Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 9 Applied Statistics Ex 9.1 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Solutions Chapter 9 Applied Statistics Ex 9.1
Question 1.
Define Time series.
Solution:
A Time Series consists of data arranged chronologically – Croxton & Cowden
When quantitative data are arranged in the order of their occurrence, the resulting series is called the Time Series – Wessel & Wallet.
A time series consists of a set of observations arranged in chronological order (either ascending or descending). Times Series has an important objective to identify the variations and try to eliminate the variations and also helps us to estimate or predict the future values.
![]()
Question 2.
What is the need for studying time series?
Solution:
Time series analysis is one of the statistical methods used to determine the patterns in data collected for a period of time. Generally, each of us should know about the past data to observe and understand the changes that have taken place in the past and current time. One can also identify the regular or irregular occurrence of any specific feature over a time period in a time series data.
Question 3.
State the uses of time series.
Solution:
It helps in the analysis of the past behavior.
It helps in forecasting and for future plans.
It helps in the evaluation of current achievements.
It helps in making comparative studies between one time period and others.
Therefore time series helps us to study and analyze the time related data which involves in business fields, economics, industries, etc.
Question 4.
Mention the components of the time series.
Solution:
There are four types of components in a time series. They are as follows
(i) Secular Trend
(ii) Seasonal variations
(iii) Cyclic variations
(iv) Irregular variations
![]()
Question 5.
Define secular trend.
Solution:
It is a general tendency of time series to increase or decrease or stagnates during a long period of time, an upward tendency is usually observed in population of a country, production, sales, prices in industries,income or individuals etc., A downward tendency is observed in deaths, epidemics, prices of electronic gadgets, water sources, mortality rate etc. It is not necessarily that the increase or decrease should be in the same direction throughout the given period of time.
Question 6.
Write a brief note on seasonal variations
Solution:
As the name suggests, tendency movements are due to nature which repeat themselves periodically in every seasons. These variations repeat themselves in less than one year time. It is measured in an interval of time. Seasonal variations may be influenced by natural force, social customs and traditions. These variations are the results of such factors which uniformly and regularly rise and fall in the magnitude. For example, selling of umbrellas’ and raincoat in the rainy season, sales of cool drinks in summer season, crackers in Deepawali season, purchase of dresses in a festival season, sugarcane in Pongal season.
Question 7.
Explain cyclic variations.
Solution:
These variations are not necessarily uniformly periodic in nature. That is, they may or may not follow exactly similar patterns after equal intervals of time. Generally one cyclic period ranges from 7 to 9 years and there is no hard and fast rule in the fixation of year for a cyclic period. For example, every business cycle has a Start-Boom – Depression. Recover, maintenance during booms and depressions, changes in government monetary policies, changes in interest rates.
Question 8.
Explain the stratified random sampling with a suitable example.
Solution:
These variations do not have particular pattern and there is no regular period of time of their occurrences. These are accidently changes which are purely random or unpredictable. Normally they are short-term variations, but its occurrence sometimes has its effect so intense that they may give rise to new cyclic or other movements of variations. For example floods, wars, earthquakes, Tsunami, strikes, lockouts etc.
![]()
Question 9.
Define seasonal index.
Solution:
Seasonal Index for every season (monthly or quarterly) is calculated as follows
Seasonal Index (S.I) = \(\frac { Seasonal Average }{Grand Average}\) × 100
If the data is given monthwise
Seasonal Index = \(\frac { Monthly Average }{Grand Average}\) × 100
If quarterly data is given
Seasonal Index = \(\frac { Quarterly Average }{Grand Average}\) × 100
Question 10.
Explain the method of fitting a straight line.
Solution:
(i) The straight line trend is represented by the equation Y = a + bX …………. (1)
Where Y is the actual value, X is time, a, b are constants.
(ii) The constants ‘a and ‘b’ are estimated by solving the following two normal Equations
ΣY = n a + b ΣX ………… (2)
ΣXY = a ΣX + b ΣX² …………… (3)
Where ‘n’ = number of years given in the data.
(iii) By taking the mid-point of the time as the ori-gin, we get ΣX = 0
(iv) When ΣX = 0, the two normal equations reduces to
ΣY = na + b(0) ; a = \(\frac { ΣY }{n}\) = \(\bar { Y}\)
ΣXY = a(0) + bΣX² ; b = \(\frac { ΣXY }{ΣX^2}\)
The constant ‘a’ gives the mean of Y and ‘b gives the rate of change (slope),
(v) By substituting the values of ‘a and ‘b’ in the trend equation (1), we get the Line of Best Fit.
