Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Guide Pdf Chapter 12 Trends in Economic Zoology Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Guide Chapter Chapter 12 Trends in Economic Zoology
11th Bio Zoology Guide Trends in Economic Zoology Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part I
Question 1.
Which one of the following is not related to vermiculture?
a) Maintains soil fertility
b) Break down of inorganic matter
c) Gives porosity, aeration and moister holding capacity
d) Degradation of non biodegradable solid waste
a) a and b is correct
b) c and d is correct
c) b and d is not correct
d) a and c is not correct
Answer:
c) b and d is not correct
Question 2.
Which one of the following is not an endemic species of earthworm?
a) Perionyx
b) Lampito
c) Eudrillus
d) Octochaetona
Answer:
c) Eudrillus
![]()
Question 3.
Match the following
1) Bombyxmori-
a) Champa – I) Muga
2) Antheraeaassamensis
b) Mulberry – II) Eri
3) Antheraeamylitta-
c) Arjun – III) Tassar
4) Attacus ricini –
d) Castor – IV) Mulberry
Select the correct one
a) 1-b-IV
b) 2-a-I
c) 3-c -III
d) 4-d-II
Answer:
c) 3-c -III
Question 4.
Silk is obtained from
a) Laccifer lacca
b) Nosema bombycis
c) Attacus ricird
d) Attacus mylitta
Answer:
c) Attacus ricird
![]()
Question 5.
Assertion: Nuptial flight is a unique flight taken by the queen bee followed by serveral drones.
Reason: The queen bee produces a chemical substance called pheromone. The drones in that area are attracted to the pheromone and then mating takes place.
a) Assertion and reason is correct but not related
b) Assertion and reason is incorrect but related
c) Assertion and reason is correct but related
d) Assertion and reason is incorrect but not related
Answer:
c) Assertion and reason is correct but related
Question 6.
Rearing of honey bee is called
a) Sericulture
b) Lac culture
c) Vermiculture
d) Apiculture
Answer:
d) Apiculture
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the statement regarding Lac insect
a) A microscopic, resinous crawling scale insect
b) Inserts its proboscis into plant tissue suck juices and grows
c) Secretes lac from the hind end of body.
d) The male lac insect is responsible for large scale production of lac.
Answer:
d) The male lac insect is responsible for large scale production of lac.
Question 8.
Aquaponics is a technique which is
a) A combination of aquaculture and fish culture
b) A combination of aquaculture and hydroponics
c) A combination of vermiculture and hydroponics
d) A combination of aquaculture and prawn culture
Answer:
b) A combination of aquaculture and hydroponics
![]()
Question 9.
Prawn belongs to the class
a) Crustacea
b) Annelida
c) Coelenterata
d) Echinodermata
Answer:
a) Crustacea
Question 10.
Pearl oyster belongs to the class
a) Gastropoda
b) Cephalopoda
c) Scaphapoda
d) Pelecypoda
Answer:
d) Pelecypoda
![]()
Question 11.
Inland fisheries are
a) deep sea fishing
b) capturing fishes from sea coast
c) Raising and capturing fishes in fresh water
d) oil extraction from fish
Answer:
c) Raising and capturing fishes in fresh water
Question 12.
Induced breeding technique is used in
a) Marine fishery
b) Capture fishery
c) Culture fishery
d) Inland fishery
Answer:
d) Inland fishery
![]()
Question 13.
Isinglass is used in
a) Preparation
b) Clearing of wines
c) Distillation of wines
d) Preservation of wines
Answer:
b) Clearing of wines
Question 14.
Animal husbandry is the science of rearing, feeding and caring, breeding and disease control of animals. It ensures supply of proper nutrition to our growing population through activities like increased production and improvement of animal products like milk, eggs, meat, honey etc.
a) Poultry production depends upon the photoperiod. Discuss
b) Polyculture of fishes is of great importance.
Answer:
a) Poultry production depends upon the photoperiod:
- The photoperiod stimulates the growth and breeding of birds.
- It increases the life span of birds
- As it increases the metabolic rate the egg-laying fowl’s wifi lay more eggs.
- The light induces the endocrine glands and increases hormone secretion.
- The light intensity depends on its wavelengths.
b) Polyculture of fishes is of great importance:
- In polyculture, fishes will not fight for food.
- No deficiency of oxygen.
- In this culture the upper layer fishes feeds on phy to and zooplanktons the middle layer fishes feeds on
- submerged plants and fishes lives in the deeper layers feeds on bottom dwellers debris of plants and animals.
- In polyculture the fishes use the maximum food to convert it into meat.
- Fishes have high growth rate in short periods.
Eg.: Catlacatla, cirrhinus mrigla labeorohita are cultured through polyculture.
![]()
Question 15.
Assertion: The best quality of pearl is known as lingha pearl and obtained from marine oysters.
Reason: Nacre is secreted continuously by the epithelial layer of the mantle and deposited around the foreign particle
a) Assertion is true Reason is false
b) Assertion and Reason is false
c) Asserion is false but Reason is true
d) Assertion and Reason are true
Answer:
d) Assertion and Reason are true
Question 16.
Choose the correctly matched pair
a) Egg layers-Brahma
c) Dual purpose-White plymouth rock
b) Broiler types -Leghorn
d) Ornamental breeds -Silkie
Answer:
d) Ornamental breeds -Silkie
![]()
Question 17.
Write the advantages of vermicomposting.
Answer:
- Vermicomposting provides excellent organic manure for sustainable agro-practices.
- Marketing of vermicompost can provide a supplementary income.
- Vermicompost is rich in essential plant nutrients.
- It improves soil structure, texture, aeration, and water holding capacity and prevents soil erosion.
- It is rich in nutrients and an eco-friendly amendment to soil for farming and terrace gardening,
- It enhances seed germination and ensures good plant growth.
Question 18.
Name the three castes in a honey bee colony.
Answer:
- Queen bee
- Drone
- Worker bee
![]()
Question 19.
Name the following
- The largest bee in the colony:
- The kind of flight which the new virgin queen takes along with the drones out of the hive:
Answer:
- The largest bee in the colony – The queen bee
- The kind of flight which the new virgin queen takes along with the drones out of the hive – Nuptial flight.
Question 20.
What are the main duties of a worker bee?
Answer:
Each worker has to perform different types of work in her lifetime. During the first half of her life, she becomes a nurse bee attending to indoor duties such as secretion of royal jelly, prepares bee- bread to feed the larvae, feeds the queen, takes care of the queen and drones, secretes beeswax, builds combs, cleans and fans the beehive. Then she becomes a soldier and guards the beehive. In the second half of her life lasting for three weeks, she searches and gathers the pollen, nectar, propolis, and water.
![]()
Question 21.
What happens to the drones after the mating flight?
Answer:
The drones are attracted to the pheromones of the queen bee and mating taking place The drone dies after copulation
Question 22.
Give the economic importance of silkworm?
Answer:
- Rearing of silkworm on a commercial scale is called sericulture.
- It is an agro-based industry comprising of
- Cultivation of food plants for the silkworms.
- Rearing of silkworms.
- Reeling and spinning of silk.
- Silk fibres are utilized in preparing silk clothes.
- Silk is used in industries and for military purposes.
- Silk is used in the manufacture of fishing fibres, parachutes, cartridge bags, insulation coils for telephone, wireless receivers, tyres of racing cars, filter fibres, in medical dressings and suture materials.
![]()
Question 23.
What are the nutritive values of fishes?
Answer:
- Fishes form a rich source of protein food.
- It is a good stable food to tide over the nutritional needs of man.
- Fish species such as sardines mackeral, tuna herrings have high amino acid concentrations.
- They have histidine which is responsible for the meaty flavor of the flesh.
- It is rich in omega 3 fatty acids.
- Minerals such as calcium magnesium phosphorus potassium iron-manganese iodine and copper is present in fishes.
Question 24.
Give the economic importance of prawn fishery?
Answer:
The flesh of prawns is palatable and rich in glycogen, a protein with low-fat content.
![]()
Question 25.
Give the economic importance of lac insect.
Answer:
- Lac is used as a sealing wax and adhesive for optical instruments.
- It is a good insulator.
- It is used in the preparations of shoe and leather polishes and as a protective coating of wood.
- It is used in laminating paper board photographs, plastic moulded articles.
- Used as a filling material for gold ornaments.
Question 26.
List any three common uses of shellac.
Answer:
- Shellac with denatured alcohol is used to remove dust on the walls.
- Coating of metals with shellac prevents rusting.
- Shellac coating on citrus fruits increases their shelf life.
![]()
Question 27.
Name any two trees on which lac insect grows?
Answer:
- Acacia catechu
- Acacia nilotica
Question 28.
What is seed lac?
Answer:
The lac after grinding the dust particles are removed. The resultant lac is called ‘seed lac’.
Question 29.
Define cross-breeding?
Answer:
Breeding between a superior male of one breed with a superior female of another breed is known as cross-breeding.
![]()
Question 30.
What are the advantages of artificial insemination?
Answer:
- It increases the rate of conception.
- It avoids genital diseases.
- Semen can be collected from injured bulls which have desirable traits.
- Superior animals located apart can be bred successfully.
Question 31.
