Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Guide Pdf Chapter 5 Digestion and Absorption Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Guide Chapter 5 Digestion and Absorption
11th Bio Zoology Guide Digestion and Absorption Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part I
I. Choose The Best Options
Question 1.
Choose the incorrect sentence from the following:
a. Bile juice emulsifies the fat
b. Chyme is a digestive acidic food in stomach
c. Pancreatic juice converts lipid into fatty acid and glycerol
d. Enterokinase stimulates the secretion of pancreatic juice
Answer:
d. Enterokinase stimulates the secretion of pancreatic juice
Question 2.
What is chyme?
a. The process of conversion of fat into small droplets.
b. The process of conversion of micelles substances of glycerol into fatty droplet.
c. The process of preparation of incompletely digested acidic food through gastric juice.
d. The process of preparation of completely digested liquid food in midgut.
Answer:
d. The process of preparation of completely digested liquid food in midgut.
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following hormones stimulate the production of pancreatic juice and bicarbonate?
a. Angiotensin and epinephrine
b. Gastrin ¿md insulin
c. Cholecystokinin and secretin
d. Insulin and glucagon
Answer:
c. Cholecystokinin and secretin
Question 4.
The sphincter of Oddi guards
a. Hepatopanci’eatic duct
b. Common bile duct
c. Pancreatic duct
d. Cystic duct
Answer:
a. Hepatopanci’eatic duct
![]()
Question 5.
In small intestine, active absorption occurs in case of
a. Glucose
b. Amino acids
c. Na+
d. All the above
Answer:
d. All the above
Question 6.
Which one is incorrectly matched?
a. Pepsin – stomach
b. Renin – liver
c. Trypsin – intestine
d. Ptyalin – mouth
Answer:
b. Renin – liver
![]()
Question 7.
Absorption of glycerol, fatty acid and monoglycerides takes place by
a. Lymph vessels within villi
b. Walls of stomach
c. Colon
d. Capillaries within villi
Answer:
a. Lymph vessels within villi
Question 8.
First step in digestion of fat is
a. Emulsification
b. Enzyme action
c. Absorption by lacteals
d. Storage in adipose tissue
Answer:
a. Emulsification
![]()
Question 9.
Enterokinase takes part in the conversion of
a. Pepsinogen into pepsin
b. Trypsinogen into trypsin
c. Protein into polypetide
d. Caseinogen into casein
Answer:
b. Trypsinogen into trypsin
Question 10.
Which of the following combinations are not matched?
| Column – I | Column – II |
| a. Bilirubin and biliverdin | (i) Intestinal juice |
| b. Hydrolysis of starch | (ii) Amylases |
| c. Digestion of fat | (iii) Lipases d Salivary gland |
| d. salivary gland | (iv) Parotid |
Answer:
a. Bilirubin and biliverdin – (i) Intestinal juice
![]()
Question 11.
Match column I with column II and choose the correct option
| Column – I | Column -II |
| P. Small intestine | i. Largest factory |
| Q. Pancreas | ii. Absorption of water |
| R. Liver | iii. Carrying electrolytic solution |
| S. Colon | iv. Digestion and absorption |
a. (P-iv) (Q-iii) (R-i) (S-ii)
b. (P- iii) (Q-ii) (R-i) (S-iv)
c. (P-iv) (Q-iii) (R-ii) (S-i)
d. (P-ii) (Q-iv) (R-iii) (S-i)
Answer:
a. (P-iv) (Q-iii) (R-i) (S-ii)
![]()
Question 12.
Match column I with column II and choose the correct option
| Column – I | Column -II |
| P. Small intestine | i. 23 cm |
| Q. Large intestine | ii. 4 meter |
| R. Oesophagus | iii. 12.5 cm |
| S. Pharynx | iv. 1.5 meter |
a. (P-iv) (Q- ii) (R- i) (S-iii)
b. (P- ii) (Q- iv) (R- i) (S-iii)
c. (P-i) (Q-iii) (R-ii) (S-iv)
d. (P-iii) (Q-i) (R-ii) (S-iv)
Answer:
b. (P- ii) (Q- iv) (R- i) (S-iii)
Question 13.
Match column I with column II and choose the correct option
| Column – I | Column -II |
| P. Lipase | i) Starch |
| Q. Pepsin | ii) Cassein |
| R. Renin | iii) Protein |
| S. Ptyalin | iv) Lipid |
a. (P-iv) (Q-ii) (R-i) (S- iii)
b. (P- iii) (Q- iv) (R- ii) (S- i)
c. (P- iv) (Q- iii) (R-ii) (S- i)
d. (P- iii) (Q- ii) (R- iv) (S- i)
Answer:
c. (P- iv) (Q- iii) (R-ii) (S- i)
![]()
Question 14.
Which of the following is not the function of the liver?
a. Production of insulin
b. Detoxification
c. Storage of glucogen
d. Production of bile
Answer:
a. Production of insulin
Question 15.
Assertion (A): Large intestine also shows the presence of a villi-like small intestine.
Reason (B): Absorption of water takes place in the large intestine
a. Both A and B are true and B is the correct explanation of A
b. Both A and B are true but B is not the correct explanation of A
c. A is true but B is false
d. A is false but B is true
Answer:
a. Both A and B are true and B is the correct explanation of A
![]()
Question 16.
Which of the following is not true regarding intestinal villi?
a. They possess microvilli
b. They increase the surface area
c. They are supplied with capillaries and the lacteal vessels
d. They only participate in the digestion of fats
Answer:
d. They only participate in the digestion of fats
Question 17.
Which of the following combinations are not matched?
a. Vitamin D – Rickets
b. Thiamine – Beriberi
c. Vitamin K – Sterlity
d. Miacin – Pellagea.
Answer:
c. Vitamin K – Sterility
![]()
Question 18.
Why are villi present in the intestine and not in the stomach?