Question 11.
State the two normal equations used in fitting a straight line.
Solution:
The constants ‘a’ and ‘b’ are estimated by solving the following two normal Equations
ΣY = n a + b ΣX ………… (2)
ΣXY = a ΣX + b ΣX² …………. (3)
Where ‘n’ = number of years given in the data.
![]()
Question 12.
State the different methods of measuring trend.
Solution:
Following are the methods by which we can measure the trend.
(i) Freehand or Graphic Method
(ii) Method of Semi-Averages
(iii) Method of Moving Averages
Question 13.
Compute the average seasonal movement for the following series
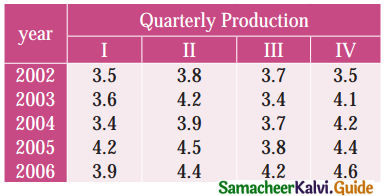
Solution:
Computation of seasonal. Index by the method of simple averages.
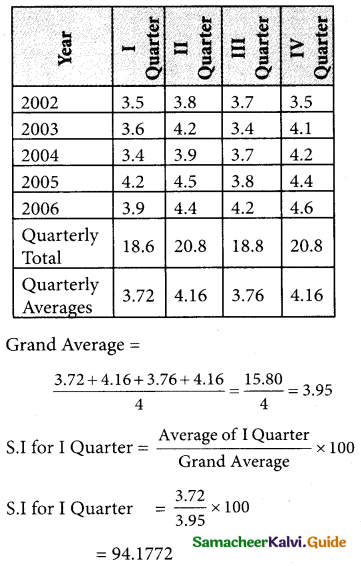

Question 14.
The following figures relates to the profits of a commercial concern for 8 years
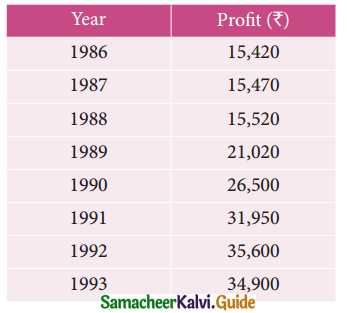
Find the trend of profits by the method of three yearly moving averages.
Solution:
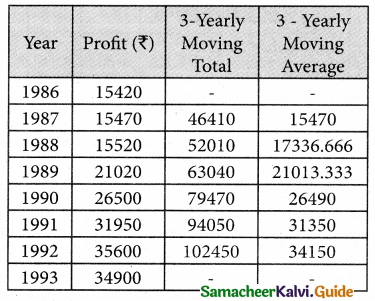
![]()
Question 15.
Find the trend of production by the method of a five-yearly period of moving average for the following data:
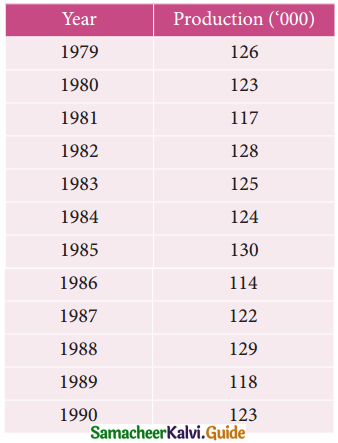
Solution:
I Computation of five – yearly moving averages
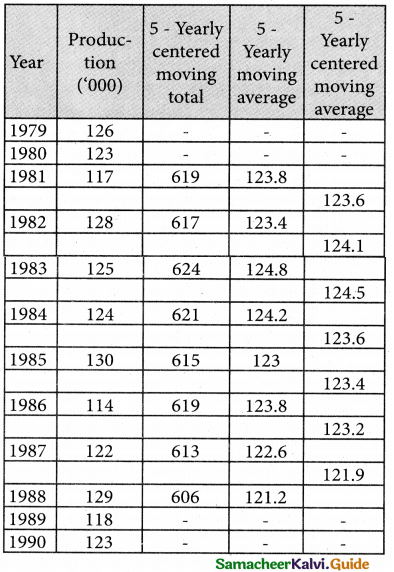
Question 16.