Discuss the various techniques adopted in cattle breeding?
Answer:
There are two methods of animal breeding, namely inbreeding and outbreeding.
1. Inbreeding:
Breeding between animals of the same breed for 4-6 generations is called inbreeding.
2. Outbreeding:
The breeding between unrelated animals is called outbreeding. It is done in three ways;
- Outcrossing: It is the breeding between unrelated animals of the same breed but having no common ancestry. The offspring of such a cross is called an outcross.
- Crossbreeding: Breeding between a superior male of one breed with a superior female of another breed. The cross-bred progeny has superior traits (hybrid vigour or heterosis).
- Interspecific hybridization: In this method of breeding mating is between male and females of two different species.
![]()
Question 32.
Mention the advantages of MOET.
Answer:
The advantage of this technology is to produce high milk-yielding females and high-quality meat-yielding bulls in a short time.
Question 33.
Write the peculiar characters of the duck.
Answer:
The peculiarity of ducks:
The ducks body is fully covered with oily feathers. They have a layer of fat under their skin which prevents it from getting wet. They lay eggs at night or in the morning. The ducks feed on rice bran, kitchen wastes, waste fish, and snails.
Part – II
11th Bio Zoology Guide Trends in Economic Zoology Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose The Best Options
Question 1.
What is the primary use of earthworm?
a) Vermicompost
b) Increase the agriculture
c) To increase the fish culture
d) All the above
Answer:
a) Vermicompost
Question 2.
Who has proposed the term vermi tech?
a) Sultan Ismail
b) Darwin
c) Linnaeus
d) Albert William
Answer:
a) Sultan Ismail
![]()
Question 3.
……………………. are the biological indicators of soil fertility?
a) Vermicast
b) Earthworm
c) Vermi excreta
d) Vermicompost
Answer:
b) Earthworm
Question 4.
Which of the following is the earthworm of the native soil?
a) Periyonx Eisenia
b) Eudrilus eugeniae lampito mauritii
c) Periyonyx excavatus, octohaetona
d) all the above
Answer:
c) Periyonyx excavates, octohaetona
![]()
Question 5.
Which is called commercial fibre?
a) Silk fibre
b) Nylon fibre
c) Cofton fibre
d) Jute fibre
Answer:
a) Silk fibre
Question 6.
Who has known the utility of silk even before 3000 years?
a) Europe
b) African’s
c) China
d) India
Answer:
c) China
![]()
Question 7.
…………………… More than countries in the world are practicing sericulture?
a) 29
b) 40
c) 10
d) 15
Answer:
a) 29
Question 8.
Match and find the correct sequences.
I. Bombyx mori – a) Erisilk
II. Antheraea assamensis – b) Tisaarsilk
III. Antheraea mylitta – c) Mugasilk
IV. Attacus ricini – d) Mulberry silk

Answer:
a) I – d, II – c, III – b, IV – a
![]()
Question 9.
Match the silk moth with their respective leaves.
I. Bombyx mori – a) Castor
II. Antheraea assamensis – b) Arjun
III. Antheraea mylitta – c) Champa
IV. Attacus ricini – d) Mulberry
![]()
Answer:
a) I -d, II – c, III – b, IV – a
Question 10.
Find the unrelated pair regarding the silk production and its states.
a) Karnataka – Mulberry silk
b) Manipur – Muga silk
c) West bengal – Tasar silk
d) Arunachala pradesh – Muga silk
Answer:
d) Arunachala pradesh – Muga silk
![]()
Question 11.
Name the branches that involve agriculture and industry.
a) Vermiculture
b) Pisciculture
c) Sericulture
d) Poultry
Answer:
c) Sericulture
Question 12.
Life span of Bombyxmori
a) 2-3 days
b) 2 – 4 days
c) 2-5 days
d) 4 – 7 days
Answer:
a) 2 – 3 days
Question 13.
What is the number of eggs laid by Bombyx mori once?
a) 500 – 800
b) 400 – 500
c) 400 – 450
d) 600-700
Answer:
b) 400 – 500
![]()
Question 14.
What is the length of matured silkworm?
a) 7.5 cm
b) 7cm
c) 8.5 cm
d) 8 cm
Answer:
a) 7.5 cm
Question 15.
What would be the length of silk fibre in a cocoon?
a) 1000-1100 m
b) 1000-1200 m
c) 1000-1500m
d) 1000 – 1300m
Answer:
b) 1000 – 1200m
![]()
Question 16.
What is meant by mariculture?
a) Rearing of mulberry plants
b) Rearing of castor plants
c) Vermiculture
d) Apiculture
Answer:
a) Rearing of mulberry plants
Question 17.
What is meant by voltinism?
a) No of broods raised
b) Cocoon
c) Spinneret
d) None of the above
Answer:
a) No of broods raised
![]()
Question 18.
What is the ideal period for mulberry culture?
a) January, February, and November, December
b) March, April and June, July
c) June, July, and Nov, December
d) October, November and December, January
Answer:
c) June, July, and November, December
Question 19.
Find the odd one out.
a) Healthy silk moths are allowed to mate for 4 hours
b) Female lays about 400 eggs in 24 hours
c) The small larvae hatch between 7-10 days after incubation
d) The optimum temperature for rearing silk moth is 25°C – 30°C
Answer:
d) The optimum temperature for rearing silk moth is 25°C – 30°C
![]()
Question 20.
Silkmoth matured in about days
a) 40 days
b) 45 days
c) 50 days
d) 35 days
Answer:
b) 4 5 days
Question 21.
The cocoon is soaked in hot water in temperature for minutes.
a) 95°C – 97°C -10 -15 minute
b) 95°C – 97°C – 5 -10 minutes
c) 90°C – 95°C – 7 -10 minutes
d) 100°C – 105°C – 2 – 5 minutes
Answer:
a) 95°C – 97°C -10 -15 minute
![]()
Question 22.
The areas where a lot of beehives can be placed.
a) Honey culture
b) Apiculture
c) Apiaries
d) all the above
Answer:
c) apiaries
Question 23.
The nectar got from the flowers is converted into honey by the enzyme.
a) Invertase
b) Zymase
c) Lipase
d) None of the above
Answer:
a) Invertase
![]()
Question 24.
Find whether the following is true or false and find the correct sequence.
I) There is only one queen bee in a colony
II) Worker bees are around 5000 – 10000
III) The queen bee in its lifetime in 2 – 4 years lays 20 lakhs eggs.
IV) When the queen loses its fertility another worker bee becomes a queen by taking royal Jelly.
a) I – true, II – False, III – False, IV – true
b) I – true, II – False, III – true, IV – True
c) I – false, II – true, III – true, IV – true
d) I – false, II – true, III – false, IV – false
Answer:
a) I – true, II – false, III -false, IV – true.
Question 25.
How many days are needed for the worker bee to becoming mature done?
a) 15 days
b) 21 days
c) 20 days
d) 18 days
Answer:
b) 21 days
![]()
Question 26.
What is the life span of a worker bees?
a) 6 weeks
b) 5 weeks
c) 7 weeks
d) 3 weeks
Answer:
a) 6 weeks
Question 27.
What are drones?
a) a male bee from unfertilised egg
b) a female bee from fertilised egg
c) a queen bee from fertilised egg
d) a worker bee after eating royal jelly becomes a queen
Answer:
a) a male bee from unfertilised egg
![]()
Question 28.
Find the wrong pair?
a) Drone cell – Comb queen bee
b) King of honeycomb – Drone
c) Swarming – Worker bee flying with the queen bee
d) Male bee – After mating it will die
Answer:
a) Drone cell – Comb queen bee
Question 29.
Read the following statement and find the correct sequence.
I) The honeycomb is built from the abdominal secretion of a worker bee
II) The chamber of the honeycomb are hexagonal in shape
III) The young stages of honey bees accommodate the lower and central cells of the hive
IV) In Apis dorsata the brood of hive cells are similar in size and shape
a) I – false, II – false, III – true, IV – true
b) I – true, II – true, III – false, IV – false
c) I – true, II – true, III – true, IV – true
d) I – false, II – true, III – true, IV – false
Answer:
c) I – true, II – true, III – true, IV – true
![]()
Question 30.
Assertion A: The pure wax is white in colour.
Reason: B The pure wax contains carotenoids pigments.
a) Assertion A true Reason B true
b) Assertion A false, Reason B false
c) Assertion A true Reason B false
d) Assertion A false, Reason B true
Answer:
c) Assertion A true Reason B false.
Question 31.
Find the correct sequence in the following.
I) Bee wax is secreted by the abdomen of the worker bees.
II) The resinous chemical substance present in the wax is called propolis.
III) The pure wax is white in colour.
IV) The yellow of the wax is due to the carotenoid pigments.
a) I – true, II – true, III – true, IV – false
b) I – false, II – false, III – true, IV – true
c) I – true, II – false, III – true, IV – true
d) I – true, II – true, III – true, IV – true
Answer:
d) I – true, II – true, III – true, IV – true
![]()
Question 32.
Find whether the statement regarding Lac insect is true or false
I) Tachardia lacca produces lac.