Answer:
In the small intestine, digestion gets completed and the absorption of digested food materials like glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, and glycerol takes place. The food materials are to be retained in the intestine by increasing the surface area. Hence villi are present in the intestine. The stomach is the temporary storing organ of food. In the stomach, HCl, pepsin, renin, and lipase are secreted. These are concerned with digestion. Hence villi are not present in the stomach.
Question 19.
Bile juice contains no digestive enzymes. yet it is important for digestion. Why?
Answer:
- The pile contains bile pigments (Bilirubin and biliverdin)
- The pile pigments are broken down products of heamoglobin of dead RBC’s
- Bile salts, cholesterol, and phospho lipids.
- Bile has no enzyme.
- Bile helps in the emulsification of fats.
- Bile salts reduce the surface tension of fat droplets and break them into small globules.
- Bile also activates lipase to digest lipids.
![]()
Question 20.
List the chemical changes that starch molecule undergoes from the time it reaches the small intestine.
Answer:

Question 21.
How do proteins differ from fats in their energy value and their role in the body?
Answer:
| Protein | Lipid |
| 1. The caloric value 5.65 Kcal/ gram | The caloric value 9.45 Kcal/gram |
| Q- Physiological fuel value 4 Kcal/gram | Physiological fuel value 9 Kcal/ gram |
Question 22.
Digestive secretions are secreted only when needed discuss.
Answer:
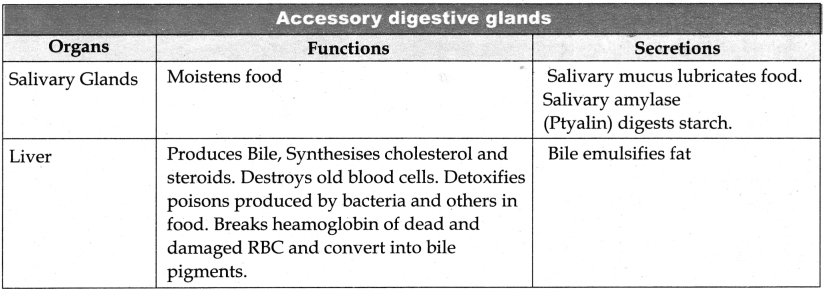
- The saliva is secreted by the salivary gland in the mouth Saliva
- The saliva contains water.
- Electrolytes – Na+, K+ , Cl–, HCo3–
- Salivary amylase (ptyalin)
- Mucus (a glycoprotein)
- Polysaccharides, starch is hydrolyzed by the salivary amylase enzyme into disaccharides (maltose)
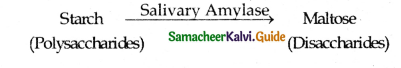
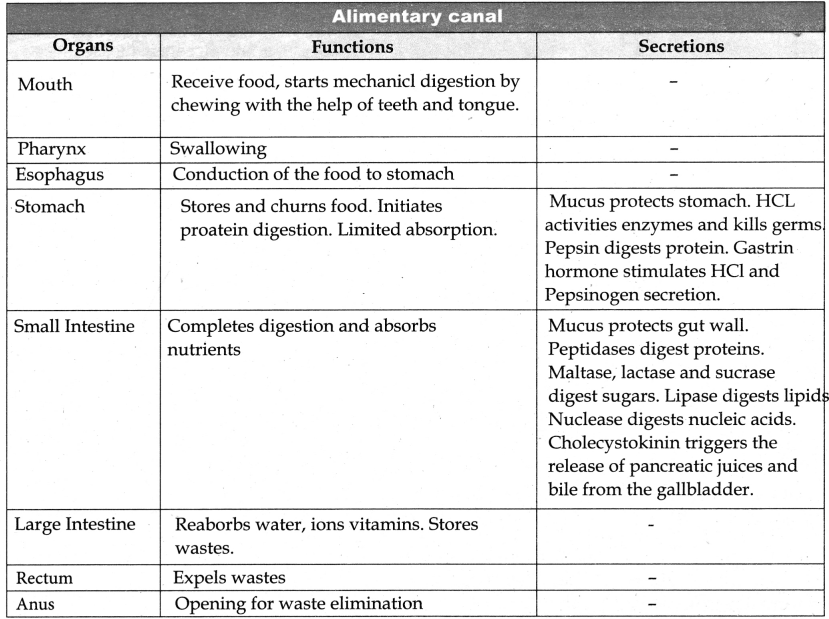
Stomach
- The gastric j uice contains HCI and proenzymes
- Proenzyme pepsinogen on exposure to HCI gets converted into active enzyme pepsin.
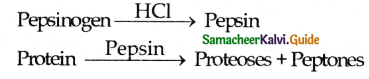
- The HCI provides an acidic medium (pH=1.8) which is optimum for pepsin, kills bacteria and other harmful organisms and avoids putrification.
- Proteolytic enzyme found in gastric juice of Infants is rennin helps in the digestion of milk protein caseinogen to casein in the presence of calcium.
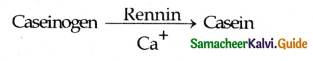
Small Intestine
Pancreatic juice:
Enzymes: Trypsinogen, Chymotrypsinogen, Carboxypeptidases, Pancreatic, Amalyse, Pancreatic Lipase, and Nucleases.
Trypsinogen is activated by an enzyme enterokinase, secreted by the intestinal mucosa into active trypsin, which in turn activates the enzyme chymotrypsinogen in the pancreatic juice.

Bile Juice:
The bile contains bile pigment (Bilirubin, and biliverdin) as the breakdown product of heamoglobin of dead RBCs, Bile salts, Cholesterol, and phospholipids. But has no enzymes. Bile helps in the emulsification of fats. Bile salts reduce the surface tension of fat droplets and break them into small globules, bile also activates lipases to digest lipids.
Pancreatic juice action:
Trypsin hydrolyses protein into polypeptides and peptones. While chymotrypsin hydrolyses peptide bonds associated with specific amino acids.