The following table gives the number of small- scale units registered with the Directorate of Industries between 1985 and 1991. Show the growth on a trend line by the free hand method.
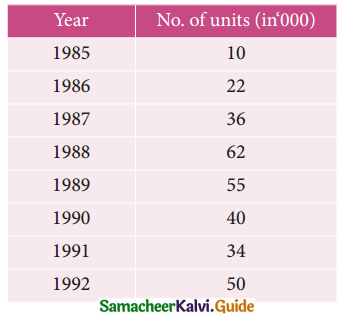
Solution:
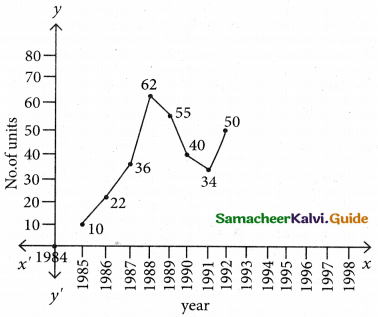
Question 17.
The annual production of a commodity is given as follows:
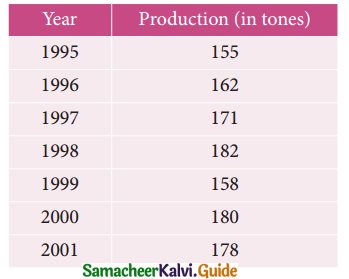
Fit a straight line trend by the method of least squares
Solution:
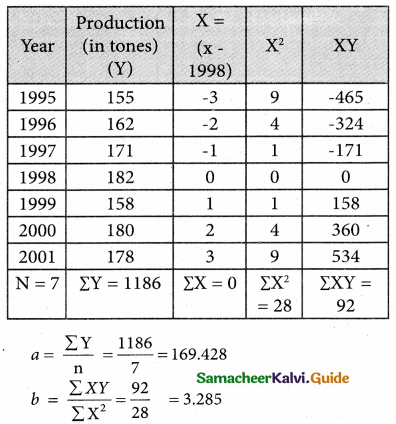
Therefore the required equation of the straight line
Y = a + bx
Y = 169.428 + 3.285 X
⇒ Y = 169.428 + 3.285 (x – 1998)
![]()
Question 18.
Determine the equation of a straight line which best fits the following data
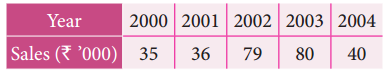
Compute the trend values for all years from 2000 to 2004
Solution:
Computation of trend values by the method of least squares (ODD Years)
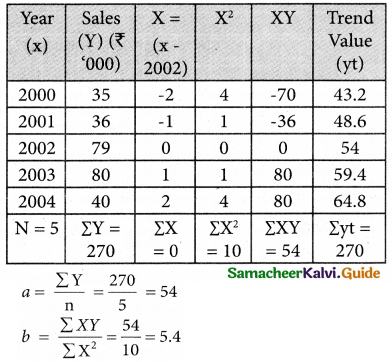
Therefore, the required equation of the straight line trend is given by
Y = a + bX
Y = 54 + 5.4X
Y = 54 + 5.4 (x – 2002)
The trend value can be obtained by when x = 2000
Yt = 54 + 5.4 (2000 – 2002)
Y = 54+ 5.4 (-2)
= 54 – 10.8
= 43.2
When x = 2001
Yt = 54 + 5.4 (2001 – 2002)
Y = 54 + 5.4 (-1)
= 54 – 5.4
= 48.6
When x = 2002
Yt = 54 + 5.4 (2002 – 2002)
V = 54 + 5.4 (0)
= 54
When x = 2003
Yt = 54 + 5.4 (2003 – 2002)
Y = 54 + 5.4 (1)
= 54 + 5.4
= 59.4
When x = 2004
Yt = 54 + 5.4 (2004 – 2002)
Y = 54 + 5.4(2)
= 54 + 10.8
= 64.8
Question 19.
The sales of a commodity in tones varied from January 2010 to December 2010 as follows: in year 2010 Sales (in tones)
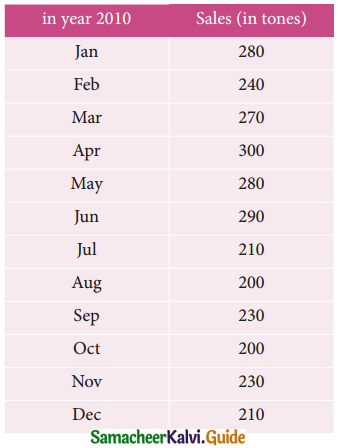
Fit a trend line by the method of semi-average.
