Students can download 11th Economics Chapter 12 Mathematical Methods for Economics Questions and Answers, Notes, Samcheer Kalvi 11th Economics Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Solutions Chapter 12 Mathematical Methods for Economics
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Mathematical Methods for Economics Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – A
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
Mathematical Economics is the integration of ………………………
(a) Mathematics and Economics
(b) Economics and Statistics
(c) Economics and Equations
(d) Graphs and Economics
Answer:
(a) Mathematics and Economics
![]()
Question 2.
The construction of demand line or supply line is the result of using ……………………..
(a) Matrices
(b) Calculus
(c) Algebra
(d) Analytical Geometry
Answer:
(d) Analytical Geometry
Question 3.
The first person used the mathematics in Economics is ……………………..
(a) Sir William Petty
(b) Giovanni Ceva
(c) Adam Smith
(d) Irving Fisher
Answer:
(b) Giovanni Ceva
![]()
Question 4.
Function with single independent variable is known as ……………………..
(a) Multivariate Function
(b) Bivariate Function
(c) Univariate Function
(d) Polynomial Function
Answer:
(c) Univariate Function
Question 5.
A statement of equality between two quantities is called ………………………
(a) Inequality
(b) Equality
(c) Equations
(d) Functions
Answer:
(c) Equations
Question 6.
An incremental change in dependent variable with respect to change in independent variable is known as ………………………
(a) Slope
(b) Intercept
(c) Variant
(d) Constant
Answer:
(a) Slope
![]()
Question 7.
(y – y1) = m(x-x1) gives the ……………………….
(a) Slope
(b) Straight line
(c) Constant
(d) Curve
Answer:
(b) Straight line
Question 8.
Suppose D = 50 – 5P. When D is zero then ………………………….
(a) P is 10
(b) P is 20
(c) P is 5
(d) P is -10
Answer:
(a) P is 10
![]()
Question 9.
Suppose D = 150 – 5P. Then, the slope is ………………………
(a) -5
(b) 50
(c) 5
(d) -50
Answer:
(d) -50
Question 10.
Suppose determinant of a matrix ∆ = 0, then the solution ……………………..
(a) Exists
(b) Does not exist
(c) Is infinity
(d) Is zero
Answer:
(b) Does not exist
![]()
Question 11.
State of rest is a point termed as ………………………
(a) Equilibrium
(b) Non – Equilibrium
(c) Minimum Point
(d) Maximum Point
Answer:
(a) Equilibrium
Question 12.
Differentiation of constant term gives ……………………..
(a) One
(b) Zero
(c) Infinity
(d) Non-infinity
Answer:
(b) Zero
![]()
Question 13.
Differentiation of xn is ………………………
(a) nx(n-1)
(b) nx(n+1)
(c) Zero
(d) One
Answer:
(a) nx(n-1)
Question 14.
Fixed Cost is the ……………………. term in cost function represented in mathematical form.
(a) Middle
(b) Price
(c) Quantity
(d) Constant
Answer:
(d) Constant
![]()
Question 15.
The first differentiation of Total Revenue function gives ………………………..
(a) Average Revenue
(b) Profit
(c) Marginal Revenue
(d) Zero
Answer:
(c) Marginal Revenue
Question 16.
The elasticity of demand is the ratio of ……………………….
(a) Marginal demand function and Revenue function
(b) Marginal demand function to Average demand function
(c) Fixed and variable revenues
(d) Marginal Demand function and Total demand function
Answer:
(b) Marginal demand function to Average demand function
![]()
Question 17.
If x + y = 5 and x – y = 3 then, Value of x ………………………
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 16
(d) 8
Answer:
(a) 4
Question 18.
Integration is the reverse process of ……………………….
(a) Difference
(b) Mixing
(c) Amalgamation
(d) Differentiation
Answer:
(d) Differentiation
![]()
Question 19.
Data processing is done by ……………………….