II) The Lac insect is a parasite on host plant karanagalli, karuvelai
III) The female lac insects are small
IV) The female lac insects after fertilisation lays about 200 to 500 eggs
a) I – true, II – false, III – false, IV – true
b) I – true, II – true, III – true, IV – false
c) I – true, II – true, III – false, IV – true
d) I – true, II – false, III – true, IV – false
Answer:
c) I – true, II – true, III – false, IV – true
Question 33.
What is the ideal salinity for fish culture in brackish water?
a) 0.5-30ppt
b) 0.1-25ppt
c) 0.1-30ppt
d) 1-10ppt
Answer:
a) 0.5 – 30 ppt
![]()
Question 34.
Which one of the following is correct pair?
a) Exotic breed – cyprinus carpiols
b) Apiculture – Reeling
c) Seri culture – Propolis
d) Milch breed – Malvi
Answer:
a) Exotic breed – cyprinus Carpio
Question 35.
Name the exotic fishes of India.
a) Catlacatla
b) Lapeorohita
c) Cirrhina mirgala
d) Cyprinus carbeo
Answer:
d) Cyprinus carbeo
![]()
Question 36.
Name the vitamin found in fishoil?
a) A and E
b) A and D
c) A and C
d) A and K
Answer:
b) A and D
Question 37.
Ising glass is received from the part of the fish
a) Dried gills
b) Dried stomach
c) Dried air sacs
d) Dried liver
Answer:
c) Dried air sacs
Question 38.
What is the nutritive value of crustaceans?
a) Rich in glycogen protein with low-fat content
b) Rich in protein low in glycogen
c) Rich in glycogen low in fat content
d) Rich in protein and fat
Answer:
a) Rich in glycogen protein with low-fat content
![]()
Question 39.
These are freshwater prawns.
a) Penaeus indicus
b) Macrobrachium rosenbergi
c) Penaeus monodon
d) Metapenaeus
Answer:
b) Macrobrochium rosenbergi
Question 40.
What is the optimum temperature and PH for prawn culture in a hatching tank
a) 24°C – 30°C PH – 7 – 8
b) 20°C – 22°C PH -10 -12
c) 20°C – 23°C PH – 5 – 6
d) 19°C – 20°C PH – 9 -10
Answer:
a) 24°C – 30°C – PH – 7 – 8
![]()
Question 41.
Find the correct statement regarding the preparations of prawn form.
I) For algal growth, and for the subsequent stocking of prawns it is essential to drain off the water and sundry the bottom.
II) Lime should be applied to absorb excess C02 and to supply calcium which is required for moulting.
III) Fertilizers like rice, bran, poultry and cattle dung are used to increase the fertility of the soil.
IV) Preservation of prawns is done by peeling and deveining or by cooking and peeling
a) I – true, II – true, III – false, IV – false
b) I – false, II – true, III – true, IV – true
c) I – true, II – true, III – true, IV – true
d) I – true, II – false, III – true, IV – false
Answer:
c) I – true, II – true, III -true, IV – true
Question 42.
Where is pearl cultured in India for the first time?
a) Thoothukudi 1973
b) Visahapattinum 1974
c) Rameshwaram 1975
d) Kulchall973
Answer:
a) Thoothukudi 1973
![]()
Question 43.
Where are pearl oysters seen?
a) Kanyakumari coastal region a Bay of Kutch
b) Rameshwaram coastal area and Bay of Mannar
c) Nagapatinum coastal area and Thoothukudi
d) Visahapatinum coastal area and Chennai
Answer:
a) Kanyakumari coastal region a Bay of Kutch
Question 44.
The pearl oysters belongs to ‘L’ genus produce Quality pearls.
a) Gastropoda
b) Pinctata
c) Pelecypoda
d) Cephalopoda
Answer:
b) Pinctata
Question 45.
……………………….. ulturing pearl in freshwater.
a) Lamellidens
b) Mytilus
c) Loligo
d) Dentalium
Answer:
a) Lamellidens
![]()
Question 46.
The marine oysters are composed of
a) Calcium carbonate
b) Sodium carbonate
c) Potassium carbonate
d) Magnesium carbonate
Answer:
a) Calcium carbonate
Question 47.
The process of killing the silkworm cocoons is called
a) Reeling
b) Stifling
c) Spinning
d) rearing
Answer:
b) Stifling
Question 48.
Assertion A: The pearl oysters got from the sea are valuable
Reason B: The pearl oysters got from freshwater is not valuable
a) Assertion A true, B false
b) Assertion A and B reason all true
c) Assertion A false, Reason B true
d) Assertion A and Bare false
Answer:
b) Assertion A and B reason all true
![]()
Question 49.
What is the name of the breed that produces mule?
a) Outbreeding
b) Crossbreeding
c) Interspecific hybridization
d) Outbreeding
Answer:
c) Interspecific hybridization
Question 50.
Assertion X: 6 – 8 eggs can be produced by induction in an artificial method
Reason Y: The embryos at 8 – 32 celled stages are transferred to a surrogate mother.
a) Assertion x false y true
b) Assertion X true, Y false
c) Assertion X false, Y false
d) Assertion X and Y are true
Answer:
d) Assertion X and Y are true
Question 51.
Which of the cattle breed yields more milk than what they eat?
a) Vechur
b) Kankeyem
c) Gir
d) Ongole
Answer:
a) Vechur
![]()
Question 52.
Which of the following is not a milch breed?
a) Sindhi
b) Malvi
c) Jersey
d) Gir
Answer:
b) Malvi
Question 53.
Which of the following belongs to America?
a) Silkie
b) White Plymouth rock
c) Chittagong
d) Aseel
Answer:
b) White Plymouth rock
![]()
Question 54.
Name the poultry which is noted for its pugnacity?
a) Leghorn
b) Silkie
c) Brahma
d) Aseel
Answer:
d) Aseel
Question 55.
Find the odd one out
a) Leghorn – Italy
b) Chittagong – good egg yielder
c) White Plymouth rock – American breed
d) Aseel-ornamental breed
Answer:
d) Aseel – ornamental breed
![]()
Question 56.
Which among the following is a wild duck?
a) Syhlet
b) Muscori
c) Pekin
d) Mallard
Answer:
d) Mallard
Question 57.
Find the wrong statement about Duck.
a) The body is covered with oily feathers.
b) The fat layer beneath their skin prevents it from getting wet
c) They lay eggs at mid-day
d) The ducks feed on rice bran kitchen wastes and snails
Answer:
c) They lay eggs at midday
(2 marks)
II. Very Short Answer
Question 1.
What is Economic Zoology?
Answer:
Economic zoology is a branch of science that deals with economically useful animals. It involves the study of the application of animals for human welfare.
Question 2.
How are animals classified on the basis of their economic importance?
Answer:
- Animals for food and food products.
- Economically beneficial animals.
- Animals of aesthetic importance.
- Animals for scientific research.
![]()
Question 3.
Name the endemic earthworms of India.
Answer:
- Periy ony x excavatus
- Lampito Mauritius
- Octo chactona serrata
Question 4.
Name the exotic species of an earthworm?
Answer:
- Eiseniafetida,
- Eudrilus eugeniae
![]()
Question 5.
Why are earthworms called ‘friends of farmers’?
Answer:
Earthworms play a vital role in maintaining soil fertility. Hence, they are called ‘friends of farmers’.
Question 6.
What decides the economic success of the industries?
Answer:
- It depends on the animals and their products.
- It depends on the proper production management and development of the next generation of farm animals.
Question 7.
What is meant by vermiculture?
Answer:
It is the process of using earthworm to decompose organic food waste into a nutrient-rich material capable of supplying necessary nutrients which help to sustain plant growth.
![]()
Question 8.
What is meant by vermicast?
Answer:
The organic matter of soil is decomposed by earthworm and becomes nutritious rich manure for plant growth.
Question 9.
What is meant by vermicompost?
Answer:
Vermicompost is composed of vermicast which contains nutrients plant growth promoters and organic matters.
Question 10.
What is meant by vermitech?
Answer:
The application of earthworm in the technology of composting and bioremediation of soil and other activities is called vermitech.
![]()
Question 11.
What are the pests of earthworms?
Answer:
Ants, springtails, centipedes, slugs, mites, certain beetle larvae, birds, rats, snakes, mice, toads and other insects or animals which feed on worms.
Question 12.
What are the special characters of vermicompost?
Answer:
- Aeration
- draining of water
- retains water.
Question 13.
What is meant by vermiwash?
Answer:
- Vermi wash is a liquid collected after the passage of water through a coloumn of vermibed.
- It is useful as foliar spray to enhance plant growth and field.
Question 14.
What is sericulture?
Answer:
Sericulture is an agro-based industry which denotes commercial production of silk through silkworm rearing.
![]()
Question 15.
What is meant by sericulture?
Answer:
Sericulture denotes commercial production of silk through silk worm rearing.
Question 16.
What is meant by moriculture?
Answer:
The cultivation of mulberry plant which is used as a food for silk worm is called moriculture.
Question 17.
Which is the suitable period for mulberry cultivation?
Answer:
June, July, November, and December
Question 18.
What are the stages involved in rearing process of silk worm?
Answer:
Disinfection of rearing house Incubation of eggs Brushing, young larval rearing Late age larval rearing.
![]()
Question 19.