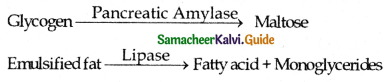
Succus enterius:
The secretions of the Brunner’s gland along with the secretions of the intestinal glands constitute the intestinal juice or succus entericus.
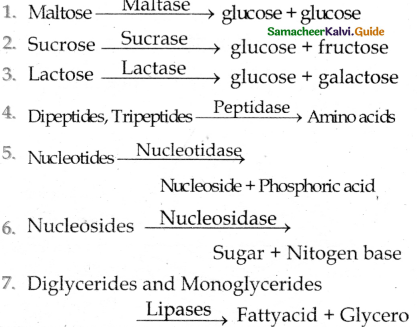
Enzymes: Maltase, lactase, sucrase (invertase), dipeptidases, lipases, nucleosidases.
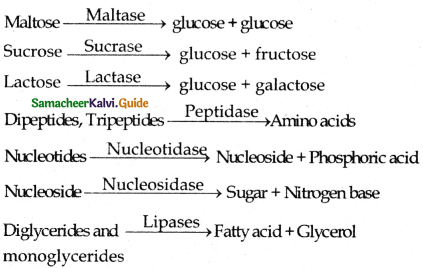
Bicarbonate ions from the Pancreas provide an alkaline medium (pH=7.8) for the enzymatic action.
All macromolecules → Micromolecules
Carbohydrate → Monosaccharides
Protein → Aminoacid
Lipids → Fatty acids and Glycerol
![]()
Question 23.
Label the given diagram.
Answer:
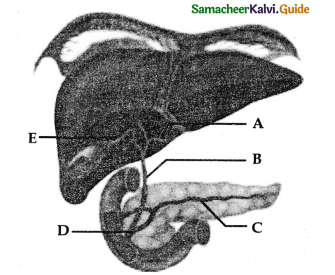
A – Right hepatic duct of the liver
B – Common bile duct
C – Pancreatic duct (duct of wirsung)
D – Hepatopancreatic duct
E – Cystic duct
Part II
11th Bio Zoology Guide Digestion and Absorption Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose The Best Option.
Question 1.
……………………… litres of digestive juice is poured into the alimentary canal and are reabsorbed each day.
a) 6 – 7 lit
b) 0 – 7 lit
c) 5-7 lit
d) 3 – 7 lit
Answer:
b) 0 – 7 lit
Question 2.
The Hard chewing surface of the teeth is made of ………………………… and helps in mastication of food.
a) Enamel
b) Crown
c) Denton
d) Plague
Answer:
a) Enamel
![]()
Question 3.
Which is the correct statement?
a) Tongue is a freely movable muscular organ attached at the anterior end by the frenulum to the floor of the buccal cavity.
b) Tongue is a freely movable muscular organ not attached at the posterior end by the frenulum to the floor of the buccal cavity.
c) Tongue is a freely movable muscular organ attached at the posterior end by the frenulum to the floor of the buccal cavity.
d) Tongue is a freely movable muscular organ attached at the anterior, posterior end by the frenulum to the floor of the buccal cavity.
Answer:
c) Tongue is a freely movable muscular organ attached at the posterior end by the frenulum to the floor of the buccal cavity.
Question 4.
Which is the correct sequence?
a) Gullet → Glottis → Epiglottis
b) Epiglottis → Glottis → Gullet
c) Glottis → Gullet → Epiglottis
d) Gullet → Epiglottis → Glottis
Answer:
a) Gullet → Glottis → Epiglottis
![]()
Question 5.
Which is a false statement?
a) Stomach divided into three region
b) Cardiac, fundic, pyloric regions
c) Pyloric region found between duodenum and jejunum
d) Cardiac region has a sphincter
Answer:
c) Pyloric region found between duodenum and jejunum
Question 6.
Find out the incorrect pair.
a) Starch – Amylase
b) Protein – Pepsin
c) Casein – Trypsin
d) Lipid – Lipase
Answer:
c) Casein – Trypsin
![]()
Question 7.
Find out the correct pair
a) Duodenum – 25 m
b) Jejunum – 2.4 m
c) Ileum – 3.7 m
d) Oesophagus – 10 m
Answer:
b) Jejunum – 2.4 m
Question 8.
Which is a wrong statement
a) Brunner’s gland doesn’t secrete mucus and enzymes
b) Brunner’s gland secretes mucus and enzymes
c) It is found in duodenum
d) It is theopenningofcaecum
Answer:
a) Brunner’s gland doesn’t secrete mucus and enzymes
![]()
Question 9.
Where is crypts of Leiberkuhn seen?
a) Small Intestine
b) Oesophages
c) Stomach
d) Rectum
Answer:
a) Small Intestine
Question 10.
The anal column may get enlarged and causes
a) Haemoralds
b) Haemorhoids
c) Elaemorods
d) Elaemorals
Answer:
b) Haemorhoids
![]()
Question 11.
Find the correct statement
a) Serosa – The outer layer formed of connective tissue
b) Serosa – Connective tissue, epithelial tissue
c) Serosa – Connective tissue, striated cells
d) Serosa – Connective tissue, thin squanmous epithelium
Answer:
d) Serosa – Connective tissue, thin squanmous epithelium
Question 12.
Match the following
1. Parotid gland – i) Pepsin
2. Sub maxillary gland – ii) Stenson’s duct
3. Sublingual gland – iii) Wharton’s duct
4. Stomach – iv) Duct of Rivinis
a) (1-ii) (2-iii) (3-iv) (4-i)
b) (1-i) (2-ii) (3-iii) (4-iv)
c) (1-ii) (2-iii) (3-i) (4-iv)
d) (1-iii) (2-ii) (3-iv) (4-i)
Answer:
a) (1-ii) (2-iii) (3-iv) (4-i)
![]()
Question 13.
Where is castle intrinsic factor secreted?
a) Intestine
b) Digestive passage
c) Stomach
d) Large intestine
Answer:
c) Stomach
Question 14.