(a) PC alone
(b) Calculator alone
(c) Both PC and Calculator
(d) Pen drive
Answer:
(c) Both PC and Calculator
Question 20.
The command Ctrl + M is applied for ………………………
(a) Saving
(b) Copying
(c) Getting new slide
(d) Deleting a slide
Answer:
(c) Getting new slide
PART – B
Answer the following Questions in one or two sentences.
Question 1.
1f 62 = 34 + 4x what is x?
Answer:
62 – 34 = 4x
⇒ 28 = 4x
28 ÷ 4 = x
∴ x = 7
![]()
Question 2.
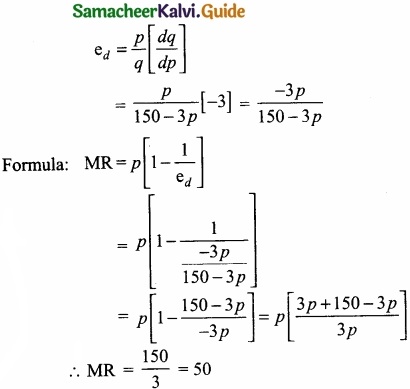
Given the demand function q = 150 – 3p, derive a function for MR?
Answer:
Demand function q = 150 – 3p
\(\frac{dq}{dp}\) = -3
Question 3.
Find the average cost function where TC = 60+ 10x + 15x2
Answer:
TC = 60 + 10x +15x2
Average Cost = \(\frac { TC }{ x }\)
= \(\frac{60+10 x+15 x^{2}}{x}\)
= \(\frac { 60 }{ x }\) + \(\frac { 10x }{ x }\) + \(\frac{15 x^{2}}{x}\)
AC = \(\frac { 60 }{ x }\) + 10 + 15x
![]()
Question 4.
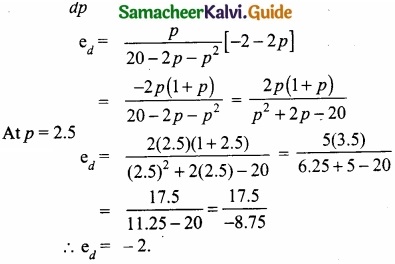
The demand function is given by x = 20 – 2p – p2 where p and x are the prices and the quantity respectively. Find the elasticity of demand for p = 2.5?
Answer:
ed = \(\frac{p}{x}\) \(\frac{dx}{dp}\)
\(\frac{dx}{dp}\) = -2-2p
![]()
Question 5.
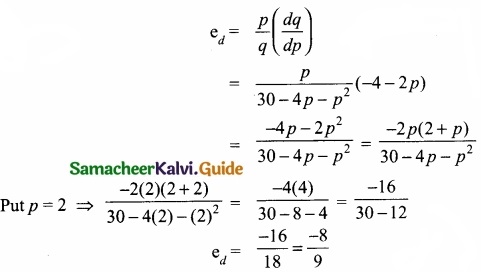
Suppose the price p and quantity q of a commodity are related by the equation q = 30 – 4p – p2 find
(I) ed at p = 2
(II) MR
Answer:
(I)
(II) MR – [Marginal Revenue]
MR = \(\frac{dq}{dp}\)
Given q = 30 – 4p – p2
\(\frac{dq}{dp}\) = 0 – 4(1) – 2p2-1
\(\frac{dq}{dp}\) = -4 – 2p
![]()
Question 6.
What is the formula for the elasticity of supply if you know the supply function?
Answer:
Elasticity of supply = \(\frac{dq}{dp}\)

Question 7.
What are the main menus of MS word?
Answer:
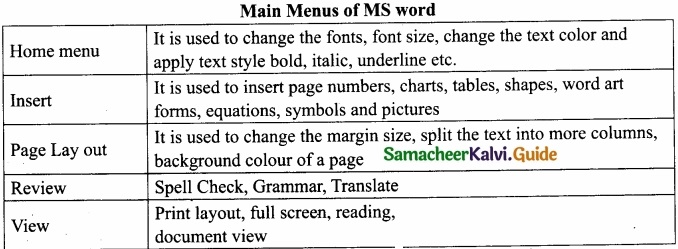
Ms Word is a word processor, which helps to create, edit, print, and save documents for future retrieval and reference.