What is meant by stifling?
Answer:
The process of killing the cocoon is called stifling.
Question 20.
What is meant by reeling?
Answer:
The process of removing the threads from the killed cocoon is called reeling.
Question 21.
What is cooking?
Answer:
The process of soaking cocoons in hot water (95° – 97°) for 10 – 15 minutes to soften the gum that binds the silk threads together is called cooking.
![]()
Question 22.
What are Uzi files?
Answer:
These files which can attack silkworm.
Question 23.
What is meant by cooking?
Answer:
The cocoons are soaked in hot water at 95° – 97°c for 10 -15 minutes to soften the gum that binds, the silk threads together are called cooking.
![]()
Question 24.
What is spun silk?
Answer:
The silk produced from silk wastes used for producing spun silk.
Question 25.
What are apiaries?
Answer:
They are areas where a lot of beehives can be placed.
Question 26.
Name the bees used for Apiculture.
Answer:
- Apis dorsata – Rock bee
- Apis florea – Little bee
- Apis indica – Indian bee
- Apismellifera – European bee
- Apis adamsoni – African bee
Question 27.
Name the types of beehives which are in practice in India?
Answer:
- Langstroth
- Newton
Question 28.
What is meant by swarming?
Answer:
The mass emergence of larvae of Lacinsect from the egg in search of a host plant is called swarming.
![]()
Question 29.
What is meant by nuptial flight?
Answer:
A unique flight that takes place by the queen bee followed by several drones is called “nuptial flight”.
Question 30.
Which is called as king of the colony? Why is called so?
Answer:
The king of colony is drone hence the sole duty of the drone is to fertilize the vergin queen.
Question 31.
Name the sugar component present in the honey?
Answer:
levulose, dextrose maltose.
![]()
Question 32.
What are the uses of honey?
Answer:
- It is used as an antiseptic
- Laxative
- Sedative
- It is used in the preparation of cakes bread and biscuits.
Question 33.
What is meant by Lac culture?
Answer:
The culture of lac insect using techniques for the procurement of Lac on large scale is known as Lac culture.
Question 34.
Name the host plants on which Lac insects live?
Answer:
Karanagalli – Acacia catechu Karuvelai – Acacia nilotica Kumbadiri – Schleichera oleosa.
![]()
Question 35.
What is meant by hyper parasitism?
Answer:
- Hyper parasitism is a condition in which a secondary parasite develops within a previously existing parasite.
- The caterpillars feed upon lac insects showing hyper – parasitism.
Question 36.
What is meant by inoculation?
Answer:
The process of introducing lac insects to the host plant is called inoculation.
![]()
Question 37.
What is meant by Harvesting?
Answer:
The collection of Lac from the host plant is known as harvesting.
Question 38.
What is meant by ‘Arilac’?
Answer:
The Immature lac insects produce a lac which is called ‘arilac’.
![]()
Question 39.
What is meant by sticklac?
Answer:
Lac cut from the host plant is called ‘stick lac’.
Question 40.
What is seed Lac?
Answer:
The Lac scraped collected grounded and the dust particles are removed to produce a lac called seedlac.
Question 41.
What is meant by Shellac?
Answer:
The seedlac is sundried and then melted to produce “Shellac”.
![]()
Question 42.
What is meant by aqua ponies?
Answer:
Aquaponics is a technique which is a combination of aquaculture and growing plants in non – soil media and nutrient-laden water.
Question 43.
What are the organisms farming through aqual culture?
Answer:
Fish molluscs crustaceans and aquatic plants are farming through aquaculture.
Question 44.
How aquaculture is classified on the basis of it source?
Answer:
- Freshwater aquaculture
- Brackish water aquaculture
- Marine water aquaculture.
Question 45.
What is meant by Brackish water culture?
Answer:
Culturing of animals in the water having salinity range 0.5 – 30ppt are called brackish water cultures.
![]()
Question 46.
Name the fishes cultured through brackish water culture?
Answer:
Milkfish, Sea bass, Grey mullet Kari meen.
Question 47.
What is meant by metahaline culture?
Answer:
Culturing of animals in the salinity ranges from 36 – 40o% is called metahaline culture (eg) Artemia salina.
Question 48.
What are the organisms rearing through aquaculture?
Answer:
- Molluscs
- Aquatic plants
- Crustaceans
Question 49.
Give notes on fishes of brackish water?
Answer:
Brackish water fishes spend most of its life in river mouths backwaters mangrove swamps and coastal lagoons.
![]()
Question 50.
What is meant by mariculture?
Answer:
Culturing of animals in the water salinity ranges from 35- 35% is called mariculture.
Question 51.
Give short notes on Artemia salina?
Answer:
It is a metahaline organism. It lives in high saline waters because of its high osmoregulatory capacity.
Question 52.
What is meant by composite fish culture?
Answer:
Few selected fishes belonging to different species are stocked together in proper proportion in the pond is called composite culture.
![]()
Question 53.
What are the organisms cultured through composite fish culture?
Answer:
- Catla Catla
- Labeo rohita
- Cirrhina mirgala.
Question 54.
What is meant by exotic fish culture?
Answer:
The fishes imported in to a country for fish culture are called exotic fishes and such fish culture is known as exotic fish culture.
Question 55.
Name the exotic fishes cultured in India?
Answer:
- Cyprinus carpio
- Oreochromis mossambicus.
Question 56.
What is meant by fish meal?
Answer:
Fish meal is prepared from fish waste after extracting oil from the fish.
![]()
Question 57.
What is meant by Ising glass?
Answer:
- Ising glass is high-grade collagen produced from dried air bladder.
- It is used for clarification of wine beer and vinegar.
Question 58.
What is meant by outbreeding?
Answer:
It is the breeding of unrelated animals. They do not have common ancestry for 4-6 generations.
Question 59.
What is the use of outbreeding?
Answer:
Outbreeding helps to produce hybrids with superior qualities and helps to create new breeds. New and favourable genes can be introduced into a population through outbreeding.
![]()
Question 60.
What is meant by outcrossing?
Answer:
It is the breeding between unrelated animals of the same breed but having no common ancertry.
Question 61.
What is meant by artificial insemination?
Answer:
Artificial insemination is a technique in which the semen collected from the male is injected to the reproductive tract of the selected female.
![]()
Question 62.
What is meant by recovery period?
Answer:
Nucleated oysters are attached with floating rafts suspended into a depth of 2 to 3 metres for about 6 to 7 days is called the recovery period.
Question 63.
What is the composition of pearl?
Answer:
- Water-2-4%
- Calcium carbonate-90%
- Organic matter-3.5-5.9%
- residue-0.1-0.8%
Question 64.
Name the species of prawn?
Answer:
Penaues indicus, Penaeus monodon, Metapenaeus dobsoni, Macrobrachium rosenbergil.
![]()
Question 65.
Where are pearl oysters cultured?
Answer:
Kanyakumari Bay of Kutch.
Question 66.
What is meant by Linga pearl or best quality pearl?
Answer:
The pearl oysters in habit the ridges of rock-forming extensive pearl banks. These pearl beds produce the best quality of pearl or Linga pearl.
Question 67.
What are the types of cultivable fish?
Answer:
- Indigenous or native freshwater fish. (cg) Catla, Labeo
- Saltwater fishes acclimatized for freshwater.
- Exotic fishes or imported from other countries. (eg) Common Carps.
Question 68.
What is Hapa?
Answer:
Hatching hapas are rectangular through shaped tanks made up of mosquito net cloth supported by bampoo poles and fixed in the river.
![]()
Question 69.
What are the advantages of composite fish farming?
Answer:
- All available niches are fully utilized.
- Compatible species do not harm each other.
- No competition among different species.
Question 70.
What is meant by animal husbandry?
Answer:
Animal husbandry is the practise of breeding and raising livestock cattle like cows, buffaloes goats and birds that are useful to human beings.
Question 71.
What is meant by breed?
Answer:
A group of animals related by descent and with similar characters like general appearance features size etc as said to belong to a breed.
![]()
Question 72.
How can we classify cattle on the basis of their utility?
Answer:
- Milch breeds
- Draught purpose breeds
- Dual-purpose breeds.
Question 73.
What are characteristic features of healthy cattle?
Answer:
- They appear bright
- Alert
- Active
- Shiny coat.
Question 74.
What are the characteristic features of unhealthy cattle?
Answer:
- They appear dull
- Restless
- Change posture frequently with a drop in milk yield.
Question 75.
Name the important cattle disease?
Answer:
- Rinder pest
- Cowpox
- Anthrax
- hemorrhagic fever.
Question 76.
What is meant by poultry?
Answer:
It is the rearing and propagation of chicken ducks turkeys geese quail and guinea fowls.
![]()
Question 77.
What are the types of chicken breeds based on their utility?
Answer:
- They are egg layers
- Broiler type
- Dual type
- Games and
- ornamental types.
Question 78.
Name the native ducks.
Answer:
- Indian Runner
- Syhletmeta.
Question 79.
Name the exotic ducks.
Answer:
- Muscari
- Pekin
- Aylesbury
- Campbell
Question 80.
What are the three stages of sericulture?
Answer:
- Cultivation of food plants for the silkworm.