The hepatic lobules are covered by …………………….. a thin connective tissue sheath.
a) Glisson’s capsule
b) Cardiac membrane
c) Renal membrane
d) Cystic membrane
Answer:
a) Glisson’s capsule
Question 15.
Find the correct statement. The differentiation of Liver
a) 4-5 week
b) 3-4 week
c) 4-7 week
d) 12-3 week
Answer:
b) 3-4 week
![]()
Question 16.
Find the wrong statement
a) Saliva – Ptyalin
b) Digestive tract – Mucous membrane
c) Stomach – Pepsin
d) Small intestine – Glucokinase
Answer:
d) Small intestine – Glucokinase
Question 17.
What is pH of food at the time of absorption?
a) 7.3
b) 7.5
c) 7.8
d) 7.7
Answer:
c) 7.8
![]()
Question 18.
True or false
a) Carbohydrate – Glucose
b) Protein – Aminoacid
c) Fat – Fatty acid
d) Bile – Pepsin

Answer:-
a) True
b) True
c) False
d) False
Question 19.
Find x-part the diagram

a) Common bile duct
b) Pancreatic duct
c) Jejunum
d) Gall bladder
Answer:
b) Pancreatic duct
![]()
Question 20.
Find the correct pair.
a) Carbohydrate -50% -400-500 gm
b) Fat-15%65-75 gm
c) Carbohydrate -51 % 400 -450 gm
d) Fat-15% -70-75 gm
Answer:
a) Carbohydrate -50% -400-500 gm
Question 21.
Name the vitamin synthesized by bacteria of the large intestine
a) D
b) K
c) C
d) E
Answer:
b) K
Question 22.
Find the correct statement.
a) Unused protein – stored in the liver
b) Unused protein – stored in the muscle
c) Unused protein – excretes as nitrogen
d) Unused protein – excretes through faeces
Answer:
c) Unused protein – excretes as nitrogen
![]()
Question 23.
What is the nature of food in the stomach?
a) Chyme
b) Fermented
c) Solid
d) Semisolid
answer:
a) Chyme
Question 24.
Which is the longest part of the digestive system?
a) Large intestine
b) Small intestine
c) Oesophages
d) Stomach
Answer:
b) Small intestine
![]()
Question 25.
Where is pyloric muscle present?
a) Junction between oesophagus and stomach
b) Junction between the large intestine and small intestine
c) Junction between small intestine and stomach
d) Junction between large intestine and rectum
Answer:
c) Junction between small intestine and stomach
Question 26.
How much protein is needed for a day?
a) 1 gm per kg
b) 2 gm per kg
c) 1.5gmperkg
d) 2.5gmperkg
Answer:
a) 1 gm per kg
(2 marks)
II. Very Short Questions
Question 1.
What are the uses of food?
Answer:
The food we eat provides energy and organic substances for growth and the replacement of worn-out and damaged tissues. It regulates and coordinates the various activities that take place in the body.
Question 2.
What are the special features that help in absorbing digested food?
Answer:
- There is an increase in the small intestine surface area.
- The villi are present in the inner walls of the intestine.
- The villi is the absorbtive unit
- The microvilli present in the villi increase the absorptive surface.
Question 3.
Why do we need a digestive system?
Answer:
The food that we eat is macromolecules, and inabsorbable. These are to be broken down into smaller macro-molecules in absorbable forms. This is done by the digestive system.
![]()
Question 4.
How is fat and other nutrients of bile helped in digestion?
Answer:
It helps in emulsifying fat. The bile salt decreases the surface tension of fat molecules and converting it to chilo micron.
Question 5.
What is the function of the digestive system?
Answer:
The function of the digestive system is to bring the nutrients, water, and electrolytes from the external environment into every cell in the body through the circulatory system.
Question 6.
What happens when there is no secretion of HCI in the stomach?
Answer:
- The HCI in the stomach coverts the inactivated pepsinogen into active pepsin.
- The activated pepsin acts on protein and converts them into proteases and peptones
- HCI provides an acidic medium which is optimum for pepsin action.
Question 7.
List out the processes starting from the ingestion of protein and storning in the muscle cells and converting them in to the parts of cytoplasm?
Answer:
Stomach:
The gastric juice contains pepsin. This is the first enzyme that works on protein.
![]()
- Rennin is present in the gastric juice of infants
- It helps in the digestion of caesinogen and converts into casein.
![]()
Pancreas:
- Trypsin hydrolyses proteins in to polypeptides and peptones.
- Chymotrypsin hydrolyses peptide bonds associated with specific amino acids.
Succus Entricus
The peptidases present in the intestinal juice convert the di and polypeptides to amino acids.
![]()
The end product of digestion the amino acids that are absorbed by the villi and reach the blood.
![]()
Question 8.
What is diphyodont dentition?
Answer:
Human beings and many mammals form two sets of teeth during their lifetime, a set of 20 temporary milk teeth which gets replaced by a set of 32 permanent teeth. This type of dentition is called diphyodont dentition.
Question 9.
Why the food prepared in the house is better than the food which is prepared by causing preservative and artificial enhancers?
Answer:
The food prepared by using artificial enhancers and preservatives creates so many diseases.
Diseases
- Heart problems
- Hypertension
- Sterility
- Stomach disorders
- Attainment of early puberty in girl children.
Question 10.
What is known as the dental formula of human beings?
Answer:
The arrangement of teeth in each half of the upper and lower jaw in the order of I, C, P, and M can be represented by the dental formula. The dental formula of man is 2123 / 2123.
![]()
Question 11.
What are the steps to be taken to care for our alimentary tract?
Answer:
- We have to take healthy foods.
- We have to take plenty of water.
- We have to regulate our stress.
- We have to take probiotics daily.
- We have to do exercise daily.
Question 12.
What are the functions of soluble and insoluble fibres?
Answer:
The food contain two types of fibres.
Soluble fibre: It soaks up toxins and waste in the digestive system.
Insoluble fibre: Roughage. It moves bulk through the intestine to help with regular bowel movements.