PART – C
Answer the following questions in one paragraph:
Question 1.
Illustrate the uses of Mathematical Methods in Economics?
Answer:
Uses of Mathematical Methods in Economics:
- Mathematical methods help to present the economic problems in a more precise form.
- Mathematical methods help to explain economic concepts.
- Mathematical methods help to use a large number of variables in economic analyses.
- Mathematical methods help to quantify the impact or effect of any economic activity implemented by the government or anybody.
![]()
Question 2.
Solve for x quantity demanded if 16x – 4 = 68 + 7x?
Answer:
16x – 4 = 68 + 7x
16x – 7x = 68 + 4
9x = 72
x = \(\frac{72}{9}\) = 8
∴ x = 8
Question 3.
A firm has the revenue function R = 600q – 0.03q2 and the cost function is C = 150q + 60,000, where q is the number of units produced. Find AR, AC, MR and MC?
Answer:
R = 600q – 0.03q2
C = 150q + 60000
(i) AR = \(\frac { R }{ q }\)
= \(\frac{600 q-0.03 q^{2}}{q}\)
= \(\frac { 600q }{ q }\) – \(\frac{0.03 \mathrm{q}^{2}}{\mathrm{q}}\)
= AR = 600 – 0.0.q
(ii) AC = \(\frac { c }{ q }\)
= \(\frac { 150q + 60000 }{ q }\)
= \(\frac { 150q }{ q }\) + \(\frac { 60000 }{ q }\)
AC = 150 + (\(\frac { 60000 }{ q }\))
(iii) MR = \(\frac { dr }{ dq }\)
R = 600q – 0.03q
\(\frac { dR }{ dq }\) = 600 (1) – 0.03 (2q)
MR = 600 – 0.06q
(iv) MC = \(\frac { dc }{ dq }\)
C = 150q + 60000
\(\frac { dc }{ dq }\) = 150 (1) + 0
MC = 150
![]()
Question 4.
Solve the following linear equations by using Cramer’s rule?
x1 – x2 + x3 = 2;
x1 + x2 – x3 = 0;
– x1 – x2 – x3 = -6
Answer:
x1 – x2 + x3 = 2
x1 + x2 – x3 = 0
– x1 – x2 – x3 = -6
AX = B
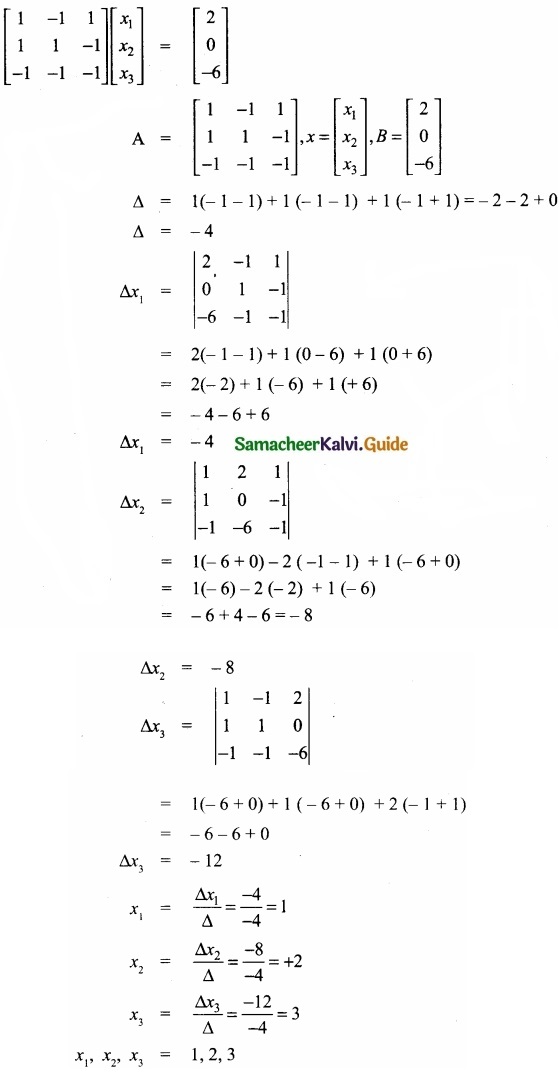
![]()
Question 5.