- rearing of silkworm.
- reeling and spinning of silk.
Question 81.
What is meant by apiculture?
Answer:
Care and management of honey bees on a commercial scale for the production of honey is called apiculture.
![]()
Question 82.
What is the importance of aquaponics?
Answer:
It maintains the ecosystem balance by recycling the waste and excretory products produced by the fish.
Question 83.
What is meant by aquaponics?
Answer:
Aquaponics is a technique which is a combination of aquaculture and growing plants in non-soil media and nutrient-laden water.
![]()
Question 84.
Based on the water resources where are aquatic organisms cultured? Give examples.
Answer:
- Freshwater culture
- Brackish water culture, Marine culture, Cultured organism, Fishes, Prawns, Crabs and oysters.
Question 85.
What are the objectives of animal breeding?
Answer:
- To improve growth rate
- enhancing the production of milk meat egg etc.
- Increasing the quality of the animal products
- Improved resistance to disease.
- Increased reproductive rate.
3 marks
III. Short answers
Question 1.
What is meant by vermiculture?
Answer:
It is the process of using earthworm to decompose organic food waste into a nutrient-rich material capable of supplying necessary nutrients which help to sustain plant growth.
Question 2.
What is meant by worm casting?
Answer:
The worm castings are pure worm waste and nutrient-rich organic soil and composed of castings, bits of bedding, and other organic matter.
![]()
Question 3.
Why earthworms are called as ‘Farmers of friends’
Answer:
- They support bacteria fungi which are essential for sustaining healthy soil.
- The breakdown of organic matter by the activity of the earthworms.
- It increases porosity aeration, drainage of the soil.
Question 4.
What are the three main components of sericulture?
Answer:
- Cultivation of food plants for the silkworms.
- Rearing of silkworms.
- Reeling and spinning of silk.
Question 5.
Name the predators of earthworms?
Answer:
- Ants,
- centipedes,
- Slugs,
- Birds,
- Rats,
- Snakes.
Question 6.
Name the honey bees used in apiculture.
Answer:
- Apis dorsate,
- Apis florea
- Apis indica
- Apis mellifera
- Apisadamsoni
Question 7.
Whatisprobolis?
Answer:
The wax is masticated and mixed with the secretions of the cephalic glands to convert it into a plastic resinous substance called probolis.
![]()
Question 8.
What are the uses of silk?
Answer:
Uses of Silk:-
1. Silk fibers are utilized in preparing silk clothes. Silk fibers are now combined with other natural or synthetic fibers to manufacture clothes like Teri-Silk, Cot-Silk etc. Silk is dyed and printed to prepare ornamented fabrics. They are generally made from Eri-silk or spun silk.
2. Silk is used in industries and for military purposes.
3. It is used in the manufacture of fishing fibers, parachutes, cartridge bags, insulation coils for telephone, wireless receivers, tyres of racing cars, filter fibres, medical dressings, and suture materials.
Question 9.
Describe the structure of Beehive?
Answer:
- The house of honey bees is a beehive.
- The hive consists of hexagonal cells made up of wax secreted by the abdomen of a worker bee.

- These hives are found hanging vertically from the rocks. building or branches of trees.
- The young stages of honey bee accommodate the lower and central cells of the hive.
- In the rock bees hives there are separate cells for queens, worker and drones.
Question 10.
Explain the structure of a beehive?
Answer:
Structure of a Bee Hive. The house of honey bees is termed a beehive or comb. The hive consists of hexagonal cells made up of wax secreted by the abdomen of worker bees arranged in opposite rows on a common base. These hives are found hanging vertically from the rocks, buildings or branches of trees. The young stages of honey bees accommodate the lower and central cells of the hive called the brood cells.
In Apis dorsata, the brood cells are similar in size and shape but in other species, brood cells are of three types viz., queen cell for queens, worker cell for workers, and drone cells for drones. The cells are intended for the storage of honey and pollen in the upper portion of the comb whereas the lower portions are for brood rearing.
Question 11.
What is meant by inbreeding? What are its effects?
Answer:
Breeding between animals of the same breed for 4 – 6 generations is called inbreeding.
Effects:
- It increases homozygosity.
- Exposes the harmful recessive genes.
- Reduces fertility.
- It produces inbreeding depression.
Question 12.
How animals are classified based on their economic importance.
Answer:
- Animals for food and food products.
- Economically beneficial animals.
- Animals of aesthetic importance.
- Animals for scientific research.
Question 13.
Give an account of earthworm based on their habitat.
Answer:
First group:
- The humus formers dwell on the surface and feed on organic matter.
- They are darker in colour.
- These worms are used for vermicomposting.
Second group:
The humus feeders are burrowing worms that are useful in making the soil porous and mixing and distributing humus throughout the soil.
![]()
Question 14.
What are the uses of honey wax?
Answer:
- It is used for making candles.
- It is used for making waterproofing materials.
- It is used for making home appliances polishes for leather.
- It is used in pharmaceutical industries.
Question 15.
What is meant by Hyper parasitism?
Answer:
A condition in which a secondary parasite develops within a previously existing parasite.
![]()
Question 16.
What are the economic importance of Lac?
Answer:
- It is used as sealing wax.
- It is used as a good insulator.
- It is used in preparations of shoe and leather polishes.
- It is a protective coating of wood.
- It is used in preparation of plastic moulded articles.
- It is used as filling material for gold ornament.
Question 17.
Name the breeds of cattle?
Answer:
- Milch breeds – Sindhi Jersey
- Draught breeds – KangeyamMalvi
- Dual-purpose breeds – Ongole Hariana
Question 18.
What is meant by Milch breed?
Answer:
They are high milk yielders with extended lactation. (eg) Sindhi, brown swiss.
![]()
Question 19.
What is Dual purpose?
Answer:
Cows are meant for yielding more milk and bullocks are used for better drought purpose, (eg) Ongole Hariana
Question 20.
What is draught purpose breeds?
Answer:
Bullocks are good for draught purposes (eg) Malvi.
Question 21.
What are the characteristic features of healthy cattle?
Answer:
A healthy animal eats drinks and sleeps well regularly.
Healthy cattle appear bright.
Alert and active in their movement with a shiny coat.
![]()
Question 22.
What are the external factors affecting fish culture?
Answer:
- Temperature,
- Light,
- Rain,
- Flood,
- Water current,
- Turbidity of water,
- pH
Question 23.
What is Aquaponics?
Answer:
Aquaponics is a technique which is a combination of aquaculture (growing fish)’ and hydroponics (growing plants in non-soil media and nutrient-laden water).
Question 24.
Name the species of prawn.
Answer:
- Penaeus indicus,
- Penaeus monodon,
- Metapenaeus dobson,
- Macrobrachium rosenbergii.
Question 25.
What are the three types of aquaculture on the basis of the source?
Answer:
On the basis of source, aquaculture can be classified into three categories. They are
- Freshwater aquaculture
- Brackish water aquaculture
- Marine water aquaculture.
Question 26.
What are the benefits of poultry farming?
Answer:
- It does not require high capital for the construction and maintenance of poultry farming.
- It does not require a big space.
- It ensures the high return on investment.
- It provides fresh and nutritious food and has a huge global demand.
- It provides employment opportunities for the people.
Question 27.
What are the uses of dairy products?
Answer:
- Milk is a rich source of vitamin A, B2, B1
- It is a complete food for infants.
- Dairy products such as yoghurt cheese butter ice cream condensed milk, milk powder are produced from milk.
![]()
Question 28.
What is the importance of meat?
Answer:
- Meat is rich in protein.
- It also contains minerals like iron zinc vitamins and selenium.
Question 29.
What is Mariculture?
Answer:
Culturing of animals in the water salinity ranges from 30 – 35% is called Mariculture. Some fishes like Chanos sp, Mugil cephalus are cultured here.
Question 30.
What are poultry diseases?
Answer:
Ranikhet, Coccidiosis, Fowl pox.
5 Marks
IV. Give Detailed Answers
Question 1.
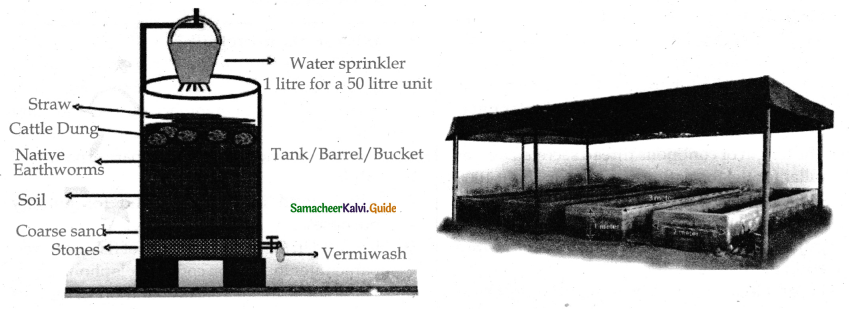
How are vermicompost produced?
Answer:
Types of Movements:
- Vermicompost is the compost produced by the action of earthworm in association with all other organisms in the compost unit.
- Vermicompost bed may be selected on upland or an elevated level.
- We have to construct a cement pit of 3 x 2 x 1m size over the ground surface using bricks.