This upper surface of the tongue has small projections called Papillae.
![]()
Question 13.
What is the function of the tongue?
Answer:
The tongue helps in the intake of food, chew and mix food with saliva, swallow food, and also speak. The upper surface of the tongue has small projections called papillae with taste buds.
Question 14.
What are Oesophages?
Answer:
Oesophages connect the buccal cavity and stomach.
Question 15.
What is gastro oesophagus reflux disorder?
Answer:
If the cardiac sphincter does not contract properly during the churning action of the stomach the gastric juice with acid may flow back into the oesophagus and cause heart bum, resulting in GERD (Gastro Oesophagus Reflex Disorder).
Question 16.
How larger food molecules are converted into small molecules?
Answer:
| Large Molecules | Small Molecules |
| 1. Carbohydrate | Monosaccharides – Glucose fructose Galactose |
| 2. Protein | Amino acids |
| 3. Fat | Amino acids |
Question 17.
What are gastric rugae?
Answer:
The inner wall of the stomach has many folds called gastric rugae which unfold to accommodate a large meal.
![]()
Question 18.
What is meant by colities?
Answer:
- The bacterial infection may cause inflammation of the innerlining of colon called colitis.
- The most common symptoms of colitis are rectal bleeding abdominal cramps and diarrhoea.
Question 19.
What is indigestion?
Answer:
- It is a digestive disorder in which the food is not properly digested leading to a feeling of fullness of stomach.
- It may be due to in adequate enzyme secretion anxiety food poisoning overeating and spicy food.
Question 20.
Give notes on vomiting?
Answer:
It is reverse peristalsis. Harmful substances are ejected through the mouth. This action is controlled by the vomit centre located in the medulla oblongate a feeling of nausea precedes vomiting.
![]()
Question 21.
What is meant by digestion? What is the different processes of digestion?
Answer:
The break down of the macromolecules of food in to the micro molecules of food is known as digestion.
Stages
- Ingestion
- Digestion
- Absorption
- Assimilation
- Elimination of undigested substances digestion
Question 22.
What is Frenulum?
answer:
The tongue is attached at the posterior end to the floor of the buccal cavity by the structure frenulum and the tongue is free in the front.
![]()
Question 23.
What is meant by GERD – GASTERO oesophagus reflex disorder?
Answer:
- There are two sphincter muscles namely cardiac sphincter and pyloric sphincter present in the stomach.
- If the sphineter does not contract properly during the churning action of the stomach of the gastric juice with acid may flow back in to the oesophagus and cause heart bum resulting in GERD.
Question 24.
How is piles or haemorrhoides formed?
Answer:
- The anal mucosa is folded into several vertical folds contains arteries and veins called anal columns.
- if these anal columns get enlarged and causes piles or haemorrhoides.
Question 25.
Name the enzyme which converts the inactivated enzymes into the active enzyme.
Answer:
1. Enterokinase:
It converts the inactivated Trypsinogen in to Trypsin.
2. Trypsin:
The inactive chymotrypsinogen is converted into chymotrypsin

Question 26.
What are the food components needed for a person for healthy living?
Answer:
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Lipids
- Vitamin
- Minerals
- Fibre
- Water
Question 27.
Define Thecodont?
Answer:
Each tooth is embedded in a socket in the jaw bone; this type of attachment is called thecodont.
![]()
Question 28.
What is meant by assimilation?
answer:
All the body tissues utilize the absorbed substances for their activities and incorporate in to their protoplasm this process is called assimilation.
Question 29.
Define Plaque.
Answer:
Minerals salts like Calcium and Magnesium are deposited on the teeth and form a hard layer of tartar or calculus called plaque.
Question 30.
What is Papillae?
Answer:
This upper surface of the tongue has small projections called Papillae.
Question 31.
What are the parts of Stomach?
Answer:
- A cardiac portion
- A fundic portion
- A pyloric portion
Question 32.
What is the portion of small intestine?
Answer:
Duod enum – 25Cm
Jejunum-2.4m
Ileum-3.5m
Question 33.
What is Gastric rugae?
Answer:
The inner wall of the stomach has much folds called gastric rugae which unfolds to accommodate a large meal.
![]()
Question 34.
What are the parts of large Intestine?
Answer:
- Caecum
- Colon
- Rectum
Question 35.
What are the regions of colon.
Answer:
The colon is divided into four region.
- An ascending region
- A Transverse region
- A Descending region
- A Sigmoid region
Question 36.
What are the layers found in the alimentary canal?
Answer:
- Serosa
- Muscularis
- Sub – mucosa
- Mucosa
Question 37.
What are the elements found in Saliva?
Answer:
- Water
- Electrolytes (Na+, K+, Cl–, HCO3–)
- Salivary Amylase (Ptyalin)
- Anti bacterial agent Lysozyme
- Lubricating agent mucus (glycoprotein).
Question 38.
What are the components present in bile?
Answer:
- Bilirubin
- Biliverdin
- Bile Salts
- Cholesterol
- Phospholipids
Question 39.
Name the gastric juices found in the stomach.
Answer:
- Hydrochloric acid (PH 1.8)
- Proenzyme – Pepsinogen
- Pepsin Rennin
Question 40.
What is the function of Pyloric Sphincter?
Answer:
- The opening of the stomach into the duodenum is guarded by the Pyloric Sphincter.
- It periodically allows partially digested food to enter the duodenum and also prevents regurgitation of food.
Question 41.
What is the Calorific value of carbohydrates?
Answer:
- The caloric value of Carbohydrates is 4.1 calories /gram.
- The physiological fuel value is 4 Kcal / gram.
Question 42.
A person is suffering from a digestion problem. What may be the reason?
Answer:
This person may be suffering from constipation.
Constipation:
The faeces are retained within the rectum, because of irregular bowel movement due to poor intake of fibre in the diet and lack of physical activities.
![]()
Question 43.
What is oral hydration therapy?
