is x = 2 and y = -2.
(a) 2
(b) -2
(c) 10
(d) 0
Solution:
(b) – 2
Hint:
The equation is 2x + 3y = m
Substitute x – 2 and y = -2 we get
2(2) + 3(-2) = m ⇒ 4 – 6 = m ⇒ -2 = m
Question 20.
Which of the following is a linear equation?
(a) x + \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 2
(b) x (x – 1) = 2
(c) 3x + 5 = \(\frac{2}{3}\)
(d) x³ – x = 5
Solution:
(c) 3x + 5 = \(\frac{2}{3}\)
![]()
Question 21.
Which of the following is a solution of the equation 2x – y = 6?
(a) (2, 4)
(b) (4, 2)
(c) (3, -1)
(d) (0, 6)
Solution:
(b) (4, 2)
Hint:
2x – y = 6
Substitute x – 4 and y = 2 we get
2(4) – 2 = 6 ⇒ 8 – 2 = 6 ⇒ 6 = 6
∴ (4, 2) is the solution
Question 22.
If (2, 3) is a solution of linear equation 2x + 3y = k then, the value of k is ……..
(a) 12
(b) 6
(c) 0
(d) 13
Solution:
(d) 13
Hint:
The equation is 2x + 3y = k
Substitute x = 2 and y = 3 we get,
2(2) + 3(3) = k ⇒ 4 + 9 = k ⇒ 13 = k
Question 23.
Which condition does not satisfy the linear equation ax + by + c = 0 ……..
(a) a ≠ 0, b = 0
(b) a = 0, b ≠ 0
(c) a = 0, b = 0, c ≠ 0
(d) a ≠ 0, b ≠ 0
Solution:
(c) a = 0, b = 0, c ≠ 0
![]()
Question 24.
Which of the following is not a linear equation in two variable?
(a) ax + by + c = 0
(b) 0x + 0y + c = 0
(c) 0x + by + c = 0
(d) ax + 0y + c = 0
Solution:
(b) 0x + 0y + c = 0
Hint:
0x + 0y + c = 0
0 + 0 + c = 0 ⇒ c = 0
There is no variable.
∴ It is not a linear equation
Question 25.
The value of k for which the pair of linear equations 4x + 6y – 1 = 0 and 2x + ky – 1 = 0 represents parallel lines is ……..
(a) k = 3
(b) k = 2
(c) k = 4
(d) k = -3
Solution:
(a) k = 3
Hint:
Slope of 4x + 6y – 1 = 0 is
6y = -4x + 1 ⇒ y = \(\frac{-4}{6}\) x + \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Slope = \(\frac{-4}{6}\) = \(\frac{-2}{3}\)
Slope of 2x + ky – 7 = 0
ky = -2x + 7
y = \(\frac{-2}{k}\)x + \(\frac{7}{k}\)
Slope of a line = \(\frac{-2}{k}\)
Since the lines are parallel
\(\frac{-2}{3}\) = \(\frac{-2}{k}\)
-2k = – 6
k = \(\frac{6}{2}\)
= 3
![]()
Question 26.
A pair of linear equations has no solution then the graphical representation is ……..
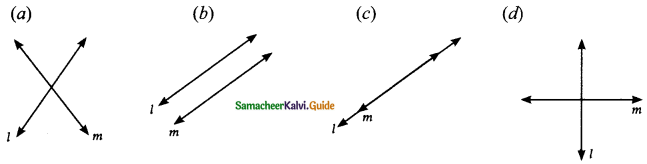
Solution:
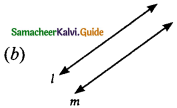
Hint:
Since there is no solution the two lines are parallel. (l11m)
Question 27.
If \(\frac{a_1}{a_2}\) ≠ \(\frac{b_1}{b_2}\) where a1x + b1y + c1 = 0 and a2x + b2y + c2 = 0 then the given pair of linear equation has …….. solution(s).
(a) no solution
(b) two solutions
(c) unique
(d) infinite
Solution:
(c) unique
Hint:
Since it has unique solution
\(\frac{a_1}{a_2}\) ≠ \(\frac{b_1}{b_2}\)
![]()
Question 28.
\(\frac{a_1}{a_2}\) = \(\frac{b_1}{b_2}\) ≠ \(\frac{c_1}{c_2}\) where a1x + b1y + c1 = 0 and a2x + b2y + c2 = 0 then the given pair of linear equation has …….. solution(s).
(a) no solution
(b) two solutions
(c) infinite
(d) unique
Solution:
(a) no solution
Hint:
\(\frac{a_1}{a_2}\) = \(\frac{b_1}{b_2}\) ≠ \(\frac{c_1}{c_2}\) the linear equation has no solution.
Question 29.
GCD of any two prime numbers is …….
(a) -1
(b) 0
(c) 1
(d) 2
Solution:
(c) 1
![]()
Question 30.
The GCD of x4 – y4 and x² – y² is ……..
(a) x4 – y4
(b) x² – y²
(c) (x + y)²
(d) (x + y)4
Solution:
(b) x² – y²
Hint:
x4 – y4 = (x²)² – (y²)²
= (x² + y²)(x² – y²)
x² – y² = (x² – y²)
G.C.D. = x² – y²