If a firm faces the total cost function TC = 5 + x2 where x is output, what is TC when x is 10?
Answer:
TC = 5 + x2
TC = 5 + 102
TC = 5 + 100
∴TC = 105
Question 6.
If TC = 2.5q3 – 13q2 + 50q + 12 derive the MC function and AC function?
Answer:
\(\frac{dc}{dq}\) = MC
AC = \(\frac{TC}{q}\)
\(\frac{dc}{dq}\) = 2.5(3)q2 – [13 × 2]q + 50
MC = 7.5q2 – 26q + 50
AC = \(\frac { 2.5q^{ 3 }-13q^{ 2 }+50q+12 }{ q } \)
∴ AC = 2.5q2 – 13q + 50 + \(\frac{12}{q}\)
![]()
Question 7.
What are the steps involved in executing a MS Excel sheet?
Answer:
- MS – Excel is used in data analysis by using formulas.
- A spreadsheet is a large sheet of paper that contains rows and columns.
- The intersection of rows and columns is termed a cell.
- MS – Excel 2007 version supports up to 1 million rows and 16 thousand columns per worksheet.
MS Excel Start From Various Options:
(I) Click Start → Program → Micro Soft Excel
(II) Double click the MS Excel Icon from the Desktop
Worksheet:
MS – Excel worksheet is a table like a document containing rows and columns with data and formula
There are four kinds of calculation operators. They are:
- Arithmetic
- Comparison
- Text Concatenation [link together]
- Reference
MS – Excel helps to do data analysis and data presentation in the form of graphs, diagrams, area charts, line chart etc.
PART – D
Answer the following questions in about a page:
Question 1.
A Research scholar researching the market for fresh cow milk assumes that Qt = f (Pt, Y, A, N, Pc) where Qt is the quantity of milk demanded, Pt is the price of fresh cow milk, Y is average household income, A is advertising expenditure on processed pocket milk, N is population and Pc is the price of processed pocket milk.
Answer:
- What does Qt = f (Pt, Y, A,N, Pc) mean in words?
- Identify the independent variables.
- Make up a specific form for this function.
(Use your knowledge of Economics to deduce whether the coefficients of the different independent variables should be positive or negative.)
1. Qt is the function of Pt, Y, A, N, Pc
Pt – Price of fresh cow milk
Y = Average household income
A = Advertising expenditure on processed pocket milk
N = Population
Pc = Price of processed pocket milk
2. Identify the Independent variables.
“Y” = Average household income
“N” = Population [“N” are Independent Variables]
Pc = Price of processed pocket milk
“Pc” = depending “Pt”
= Pc depending “A”
“A” = depending “N”
∴ Pc depending “Pt”, “A”, and “N”.
3. Make up specific form for this function [use your knowledge of Economics to deduce whether the co-efficient of the different independent variables should be positive or negative]
- “Pc ” = Price of processed pocket milk
When the price of processed milk increases and the quantity demanded of fresh milk decreases. - “N” = Population
When the population increases and the quantity of milk demanded Increases. - “A” = Advertising expenditure on processed pocket milk
When advertising expenditure on processed pocket milk increases the quantity of milk demanded. Increases.
“Y” – Average household Income
When average household income Increases and the quantity of milk demanded Increases.
“Pt” – Price of fresh cow milk
When the price of fresh cow milk Increases the quantity of milk demanded decreases.