- The vermibed should not be exposed to direct sunlight.
- The first layer of vermibed contains gravel at about 5 cm in height followed by coarses and to a thickness of 3.5 cm which will facilitate the draniage of excess water.
- The unit can now be loaded with digested biomass or animal dung.
- Earthworms such as periyonyx excavatus Eisenia fetida or Eudrilus eugeniae are introduced on the top.
- Earthworms release their castings on the surface.
- Vermiwash is a liquid collected after the passage of water through a column of vermibed. It is useful as a foliar spray to enhance plant growth.
Question 2.
Describe the life cycle of bombyx mon?
Answer:
- This moth is unisexual.
- Just after emergence male moth copulates with females for 2-3 hours.
- Just after copulation female starts laying about 400-500 eggs.
- The eggs after ten days of incubation hatch into larva called a caterpillar.
- The newly hatched caterpillar is about 3mm in length and is pale yellowish-white colour.
- The mandibulate type of mouthparts adapted to feed easily on the mulberry leaves.
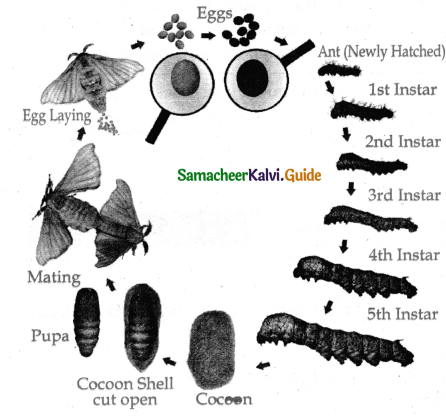
- After 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th moulting caterpillars get transformed into 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th instars respectively.
- It develops salivary glands, stops feeding and undergoes pupation.
- The cafter pillars stop feeding and moves towards the comer among the leaves and secrete a sticky fluid through their silk gland.
- The secreted fluid comes out through spinnerret which hardens on exposure to air and is wrapped around the body of cater pillar in the forms of a covering called a cocoon.
- The length of continous thread secreted a caterpillar for the formation of cocoon is about 1000 -1200 metres.
- The pupal period lasts for 10-12 days and the pupae cut through the cocoon and emerge into adult moth.
- In larvel stages the larvae moults for 3 or 4 times or 5 times and become a matured moth.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the uses of vermicompost?
Answer:
- Vermicompost is rich in essential plant nutrients.
- It improves soil structure texture aeration and water holding capacity and prevents soil erosion.
- Vermicompost is rich in nutrients and an eco-friendly amendment soil for farming and terrace gardening.
- It enhances seed germination and ensures good plant growth.
Question 4.
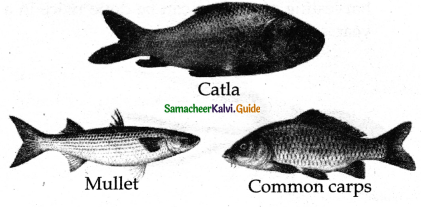
What are the reasons for culturing carps in India?
Answer:
Major carps have proved to be best suited for culture in India because the carps
- Feed on zooplankton and phytoplankton, decaying weeds, debris, and other aquatic plants.
- They can survive in turbid water with slightly higher temperatures.
- Can tolerate O2 variations in water.
- Can be transported from one place to another easily.
- They are highly nutritive and palatable.
Question 5.
What are the uses of silk?
Answer:
- Silk fibres are utilized in preparing silk cloths.
- Silk fibres are combined with natural or synthetic fibres to manufacture Teri – silk and cot silk.
- Silk is dyed and printed to prepare ornamental fabrics.
- Silk is used in industries and for military purposes.
- It is used in the manufacturing of fishing fibres, parachutes insulation coils for telephones.
- They are used in the preparation of tyre of racing cars, filter fibres in medical dressings and as suture materials.
![]()
Question 6.
Name the pests and diseases of the silkworm.
Answer:
1. Predators:
They feed on silkworms.
- Birds,
- ants,
- crows,
- kites,
- rats.
2. Diseases:
- Pebrin – It is a disease caused by protozoa Nosema bombycis.
- Flacherie – It occurs in the mature larvae caused by bacteria like streptococcus and staphylococcus.
- Grasserie – It is aviral disease caused by Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus.
- White Muscardine – It is caused by fungus Beauveria bassiana.
Question 7.
Describe the social organziation of honey bee.
Answer:
- In honey bee a highly organized division of labour is found.
- There are three type of honey bees seen in the colony.
- There are one queen 10000 – 30000 workers and few hundred drones in a colony.
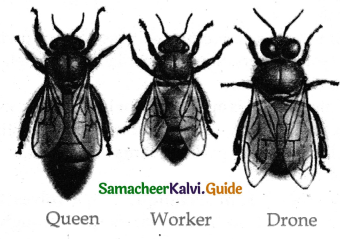
Queen bee:
- It feeds on royal Jelly.
- It is only function is to lay eggs throughout its life span.
- During breeding season in winter, a unique flight takes place by the queen bee followed by several drones is called nuptial flight.
- After mating the queen bee lays about 15 lakh eggs in two to four years.
Worker bee:
- These are sterile females.
- Worker bee lives in a worker well and it takes, about 21 days to develop from the egg to adult, and its life span is about six weeks.
Works:
- It secretes royal Jelly.
- Prepares bee – bread to feed the larvae.
- Takes care of the queen and drones.
- Secretes bee wax.
- In last three weeks she searches and gathers the pollen nectar.
Drones:
- The drone develops from an unfertilized egg.
- It lives in a chamber called a drone cell.
- The only duty of the drone is to fertilize the queen and it is called as the king of the colony.
Question 8.
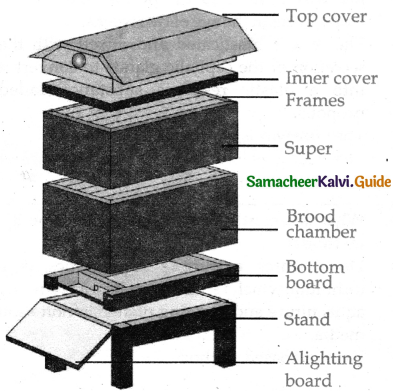
Describe the structure of the Langstroth beehive?
Answer:
- Stand – It is a basal part of the hive and are adjusted to make a slope for rainwater to drain.
- Bottom board – It is situated above the stand. It has two gates one gate is an entrance the other acts as an exit.
- Brood chamber – It is an important part of the hive. It is provided with 5 to 10 frames arranged one above the other through which the workers can easily pass.
- The frame is composed of wax – sheet which is held in a vertical position up by a couple of wires.
- It is strong that can be used repeatedly.
- Super – It is a chamber without cover and base. It is provided with many frames to provide additional space for expansion of the hive.
- Inner cover – It is a wooden piece used for covering the super with many holes for proper ventilation.
- Top cover – It is meant for protecting the colonies from rains. It is covered with a sheet which is plain and sloping.
Question 9.
Give an account of equipments of beehives and its uses.
Answer:
- Queen Excluder – It is utilized to prevent the entry of queen bee from the brood chamber into the super chamber.
- Comb foundation – It is a sheet of bee wax.
- Bee gloves – They are used by keepers for protecting their hands.
- Bee veil – It is a device to protect the beekeeper from a bee sting.
- Smoker – It is used to scare the bees during honey collecting.
- Hive Tool – It helps in scraping excess propolis or wax.
- Un capping knife – It helps in removing the cap from the combs.
- Bee brush – It is used to brush off bees from honeycombs.
- Queen introducing cage – It is made of wire nets used for keeping the queen for 24 hours with worker bees.
- Feeder – It is a basin with sugar syrub covered by grass to feed the bees during the drought season.
- Honey extractor – This spins the combs rapidly to extract honey.
- Hive entrance guard – It is a device which prevents the escape of the queen during the warming season.
![]()
Question 10.
Describe the process of rearing silkworms?
Answer:
- A typical rearing house 6 m x 4m x 3.5m is constructed on an elevated place under shade to accommodate 100 dfls.
- The windows and ventilators should be covered with a nylon net to restrict the entry of uziflies and other insects.
- The selected healthy silk moths are allowed to mate for 4 hours.
- The female moth is kept in a dark plastic bed it lays about 400 eggs in 24 hours.
- The small larvae hatch between 7 – 10 days.
- The larvae are kept in trays at a temperature of about 20°C-25°C.
- As the larvae grow they are transferred to fresh leaves on clean trays.
- Their maturity is achieved in about 45 days.
- At this stage the salivary glands start secreting silk to spin cocoons.
Question 11.
What is meant by aquaponics? Describe its methods?
Answer:
1. Deepwater culture – Aquaponics is a technique which is a combination of aquaculture and growing plants in non – soil media.
- It is a raft-based method.
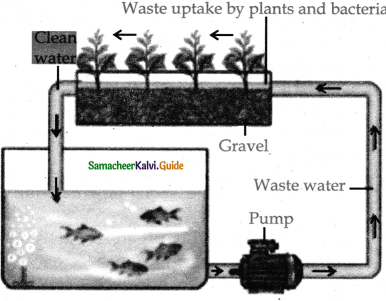
- In this method, the raft floats in water plants are kept in the holes of the raft and the root floats in water. Fast-growing plants are cultivated.