Answer:
If there is more loss of water due to diarrhea dehydration may occur. Treatment is known as oral hydration therapy.
This involves drinking plenty of fluids sipping small amounts of water at a time interval to rehydrate the body.
Question 44.
Define Obesity.
Answer:
It is caused due to the storage of excess of body fat in adipose tissue.
It may induce hypertension, atherosclerotic heart disease and diabetes.
Question 45.
What is BMI Calculation?
Answer:
BMI is calculated as body weight in Kg, divided by the square of height in meter.
\(\mathrm{BMI}=\frac{\text { Body Weight in } \mathrm{Kg}}{\text { (Body Height) }^{2} \text { in meter }}\)
For example :
A person Weight = 50 Kg
Height = 1.6m
\(=50 / 1.6^{2}\)
BMI = 19.5
(3 marks)
III. Short Questions
Question 1.
Define Gingivitis?
Answer:
The plaque formed on teeth is not removed regularly, it would spread down the tooth into the narrow gap between the gums and enamel and cause inflammation, called gingivitis.
Symptoms;
It leads to redness and bleeding of gums and leads to bad smell.
Question 2.
What is Heterodont?
Answer:
The permanent teeth are of four different types (heterodont).
Incisors – Chisel like cutting teeth
Caniues – Dogger shaped tearing teeth
Premolar -Grinding Molar – Grinding and Crushing
\(\frac{2123}{2123} \times 2=\frac{16}{16}\)
Upper Jaw – 16 teeth
Lower Jaw – 16 teeth
![]()
Question 3.
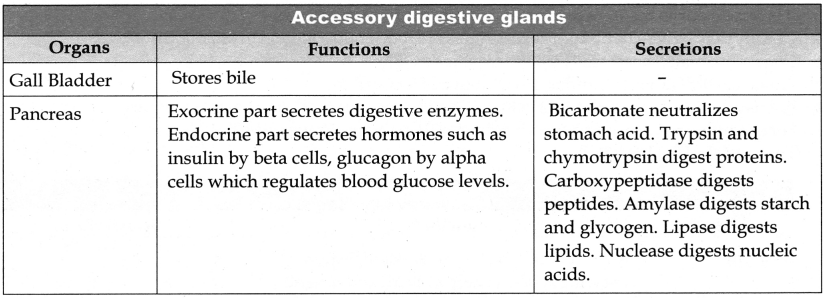
What are the signifance of Liver?
Answer:
1. Destroy aging and defective bloodcells.
2. Stored glucose in the form of glycogen or disperses glucose into the blood stream with the help of pancreatic hormones.
3. Stores fat soluble vitamins and iron.
4. Detoxifies toxic substances.
5. Involves in the synthesis of non – essential aminoacids and urea.
Question 4.
Explain about the protein deficiency disease.
Answer:
Protein Energy Malnutrition (PEM):
- Marasmus
- Kwarshiorkor Marasmus:
- Children are suffering from diarrhoea Body becomes lean and weak
- Reduced fat and muscle tissue with thin and folded skin.
Kwashiorkor:
- Dry skin
- Potbelly
- Edema in the legs and face
- Stunted growth
- Changes in hair colour
- Weakness and irritability
Question 5.
Name the digestive secretions.
Answer:
- Salivary glands
- Bile juice
- Pancreatic juice Gastric juice Small Intestinal juice.
Question 6.
What are the types of Salivary glands and their ducts?
Answer:
| Gland | Location | Ducts |
| 1.Parotids | Cheeks | Stenson’s duct |
| 2. Submandibular | Lower Jaw | Wharton’s duct |
| 3. Sublingual | Beneath the tonguç | Bartholin’s duet (or) ducts of Rivinis |
| The daily secretion of Saliva from Saliva glands ranges from 1000 to 1500ml. | ||
Question 7.
What are the cells of gastric gland and their Secretions?
Answer:
| Gastric cells of glands | Secretion |
| 1. Chief cells (or) Peptic cells (or) Zymogen cells | Gastric enzymes |
| 2. Goblet cells | Mucus |
| 3. Parietal (or) Oxyntic cells | HCI an intrinsic factor responsible for the absorption of vitamin B12 is called castle’s intrinsic factor. |
Question 8.
Draw and label the layers of the alimentary canal.
Answer:
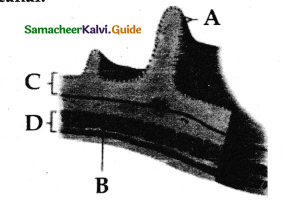
A – Microvilli
B – Circular muscle
C – Mucous
D – Muscular layer
![]()
Question 9.
Explain the protein deficiency diseases.
Answer:
Growing children require more amount of protein for their growth and development. Protein deficient diet during the early stage of children may lead to protein-energy malnutrition such as Marasmus and Kwashiorkor. Symptoms are dry skin, pot-belly, oedema in the legs and face, stunted growth, changes in hair colour, weakness, and irritability.
Marasmus is an acute form of protein malnutrition. This condition is due to a diet with inadequate carbohydrates and protein. Such children are suffering from diarrhea, the body becomes lean and weak (emaciated) with reduced-fat and muscle tissue with thin and folded skin.
Question 10.
What are the ill effects of adulteration of food?
Answer:
- Food adulteration causes harmful effects in the form of head ache palpitations allergies, cancers.
- It reduces the food quality common adulteration are addict onto citric acid to lemon juice.
- Papaya seeds to pepper melamine to milk.
Question 11.
A person has diet control in particular time, he takes large amount of rice, curd, buttermilk and onion why? and write about it?
Answer:
Yes the person is suffering from Jaundice.
Jaundice:
- It is the condition in which liver is affected and the defective liver fails to break down haemoglobulin and to remove bile pigments from the blood.
- Deposition of these pigments changes the colour of eyes and skin yellow.
- Jaundice is caused due to hepatitis Viral Infection
![]()
Question 12.
What is the effects of crystallized cholesterol?
