Students can download 10th Social Science History Chapter 2 The World Between Two World Wars Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Solutions History Chapter 2 The World Between Two World Wars
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science The World Between Two World Wars Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
With whom of the following was the Lateran Treaty signed by Italy?
(a) Germany
(b) Russia
(c) Pope
(d) Spain
Answer:
(c) Pope
Question 2.
With whose conquest did the Mexican civilization collapse?
(a) Heman Cortes
(b) Francisco Pizarro
(c) Toussaint Louverture
(d) Pedro I
Answer:
(a) Heman Cortes
Question 3.
Who made Peru as part of their dominions?
(a) English
(b) Spaniards
(c) Russians
(d) French
Answer:
(b) Spaniards
![]()
Question 4.
Which President of the USA pursued “Good Neighbour” policy towards Latin America?
(a) Roosevelt
(b) Truman
(c) Woodrow Wilson
(d) Eisenhower
Answer:
(a) Roosevelt
Question 5.
Which part of the world disliked dollar imperialism?
(a) Europe
(b) Latin America
(c) India
(d) China
Answer:
(b) Latin America
Question 6.
Who was the brain behind the apartheid policy in South Africa?
(a) Verwoerd
(b) Smut
(c) Herzog
(d) Botha
Answer:
(a) Verwoerd
Question 7.
Which quickened the process of liberation in South America?
(a) Support of US
(b) Napoleonic Invasion
(c) Simon Bolivar’s involvement
(d) French Revolution
Answer:
(b) Napoleonic Invasion
Question 8.
Name the President who made amendment to Monroe Doctrine to justify American intervention in the affairs of Latin America.
(a) Theodore Roosevelt
(b) Truman
(c) Eisenhower
(d) Woodrow Wilson
Answer:
(a) Theodore Roosevelt
II. Fill in the blanks
- The founder of the Social Democratic Party was ……………
- The Nazi Party’s propaganda was led by ……………
- The Vietnam Nationalist Party was formed in ……………
- The Secret State Police in Nazi Germany was known as ……………
- The Union of South Africa came into being in May ……………
- The ANC leader Nelson Mandela was put behind the bars for …………… years
- …………… were a military nation.
- Boers were also known as ……………
Answers:
- Ferdinand Lassalle
- Josef Goebbels
- 1927
- The Gestapo
- 1910
- 27
- Aztecs
- Afrikaners
![]()
III. Choose the correct statement
Question 1.
(i) During World War I the primary task of Italy was to keep the Austrians occupied on the Southern Front.
(ii) Germany took to Fascism much later than Italy.
(iii) The first huge market crash in the US occurred on 24 October 1929.
(iv) The ban on African National Congress was lifted in 1966.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (iii) is correct
(c) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
Answer:
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
Question 2.
Assertion (A): A new wave of economic nationalism which expressed itself in protectionism affected the world trade.
Reason (R): This was because the USA was not willing to provide economic aid to the debtor countries.
(a) Both A and R are correct.
(b) A is right but R is not the correct explanation.
(c) Both A and R are wrong.
(d) R is right but it has no relevance to A.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct.
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion (A): The Berlin Colonial Conference of 1884-85 had resolved that Africa should be divided into spheres of influence of various colonial powers.
Reason (R): The war between the British and Boers in South Africa, however, was in defiance of this resolution.
(a) Both A and R are right.
(b) A is right but R is not the right reason.
(c) Both A and R are wrong.
(d) A is wrong and R has no relevance to A.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are right.
IV. Match the Following
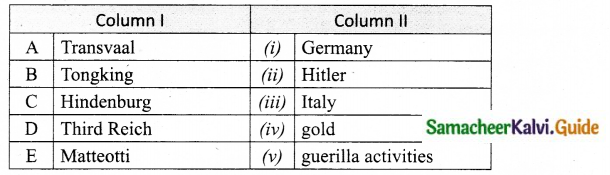
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (v)
C. (i)
D. (ii)
E. (iii)
V. Answer briefly
Question 1.
What do you know of the White Terror in Indo-China?
Answer:
In general, the various periods of violent repression led by the counter-revolutionary forces in any country is called as White terror. In Indo-China, when a large number of peasants revolted against the French government, . headed by the communists. It was crushed by the White terror. Many rebels were killed in this incident.
![]()
Question 2.