∴ Qt = (-Pt) (+Y) (+A) (+N) (- Pc)
(-) means decreases; (+) means Increases
∴ Qt = [- Pt + Y + A +N – Pc]
![]()
Question 2.
Calculate the elasticity of demand for the demand schedule by using differential calculus method P = 60 – 0.2Q where price is –
- Zero
- ₹20
- ₹40
Answer:
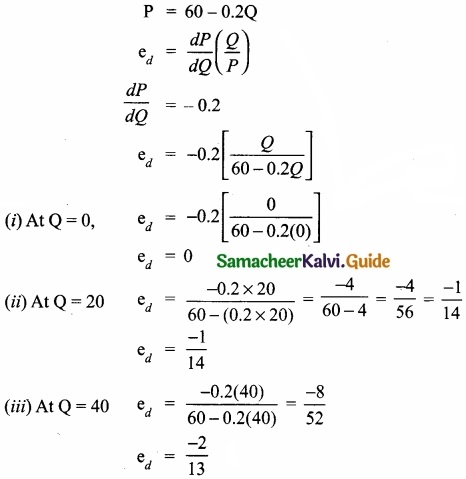
![]()
Question 3.
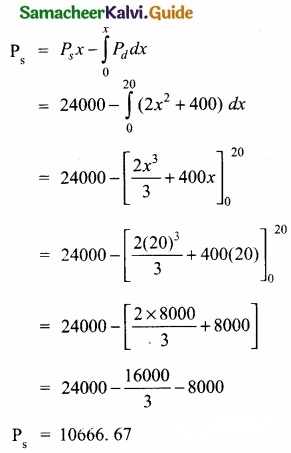
The demand and supply functions are Pd = 1600 – x4 and Ps = 2x2 + 400 respectively. Find the consumer’s surplus and producer’s surplus at the equilibrium point?
Answer:
Pd = 1600 – x2
Ps = 2x2 + 400
Pd = Ps
1600 – xc = 2x2 + 400
⇒ 1600 – x2 – 2x2 – 400 = 0
⇒ -3x2 + 1200 = 0
x2 = \(\frac{1200}{3}\) = \(\frac{400}{1}\)
x = ±\(\sqrt{400}\)
x = 20
When x = 20
Pd = 1600 – x2
= 1600 – (20)2
= 1600 – 400 = 1200
Pd = 1200
Ps = 2x2 + 400
= 2(20)2 + 400 = 2(400) + 400
Ps = 1200
Consumer’s Surplus (CS):
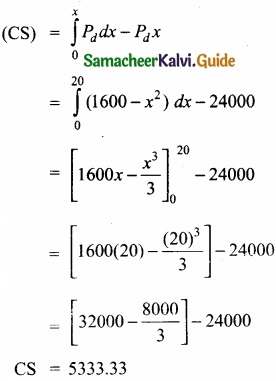
Producers Surplus(PS):
![]()
Question 4.
What are the ideas of Information and communication technology used in economics?
Answer:
Introduction: Information and Communication Technology [ICT] is the infrastructure that enables computing faster and accurate. The following table gives an idea of the range of technologies that fall under the category of ICT.
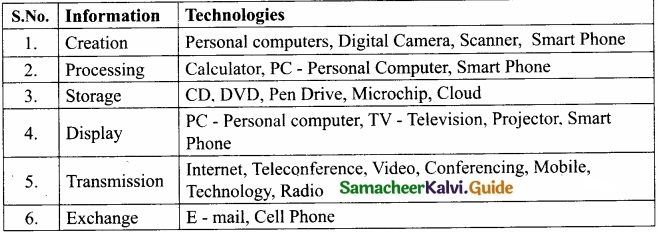
The evaluation of ICT has five phases:
They are evaluation in:
- Computer
- PC – Personal Computer
- Microprocessor
- Internet
- Wireless links
In Economics, the uses of mathematical and statistical tools need the support of ICT for:
- Data Compiling
- Editing
- Manipulating
- Presenting the results
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Mathematical Methods for Economics Additional Important Questions and Answers
PART – A
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
The point of intersection of demand line and supply line is known as ……………………
(a) Equilibrium
(b) Intersect
(c) Midpoint
(d) Equal
Answer:
(a) Equilibrium
![]()
Question 2.