Answer:
The effects of crystallized cholesterol is Gall Stones.
Gall Stones:
- Any alteration in the composition of the bile can cause the formation of stones in the gall bladder.
- The stones are mostly formed of crystallized cholesterol in the bile.
- The gall stone causes obstruction in the cystic duct, hepatic duct and also hepatopancreatic duct, causing pain, Jaundice and pancreatitis.
Question 13.
What is indigestion?
Answer:
It is a digestive disorder in which the food is not properly digested leading to a feeling of fullness of stomach. It may be due to inadequate enzyme secretion, anxiety, food poisoning, overeating and spicy food.
Question 14.
Writes notes on Peptic Ulcer.
Answer:
- It refers to an eroded area of the tissue lining (Mucosa) in the stomach or duodenum.
- A duodenal ulcer occurs in people in the age group of 25-45 years.
- Gastric ulcer is more common in person above the age of 5üyears.
- Ulcer mostly due to infections caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylon.
- It may be due to uncontrolled usage of aspirin or certain anti-inflammatory drugs.
- It is caused due to smoking, alcohol, caffeine, and psychological stress.
Question 15.
What is a hiatus hernia or diaphragmatic hernia?
Answer:
It is a structural abnormality in which the superior part of the stomach protrudes slightly above the diaphragm. The exact cause of hiatus hernias is not known. In some people, injury or other damage may weaken muscle tissue, by applying too much pressure (repeatedly) on the muscles around the stomach while coughing, vomiting, and straining during bowel movement and lifting heavy objects.
Question 16.
Give notes on the stomach.
Answer:
- Stomach functions as the temporary storage organ for food.
- It consists of three parts cardiac fundic and pyloric stomach.
- The oesophagus opens into a cardiac stomach and guarded by cardiac sphincter.
- The pyloric stomach opens into duodenum and is guarded by the pyloric sphincter.
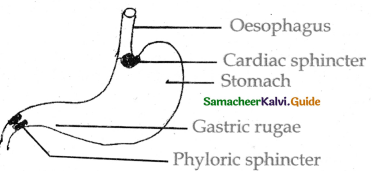
- It allows partially digested food to enter the duodenum and prevents regurgitation of food.
- The inner walls of stomach has many folds which unfolds to accommodate a large meal.
Question 17.
Give short notes on intestinal villi?
Answer:
- The ileal mucosa has numerous vascular projections called villi which are involved in the process of absorption.
- The cells lining the villi produce numerous microscopic projections called microvilli giving a brush border appearance and increase the surface area enormously.
- Along with villi the clear mucosa contain mucous secreting goblet cell and peyer patches which produce lymphocytes.
- The wall of the small intestine bears crypts between the base of villi called crypts of leiberkuhn.
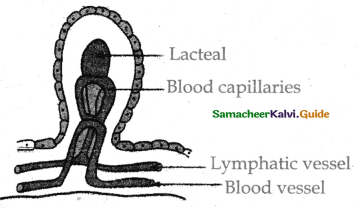
Question 18.
Write a paragraph on peptic ulcers.
Answer:
It refers to an eroded area of the tissue lining (mucosa) in the stomach or duodenum. A duodenal ulcer occurs in people in the age group of 25 – 45 years. Gastric ulcer is more common in persons above the age of 50 years. An ulcer is mostly due to infections caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. It may also be caused due to uncontrolled usage of aspirin or certain anti-inflammatory drugs. An ulcer may also be caused due to smoking, alcohol, caffeine, and psychological stress.
![]()
Question 19.
Give an account of the Pancreas.
Answer:
- The Pancreatic is the second-largest gland in the digestive system which is a yellow coloured compound organ.
- It consists of exocrine and endocrine cells.
- It is situated between the limbs of the ‘U’ shaped duodenum.
- The exocrine portion secretes trypsin, pancreatic lipase, amylase.
- The islets of Langerhans cells of the pancreas secrete insulin and glucogen hormone.
Question 20.
Name the alimentary canal parts and the absorptive substance.
Answer:
| Organ | Substances tube absorbed |
| 1. Mouth | Water Simple Sugar |
| 2. Stomach | Alcohol, Medicine, Simple Sugar |
| 3. Intestine | Simple Sugar, Amino acids, Fatty Acids, Glycerol |
| 4. Colon | More Water, Minerals, Vitamins, Medicines |
(5 marks)
IV. Essay Questions
Question 1.
Describe the structure of the large intestine with a diagram.
Answer:
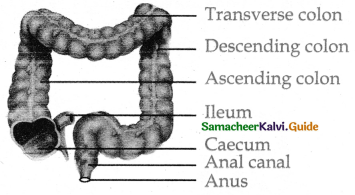
1. The Caecum:
- It is a small blind pouch-like structure that opens into the colon and it possesses a narrow finger-like tubular projection called vermi form appendix.
- Caecumand vermiform appendix is large in herbivorous animals and act as an important site for cellulose digestion with the help of symbiotic bacteria.
2. The Colon:
The colon is divided in to four regions an ascending transverse a descending part and a sigmoid Colon. The Colon is lined by dilations called haustra.
3. Sigmoid Colon:
- ‘S’ shaped sigmoid colon opensinto the rectum.
- The anus is guarded by two anal sphincter muscles. The anal mucosa is folded in to several vertical folds and contains arteries and veins called anal column.
- Anal colomn may get enlarged and causes piles.
Question 2.
Describe the structure of liver with a diagram.
Answer:
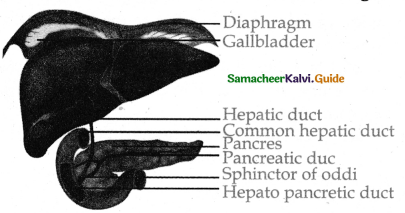
- The liver is the largest gland in our body.
- It is situated below the diaphragm.
- The liver consists of two major left and right lobes and two minor lobes.
- Each lobe has many hepatic lobules called a functional unit of liver and is covered by a thin connective sheath called Glissons capsule.