Discuss the importance of Ottawa Economic Summit.
Answer:
Bilateral trade treaties between Britain and the member states of the British Empire were signed at an economic summit in Ottawa in 1932. In this summit the participants (including India) agreed to give preference to imperial (British) over non-imperial goods.
Question 3.
Explain the Monroe Doctrine.
Answer:
The president of the USA, Monroe declared that if any of the Europeans interfere anywhere in America, it would be equal to waging a war against the Americans. This threat frightened the European powers. By 1930, the whole of South America was free from European domination. This was called the Monroe Doctrine.
Question 4.
What was the result of Mussolini’s march on Rome?
Answer:
In October 1923, in the context of a long ministerial crisis, Mussolini organised the fascist March on Rome. Impressed by the show of force, the king invited Mussolini to form a government.
![]()
Question 5.
Point out the essence of the Berlin Colonial Conference, 1884-85.
Answer:
The Berlin colonial conference of 1884-85 put forward the idea that Africa should be divided into spheres of influence of various colonial powers.
Question 6.
How did Great Depression impact on Indian agriculture?
Answer:
The Great Depression had a deep impact on Indian agriculture. The value of farm produce, declined by half, while the land rent to be paid by the peasant, remained unchanged. In terms of prices of agricultural commodities, the obligation of the farmers to the state doubled.
Question 7.
Explain the reason for the Smuts-Herzog alliance.
Answer:
When the world economic depression affected South Africa very badly, Smuts believed that coalition Government was necessary to solve the economic problems of the country. Therefore, the South Africa party and the United party made an alliance in 1934. The alliance continued till 1939,
Question 8.
Define “Dollar Imperialism”.
Answer:
‘Dollar Imperialism’ is the term used to describe the policy of the USA in maintaining and dominating over distant lands through economic aid.
![]()
VI. Answer the questions given under each caption
Question 1.
Anti-Colonial Struggle in Indo-China
(a) Define the concept of decolonisation.
Answer:
Decolonisation is a process through which colonial powers transferred institutional and legal control over their colonies to indigenous nationalist government.
(b) What were the three States that formed Indo-China?
Answer:
Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam.
(c) How did Communist ideas help in developing the spirit of anti-colonialism.
Answer:
Communist ideas from mainland China helped in developing the spirit of anti-colonalism in Indo-china. Many became convinced that the considerable wealth of Ind-ochina was benefiting only the colonial power. This aroused the feeling of nationalism which resulted in violence. In 1916 there was a major anti-colonial revolt which was crushed brutally. There were also guerrilla activities in Tongking.
(d) Which was the mainstream political party in Indo-China?
Answer:
The mainstream political party in Indo-china was the Vietnam Nationalist Party. It was composed of the wealthy and middle-class sections of the population.
![]()
Question 2.
Ho Chi Minh
(a) Where was Ho Chi Minh born?
Answer:
Ho Chi Minh was bom in Tongking in 1890.
(b) How did Ho Chi Minh become a popular Vietnam Nationalist?
Answer:
In the Paris peace conference, he insisted the right for Vietnam independence. His articles on newspapers the Pamphlet, “French colonialism on Trial’’, made him popular as a Vietnam nationalist.
(c) What do you know of Ho Chi Minh’s Revolutionary Youth Movement?
Answer:
In 1923, he went to Moscow and learnt revolutionary techniques. In 1925, he founded the Revolutionary Youth Movement.
(d) How was the League for Independence called in Indo-China?
Answer:
League for Independence was called as Viet Minh in Indo-China.
![]()
Question 3.
Political developments in South America
(a) By which year did the whole of South America become free from European domination?
Answer:
By 1830 the whole of South America was free from European domination.
(b) How many republics came into being from Central America?
Answer:
Five republics came into being from the Central America.
(c) In which year was Cuba occupied by the USA?
Answer:
The USA occupied Cuba in the year 1898.
(d) What made oligarchic regimes unpopular in South America?
Answer:
Economic growth, urbanisation and industrial growth in countries like Argentina, Chile, Brazil, and Mexico helped consolidate the hold of middle class and the emergence of militant working class oganisations. At the same time American power and wealth came to dominate Central and South America. These factors made olgarchic regimes unpopular in South America.
VII. Answer in Detail
1. Trace the circumstances that led to the rise of Hitler in Germany.
Answer:
- Germany’s defeat and humiliation at the end of the first world war causa! great shock to the German people.