2. Media-based method – It involves growing plants in inert planting media likely pellets or shales.
This method is applicable for home and hobby scale system. Large number of fruiting plants leafy green plants herbs can be cultivated.
3. Nutrient film technique – It involves the passage of nutrient-rich water through a narrow trough or pvc pipe.
Plants are kept in the holes of the pipe to allow the roots to be in free contact with the water stream.
4. Aquavertica or vertical aquaponics – Plants are stacked in top of each other in tower systems.
This method is suitable for growing leafy green, strawberries and crops that do not need supporting solid substratum to grow.
Question 12.
Describe the structure of honey bee hive?
Answer:
- The house of honey bee is termedas bee hive or comb.
- The hive consists of hexagonal cells made up of wax secreted by the abdomen of worker bee arranged in opposite rows on a common base.
- These hives are found hanging vertically from the rocks building or branches of trees.
- The young stages of honey bees accomodate the lower and central cells of the hive called the brood cells.
- There are separate cells for queen. Drones and workers.
- In the upper portion of the comb honey and pollen are stored.
- In the lower portion are for brood rearing.
Question 13.
What is Natural breeding of fishes?
Answer:
Natural breeding (Bundh breeding): These are special types of ponds where natural riverine conditions or any natural water resources are managed for the breeding of culturable fishes. These bundhs are constructed in large low-lying areas that can accommodate large quantity of rainwater. The shallow area of such bundhs is used as a spawning ground.
Question 14.
What are the characteristic features of cultivable fishes.
Answer:
- Fishes should have high growth rate in short period for culture.
- They should accept a supplementary diet.
- They should be hardly enough to resist some common diseases and infection of parasites.
- Fishes proposed for polyculture should be able to live together without interferring or attaching other
fishes. - They should have high conversion efficiency so that they can effectively utilize the food.
![]()
Question 15.
Why carps have proved to be best suited for culture in India?
Answer:
- Feed on zooplanktons and phytoplanktons decaying weeds debris and other aquatic plants.
- They can survive in turbid water with slightly higher temperatures.
- Can tolerate O2 variations in water.
- Can be transported from one place to another easily.
- They are highly nutritive and palatable.
Question 16.
Give an account of induced breeding.
Answer:
- To improve the quality of fish seed by the artificial method of fertilization is developed.
- The gonadotrophin (FSH+ LH) secreted by the pituitary gland influences the maturation of gonads and spawning in fishes.
- The pituitary gland is removed from a healthy mature fish.
- The pituitary extract is prepared by homogenizing in 0.3% saline and centrifuged for 15 minutes at 8000rpm.
- The supernatant is injected at the base of the caudal fin.
- Male and Female fishes start to releasing gametes and are fertilized.
![]()
Question 17.
What are the types of prawn fishery?
Answer:
- Shallow water prawn fishery – This is located on the west coast restricted to shallow waters.
- Estuaries prawn fishery – In the backwater areas of the western coast, Ennur pulicat chilka lake and Estuaries of Ganga and Brahmaputra culture is done.
- Freshwater prawn fishery – Prawns are caught from the rivers and lakes throughout India.
- Marine prawn fishery – Prawn belongs to the family, penaeidae are caught along the Indian coast.
Question 18.
Give an account of the culture of freshwater prawns?
Answer:
- Macrobrachium rosenbergii is seen in rivers fields and low – saline estuaries.
- For fertilization, one pair of prawn are kept in a separate tank.
- After mating the eggs are laid.
- Temperature 24°C – 30°C and PH 7-8 should be maintained in the hatching tank.
- The hatched larvae are supplied with artificial feed.
- Young ones 5cm length can be reared in fresh or slightly brackish water ponds and harvesting of prawns can be done twice a year.

Question 19.
What are the methods of animal breeding?
Answer:
Methods of Animal breeding:
There are two methods of animal breeding, namely inbreeding and outbreeding:
1. Inbreeding: Breeding between animals of the same breed for 4-6 generations is called inbreeding. Inbreeding increases homozygosity and exposes the harmful recessive genes.
Continuous inbreeding reduces fertility and even productivity, resulting in “inbreeding depression”. This can be avoided by breeding selected animals of the breeding population and they should be mated with superior animals of the same breed but unrelated to the breeding population. It helps to restore fertility and yield.
2. Outbreeding: The breeding between unrelated animals is called outbreeding. Individuals produced do not have common ancestors for 4-6 generations.
Outbreeding helps to produce new and favourable traits, to produce hybrids, with superior qualities, and helps to create new breeds. New and favourable genes can be introduced into a population through outbreeding
![]()
Question 20.
What are the types of cultivable fish Types of cultivable fishes?
Answer:
Types of Cultivable fishes:
- Indigenous / Native freshwater fishes, (eg) Major Carps Catla Labeo Clarias.
- Saltwater fishes acclimatized for freshwater. (eg)Chanos, Mullet
- Exotic fishes. Imported from other countries, (eg) Common Carps.
Characteristic features of Carps:
- Feed on Zooplanktons and phytoplanktons decaying weeds debris and other aquatic plants.
- They can survive in turbid water with slightly higher temperatures.
- Can tolerate 02 variations in water.
- Can be transported from one place to other.
- They are highly nutritive and palatable easily
Question 21.
Give an account of the management of fish farms?
Answer:
To culture fish one should have an idea about different stages of fish culture such as topographic situation quality source physical-chemical and biological factors of water.
Stages of fish farming:
Breeding Pond:
The first step in fish culture is the breeding of fishes therefore for proper breeding special types of ponds are prepared called breeding ponds. These ponds are prepared near the rivers of natural water resources.
a) Natural breeding:
These bundhs are constructed in large low-lying areas that can accommodate a large quantity of rainwater.
b) Induced breeding:
- This involves the removal of ova and sperm from female and male by artificial mechanical process and the eggs are fertilized.
- The fertilized eggs are removed from the spawning place and kept in hatching hapas. Fish seeds: The fish seed is collected from breeding ponds and transferred to the hatching pits.

3. Hatching Pit:
The fertilized eggs are kept in hatching pits. The hatching pits should be nearer to the breeding grounds should be smaller in size with good quality water.
There are two types of hatching pits:
- Hatcheries: These are small-sized ponds in which unfertilized eggs are transferred and hatching happens.
- Hatching hapas: These are rectangular trough-shaped tanks made up of mosquito net cloth supported by bamboo poles and fixed in the river.
4. Nursery Pond:
The newly hatched fries are transported from the hatching happa to nursery ponds where they grow into fingerlings.
5. Rearing Pond:
This pond is long and narrow and this pond should be free from toxicants and predators. The fingerlings are transferred to the stocking ponds.
6. Stocking Ponds:
- This pond should be devoid of weeds and predatory fishes.
- Proper organic manuring should be done to the production with cow dung.
7. Harvesting:
- Well-grown fishes are taken out for marketing is harvesting.
- Small-sized fishes are again released into the stocking ponds for further growth.
- The harvested fishes are preserved and then marketed.
![]()
Question 22.
a) What is meant by composite fish farming?
b) What are the significance?
c) What are the fishes cultured through composite fish farming.
Answer:
a. Composite fish farming: Few selected fishes belonging to different species are stocked together in proper proportion in a pond is called composite fish farming.
b. Merits :
- All available niches are fully utilized.
- Compatible species do not harm each other.
- No competition among different species is found.
c. Fishes that are cultured :
- Catla Catla
- Labeo rohita
- Cirrhinus mrigala
Question 23.
Give an account of the economic importance of fish.
Answer:
1. Fishes form a rich source of protein food the sardines, mackerel tuna herrings have high amino acid concentrations.
2. These fishes have histidine and omega falty acids.
3. Minerals such as calcium magnesium phosphorus potassium and copper and present.
a) Fish Oil:
- It is an important fish product it is derived from fish liver and from the fish body.
- This is rich in vitamin A and O and iodine.
- It is used in the manufacture of laundry soap paints and cosmetics.
b) Fish Meal:
- It is prepared from fish waste after extracting oil from the fish.
- These dried wastes are used to prepare food for pig, poultry and cattle.
- The wastes obtained during the preparation of fish meal are used as manure.
c) Ising glass:
- It is high-grade collagen produced from dried air bladder of cat fish and carps.
- It is used for clarification of wine beer and vinegar.
Question 24.
Give notes on
a) Pearl Culture
b) Formation of pearl.
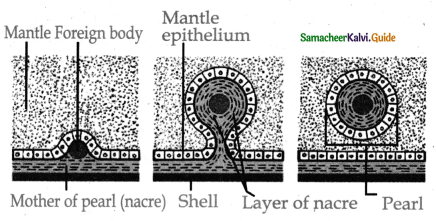
Answer:
a) Pearl Culture:
- Pearl is a white shining globular concretion found within the shell of an oyster.
- In India it was cultured for the first time in 1973 at Thoothukudi.
- High-quality pearls are obtained from Genus Pinctada that can be cultured in the salinity range of 30 ppt in racks raft and long-line method.