Solution:
Since the number of years is even (twelve). We can equally divide the given data it two equal parts and obtain averages of first six months and last six.
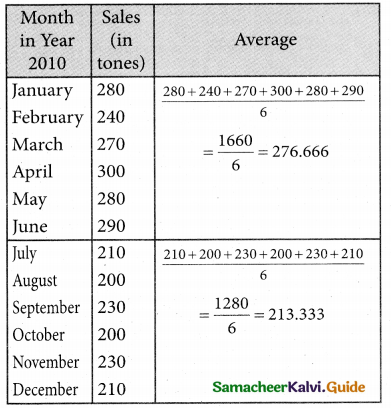
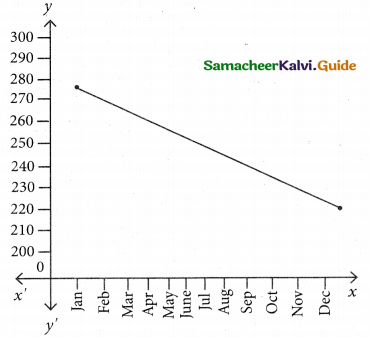
![]()
Question 20.
Use the method of monthly averages to find the monthly indices for the following data of production of a commodity for the years 2002, 2003 and 2004.
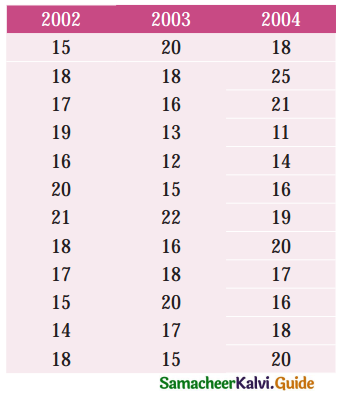
Solution:
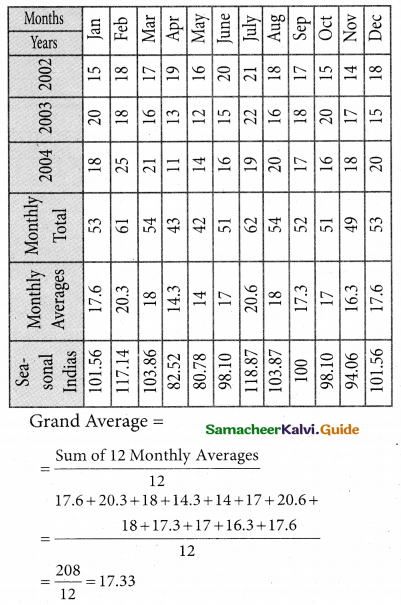
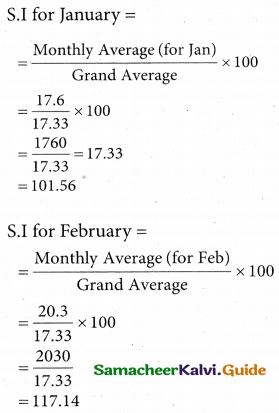
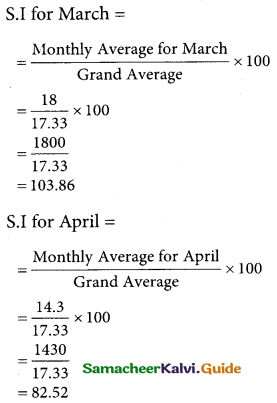
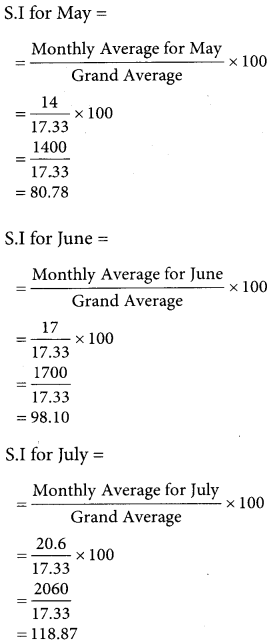
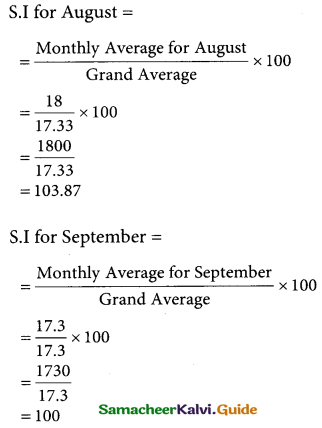

![]()
Question 21.