- Liver cells secrete and is stored in gall bladder. The duct of gall bladder and the hepatic duct form the common bile duct.
- The bile duct and the pancreatic duct joined to gether formed a common duct and opens into duodenum and is guarded by a sphincter of oddi.
- Liver has high power of regeneration and liver cells are replaced by new ones every 3-4 weeks.
Question 3.
Describe the process of digestion in the mouth.
Answer:
- The smell the sight and taste as well as the mechanical stimulation of food in the mouth trigger a reflex action that results in the secretion of saliva.
- The mechanical digestion starts in the mouth by grinding and chewing of good.
- The saliva contains water electrolytes like Na, K, C1, HCO3 salivary amylase or ptyalin antibacterial agent lysozyme and a lubrication agent mucus.
- The saliva moistening lubricating and adhering the masticated food into a bolus.
- The ptyalin in the saliva hydrolyzes 30% of the poly saccharide into disaccharides.
- The bolus is passed into the pharynx and then into the oesophagus by swallowing or deglutition.
- The bolus reaches the stomach by successive waves of muscular contraction called peristalsis.
![]()
Question 4.
Describe the process of digestion in the stomach
Answer:
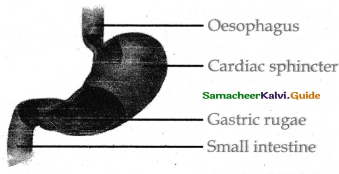
- The secretion of gastric juice begins when the food is in the mouth.
- The gastric juice contains HCI pepsinogen renin etc.
- The HCI changes the pepsinogen into pepsin.
![]()
- Pepsin acts on protein and converts into proteoses and peptones.
![]()
- The HCI provides an acidic medium which is optimum for pepsin kills bacteria and other harmful organisms and avoids putrefaction.
- The mucous and bicarbonates protect the stomach from acidic HCl.
- The rennin converts the milk protein caesinogen to casein in the presence of calcium ions.
![]()
Question 5.
Describe the process of digestion in the small intestine.
Answer:
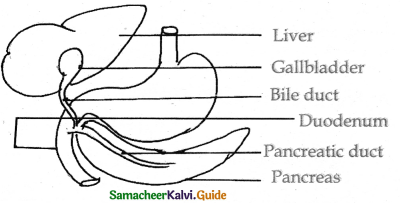
The bile pancreatic juice and intestinal juice the secretions released into the small intestine.
Bile:
- The bile contains bile pigments bilirubin and biliverdin as the break down products of haemoglobin of dead RBCs bile salts.
- Bile helps in emulsification of fats Bile salts reduce the surface tension of the fat droplets and break them into small globules.
- Bile also activates lipases to digest lipids.
Pancreas:
- The pancreatic juice contains enzymes such as trypsinogen, Chymotrypsinogen.
- Trypsinogen is activated by an enzyme enterokinase into active trypsin.
- Trypsin activate the chymotrypsinogen into chymotrypsin.
- Trypsin hydrolyses protein into polypeptides and peptones.
![]()
Chymotrypsin hydrolyses peptide bonds associated with specific aminoacids.
The amylase converts glycogen and starch into maltose.
Lipase acts on tri glycerides and hydrolyes them into free fatty acid and mono glycerides.

Succtts entricus:
![]()
Question 6.
What is meant by absorption? How is digested food absorbed in the digestive system?
Answer:
Absorption is a process by which the end product of digestion passes through the intestinal mucosa in to the blood and lymph.
Process of absorption:
1. Simple Diffusion:
Small amounts of glucose amino acids and chloride ions are absorbed by simple diffusion.
2. Facilitated Transport:
Fructose arc absorbed with the help of the carrier ions like Na.
3. Active Transport:
Aminoacids, Glucose and Sodium are absorbed by active transport.
4. Passive Transport:
Fatty acid are absorbed by the Lacteals of Villi.
Question 7.
What is the caloric value of carbohydrates, proteins and fats?
Answer:
We obtain 50% of energy from carbohydrates 35 % from fats and 15 % from proteins.
We require about 400 – 500 gm of carbohydrates. 60 – 70 gm of fat 65 to 75 gm of proteins per day.
Carbohydrate:
The caloric valve of Carbohydrate is 4.1 calories gram and its physiological fuel value is 4 Kcal per gram.
Lipid:
Fat hasa caloric valve of 9.45 KCal and a physiological fuel value of 9 KCal per gram.
Protein:
The caloric and physiological fuel value of one gram of protein are 5.65 Kcal and 4 KCal respectively.
![]()
Question 8.
What is meant by Hiatus hernia or Oesophagus Hernia
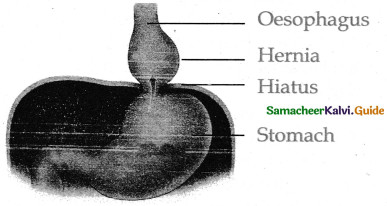
- It is a structural abnormality in which superior part of the stomach protrudes slightly above the diaphragm.
- Applying toomuch pressure on the muscles around the stomach while coughing, vomiting and straining during bowel movement and lifting heavy object it may weaken the muscle tissues of stomach.
- In some people injury or the damage may weaken muscle tissue.
- Heart burn is common in this disease.
- The stomach contents travel back into the oesophagus or even into oral cavity and causes pain in the centre of the chest due to the eroding nature of acidity.
Question 9.
Obesity – Explain.
Answer:
- It is caused due to the storage of excess of body fat in adipose tissue.
- Obesity may be genetic or due to excess intake of food endocrine and metabolic disorders.
- Degree of obesity is assessed by body mass index (BMI).
- A Normal BMI range for adult is 19 – 25 above 25 is obese.
- BMI is calculated as body weight in Kg divided by the square of body height in metres.
- For example a 50 Kg person with a height of 160 Cms would have a BMI of 19.5.
- That is BMI \(=50 / 1.6^{2}\) = 19.5