…………………… is a rectangular array of numbers systematically arranged in rows and columns within brackets.
(a) Maths
(b) Geometry
(c) Graph
(d) Matrix
Answer:
(d) Matrix
Question 3.
……………………. means a change in the dependent variable with respect to a small change in the independent variable.
(a) Differential
(b) Differentiation
(c) Differentiating
(d) Derivative
Answer:
(a) Differential
![]()
Question 4.
……………………….. is an addition to the total cost caused by producing one more unit of output.
(a) Marginal Cost
(b) Marginal Product
(c) Marginal Concepts
(d) Marginal Revenue
Answer:
(a) Marginal Cost
Question 5.
Consumer’s surplus theory was developed by the ………………………….
(a) Alfred Marshall
(b) Adam Smith
(c) Lionel Robbinson
(d) Malthus
Answer:
(a) Alfred Marshall
Question 6.
……………………… is a word processor.
(a) MS Word
(b) Microprocessor
(c) Scanner
(d) Personal computer
Answer:
(a) MS Word
![]()
Question 7.
……………………. is the infrastructure that enables computing faster and accurate.
(a) Information and Communication Technology
(b) Information and Computer Technology
(c) Information and Connection Technology
(d) Information and Communication Technology
Answer:
(d) Information and Communication Technology
Question 8.
…………………… is used in data analysis by using formula.
(a) MS Word
(b) Microsoft
(c) Word processer
(d) Microprocessor
Answer:
(b) Microsoft
![]()
Question 9.
……………………. is a table like a document containing rows and columns with data and formula.
(a) Work Excel
(b) Work Microsoft
(c) Work Processor
(d) Work Sheet
Answer:
(d) Work Sheet
Question 10.
……………………… helps to do data analysis and data presentation in the form of graphs.
(a) MS Excel
(b) Microsoft
(c) Start Excel
(d) Microprocessor
Answer:
(a) MS Excel
ACTIVITY
Question 1.
The petrol consumption of your car is 16 Kilometers per litre. Let x be the distance you travel in Kilometers and p the price per litre of petrol in Rupees. Write expressions for the demand for Petrol?
Answer:
x – Total distance in Km.
p – Price per litre in rupees.
Equation of demand function joining two data points (16, 1) and (8, 2) respectively.
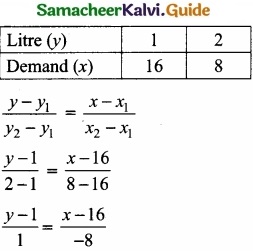
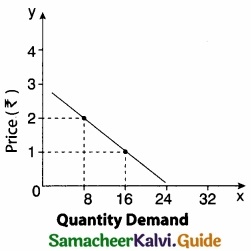
– 8y + 8 = x – 16
x – 16 – 8 + 8y = 0
x + 8y – 24 = 0
x = 24 – 8y
y = p
∴ The demand function x = 24 – 8p
Demand ∝ \(\frac{1}{Price}\)
![]()
Question 2.
Make up your own demand function and then derive the corresponding MR function and find the output level which corresponds to zero marginal revenue?
Question 3.
Use an Excel spreadsheet to calculate values for Quantity of demand at various prices for the function Q = 100 – 10P then plot these values on a graph?
Question 4.
Open MS – Word and put the title as PRESENT AND ABSENT OF STUDENTS and insert the table and collect the data for all classes of your school and find the class of highest absentees in a month. Justify with the reason for the absentees in a paragraph by using MS Word?
Activity 2, 3, and 4 can be done by the students individually.