Use the method of monthly averages to find T the monthly indices for the following data of production of a commodity for the years 2002, 2003 and 2004.
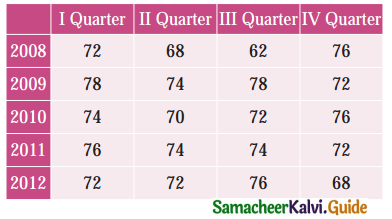
Solution:
Computation of Seasonal Index by the method of simple averages
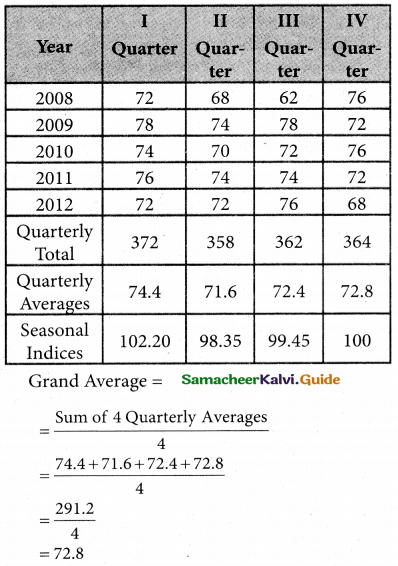
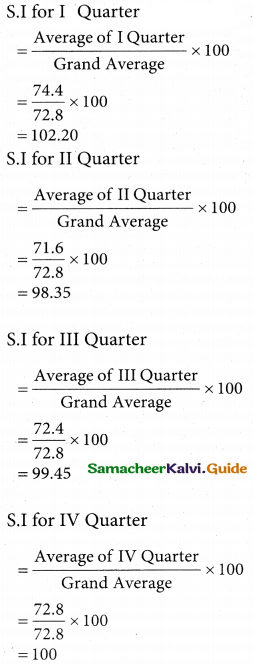
Question 22.
The following table shows the number of salesmen working for a certain concern:
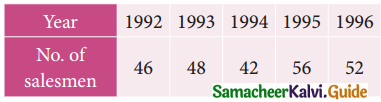
Use the method of least squares to fit a straight line and estimate the number of salesmen in 1997
Solution:
Computation of trend values by the method of least squares (ODD Years)
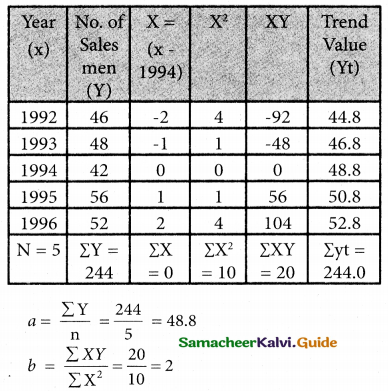
Therefore, the required equation of the straight line trend is given by
Y = a + bX
Y = 48.8 + 2X
(i.e) Y = 48.8 + 2 (x – 1994)
When x = 1992
Yt = 48.8 + 2 (1992 – 1994)
Y = 48.8 + 2 (-2)
= 48.8 – 4
= 44.8
When x = 1993
Yt = 48.8 + 2 (1993 – 1994)
Y = 48.8 + 2 (-1)
= 48.8 – 2
= 46.8
When x = 1994
Yt = 48.8 + 2 (1994 – 1994)
Y = 48.8 + 2(0)
= 48.8
When x = 1995
Yt = 48.8 + 2 (1995 – 1994)
Y = 48.8 + 2(1)
= 50.8
When x = 1996
Yt = 48.8 + 2 (1996 – 1994)
Y = 48.8 + 2 (2)
= 48.8 + 4
= 52.8
When x = 1997
Yt = 48.8 + 2 (1997 – 1994)
Y = 48.8 + 2 (3)
= 48.8 + 6
= 54.8
![]()