- The pearl oysters in habit the ridges of rocks or dead coral forming the best quality pearl.
b) Pearl Formation:
- When a foreign particle accidentally enters into the space between the mantle and shell of the oysters it adheres to the mantle.
- The mantle epithelium encloses its likes sac and starts to secrete concentric layers of nacre around it as a defensive mechanism.
- The repeated layers of calcium carbonate make the hard and glossy pearl that are separated and graded.
Question 25.
Give an account of artificial pearl culture?
Answer:
- Oysters are caught by a special type of cages.
- This cage is dipped into a sand cement mixture providing a rough surface to the cages and are suspended at a depth of 6 meters.
2. Rearing of oysters:
- The collected oysters are placed into the culture cages for a period of 10 – 20 days.
- These cages are protected from enemies like octopus, Eel and devil fishes.
3. Insertion of nucleus:
a) Fitness of oysters for operation:
The selected oysters for the insertion of nucleus should be healthy and strong enough to overcome the stress during operation.
b) Preparation of graft tissues:
- The piece of tissue which is inserted inside the mantle is called as “graft” tissue.
- It is essential to keep the outer surface in contact with the inserted nucleus as nacre secreting cells are found only on the outer surface.
c) Preparation of nucleus:
- Any small particle may function as a nucleus to initiate pearl formation.
- If it is calcareous the deposition of nacre was found to be more on the calcareous nucleus.
d) Insertion of the nucleus:
For the insertion of nucleus, oysters are fixed in a desk clamb and mantle folds are smoothly touched to expose the foot followed by an incision into the epithelium of the foot and the nucleus is inserted.
e) Post Operation Care:
- Nucleated oysters are placed into cages and suspended into 2-3 metres of depth for 6-7 days.
- These periods are known as “Recovery Period”.
- These oysters are kept for 3-6 years undisturbed.
f) Harvesting of Pearl:
After the completion of 3 years pearl oysters are harvested. It is usually done during December to February.
g) Clearing of Pearls:
After taking out the pearls from the oyster’s shell. They are washed properly cleared with the soap solution.
![]()
Question 26.
What is inbreeding? What are its merits and demerits?
Answer:
Breeding between animals of the same breed for 4-6 generations is called inbreeding.
Merits:
- It increases homozygosity.
- It exposes the harmful recessive genes. Demerits:
1. Continuous inbreeding reduces fertility
2. And results in inbreeding depression. Avoiding inbreeding depression:
This can be avoided by breeding selected animals be mated with superior animals of the same breed but unrelated to the breeding population.
Question 27.
What is Dairying and Dairy Operation?
Answer:
Dairying is the production and marketing of milk and its products. The dairy operation consists of proper maintenance of cattle, the collection, and processing of milk, and its by-products.
Question 28.
What are the types of outbreeding?
Answer:
1. Out Crossing:
It is the breeding between unrelated animals of the same breed but having no common ancestry.
Out Cross: This method is suitable for breeding animals that are below average in productivity.
2. Crossbreeding:
- Breeding between a superior male of one breed with a superior female of another breed.
- The cross-breed progeny has superior traits. This is called hybrid vigour or heterosis.
3. Interspecific hybridization:
- Mating between male and female of two different species.
- The progeny obtained from such crosses are different from their parents.
- Mule is produced by the crosses between male donkey and a female horse.
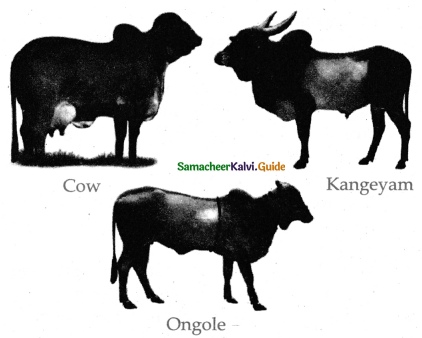
Question 29.
Give an account of Multiple Ovulation embryo transfer technology? MOET.
Answer:
MOET:
- This method is applied when the success rate of crossing is low even after artificial insemination.
- In this method, the follicle-stimulating hormone is administered to cows for inducing follicular maturation and superovulation.
- Instead of one egg per cycle, 6-8 eggs can be produced.
- The eggs are carefully recovered non-surgically from the genetic mother and fertilized artificially.
- The embryos at the 8 – 32 celled stage are recovered and transferred to a surrogate mother.
- This technology can be applied to cattle sheep and buffaloes.
- It can produce high milk-yielding females and high-quality meat-yielding bulls in a short time.
![]()
Question 30.
a) What is meant by dairying?
b) Classify them on the basis of their utility.
c) Give an account of dairy products.
Answer
a) Dairying:
- It is the production and marketing of milk and its products.
- The dairy operation consists of maintenance of cattle the collection, processing of the milk, and its by-products.
- These are 26 well-defined breeds of cattle and 6 breeds of buffaloes in India.
b) Classification of Cattle
- Dairy breeds: They are high milk yielder with extended lactation, (eg) Sindhi, Jersey Sahiwal
- Drought breed: Bullocks are good for draught purposes, (eg) Kangeyam Malvi.
- Dual-purpose breeds: Cows are meant for yielding more milk and bullocks are used for better drought purposes (eg) Ongole Hariana.
c) Uses of dairy product:
1. Milk: Milk is a rich source of vitamin A, B2, B and deficient in Vitamin C.
Dairy products such as yoghurt cheese butter ice cream condensed milk powder are produced from milk.
2. Meat: Meat is rich in protein and also contains minerals like iron zinc vitamins and selenium.
3. Land Management: Grazing of live stocks sometimes used as a way to control weeds.
4. Manure: Manure can be spread on agriculture fields to increase crop yields.
Question 31.
Describe the types of Chicken breeds?
Answer:
1. Egg layers: These are farmed mainly for the production of eggs.
Leghorn:
- It is originated in Italy. They are small compact with a single comb.
- They mature early and begin to lay eggs at the age of 5 or 6 months.
Chittagong:
- They are good egg layers and are delicious.
- They are found in West Bengal.
2. Selection of eggs for hatching:
Eggs should be fertile medium-sized dark brown shelled and freshly laid eggs are preferred for rearing.
3. Incubation and hatching:
- The maintenance of newly laid eggs in optimum condition till hatching is called incubation.
- The fully developed chick emerges out of egg after an incubation period of 21 – 22 days.
- There are two types of incubation namely natural incubation and artificial incubation.
- In the Natural incubation method, only a limited number of eggs can be incubated by a mother hen.
- In artificial incubation, more eggs can be incubated.
4. Brooding:
- Caring and management of young chicks for 4 – 6 weeks immediately after hatching is called brooding.
- They are natural and artificial brooding. The housing of Poultry:
- To protect the poultry from the sun.
- Rain and predators it is necessary to provide housing to poultry.
- Poultry house should be moisture-proof rat-proof and it should be easily cleanable and durable.
5. Poultry feeding:
The diet of chicks should contain an adequate amount of water carbohydrates proteins fats vitamins and minerals.
Poultry Products:
- The main products of poultry farmings are eggs and meat.
- The primary aim of poultry farming is to obtain eggs.
C. Poultry by-products:
- The feathers: They are used for making pillows and quilts.
- Droppings: The droppings are rich in nitrogen potash and phosphates.
- The by-products of poultry are used as good sources of nutrients for meat-producing animals and poultry.
- These by-products supply proteins fats Vitamins and minerals.
Poultry diseases: Ranikhet coccidiosis Fowl Pox is a common poultry disease.
Merits:
- They can adapt themselves to all types of environmental conditions.
- And for the breed for feed efficiency.
- Growth rate and resistance to diseases.
- They are exhibited in poultry shows they are calm friendly and can be maintained as pets.
![]()
Question 32.
What are the types of poultry farming? What are the stages involved in rearing? What are the poultry by-products?
Answer:
Types:
- Organic method
- Yarding method
- Battery cage method
- Furnished cage method.

Stages involved in rearing:
1. Selection of the best layer.
- An active intelligent-looking bird with a bright comb not obese should be selected.
- They are golden or light yellow coloured.
2. Broiler type :
- White Plymouthrock is a fast-growing breed and soft quality meat.
- They have white plumage throughout the body. This is an American breed. It is a fast-growing breed.
3. Dual Purpose breed:
It is known for its massive body having heavy bones. Well feathered and Peacomb is one of the important breed characters.
4. Game breeds:
Aseel:
- The hens are not good egg layers but are good in the incubation of eggs.
- Aseel is noted for its pugnacity high stamina majestic gait.
- This breed is well known for its meat qualities.
5. Ornamental breeds:
Silkie:
- They are reared as pets and for egg production and meat.
- The chicken has a fluffy plumage which is said to feel like silk and satin.
- It has black skin and bones blue ear lobes and five toes on each foot.
Question 33.
Write a note on milk products?
Answer:
Milk products:
Milk is produced by dairy animals which is an emulsion of fat and lactose. Milk also contains enzymes which are destroyed during pasteurization.
Milk is a rich source of vitamin A, B„ Bp and deficient in Vitamin C. Due to its high nutrition value, it serves as a complete food for infants. Dairy products such as yoghurt, cheese, butter, ice cream, condensed milk, curd, and milk powder processed from milk make dairy, a highly farming attraction.