- A group of seven men including Adolf Hitler met in Munich and founded the National Socialist German Worker’s party which was in short called as Nazi party.
- His attempt to capture Bavaria in 1923.
- His National Revolution on the outskirts of Munch took him to the prison.
- There he wrote his autobiography. Mein Kampf (My struggle) which contained his political ideas.
- In 1932, Presidential election, the communist party won but refused to collaborate with the social democratics.
- Thereafter, Hitler became chancellor in 1933, when Von Hindenburg as president.
- The Nazi state of Hitler, known as Third Reich brought an end to the parliamentary democracy.
- Hitler replaced the Weimar Republic flag by Swastika symbol of Nazi party.
- He declared all the other political parties except Nazi party as illegal.
- He expanded his army of brown shirt and Jack booted wearing men.
- He abolished trade unions, their leaders were arrested. Strikes become illegal, Labour Front was used by the state to control industry, State also controlled press, theatre, cinema, radio and over education.
- Hitler secret police, The Gestapo was formed and run by Himmler, and second in command was Heydrich, who concentrated on army camps.
- Hitler’s foreign policy aimed at restoring the armed strength of Germany.
- All the above circumstances helped the rise of Hitler in Germany.
![]()
Question 2.
Attempt a narrative account of how the process of decolonization happened in India during the inter-war period (1919-39).
Answer:
(i) The decolonisation process started in India with the launch of the Swadeshi Movement in 1905. The outbreak of the First world war in 1914 brought about rapid political and economic changes.
(ii) In 1919, the Government of India Act introduced Dyarchy that provided for elected provinical assemblies as well as for Indian ministers to hold certain portfolios under transferred subjects. The Indian National Congress rejected the arrangements under Dyarchy and decided to boycott the legislature.
(iii) The Government of British India provided incentives for the British iron and steel industry by guaranteeing purchasing contracts. But in case of indigenous industries, support was only in the form of providing ‘technical advice and education’ and the establishment of pioneer factories in new industries sponsored by the government.
(iv) The Government of British India also raised revenue tariffs in the Depression years to gain foreign currency earnings. Britain’s need for gold in the crisis years was met from the export of gold from India. By overvaluing Indian currency, the British made imports cheaper. The currency exchange policy pursued by the British government fuelled tensions between the colonial government and its subjects, and intensified the political agitation against British rule.
(v) The Great Depression shattered Indian agriculture. The value of farm produce declined by half, while the land rent to be paid by the peasant remained intact. The great fall in prices prompted Indian nationalists to demand protection for internal economy. The 1930s saw the emergence of the Indian National Congress as a militant mass movement.
Question 3.
Describe the rise and growth of nationalist politics in South Africa.
Answer:
- The two main political parties in South Africa were:
- (a) The Unionist party which was mainly British and
- (b) The south Africa party which had mainly Afrikaners (or) Boers.
- Botha was the first Prime Minister who belonged to the South African party ruled in co-operation with the British.
- But, the militant section of the South African party formed the National party under Herzog.
- In 1912, The African national Congress was formed by Nelson Mandela. But it was banned and he was put into prison for 27 years.
- In 1920 elections, the National Party won, with 44 seats..
- Herzog wanted a twin policy of supremacy of Whites over the Blacks and Afrikaners over British.
- The South African party was led by smuts, secured 41 seats.
- In this moment, the Unionist party and the South African party merged together. Therefore Smuts gained majority over National party.
- In 1924 elections, National party won supported by the Labour Movement, (composed of white miners)
- The Act passed in 1924 prevented blacks from joining trade Unions. Native blacks suffered in Social, Political and Economic spheres.
- The Great Economic depression brought sufferings to South Africa, therefore, the South African party and the Nationalist party unite in 1934. This smuts-Herzog alliance lasted till 1939.
- Herzog resigned when the parliament decided infavour of second world war.
- Smuts continued as prime minister. When Herzog died, many from that party joined the nationalist.
- Therefore, in 1948, election Reunified National party won over United party.
![]()
VIII. Activity
Question 1.
Each student may be asked to write an assignment on how each sector and each section of population in the USA came to be affected by the Stock Market Crash in 1929.
Answer:
Agriculture sector: The prices of the agricultural crops dropped, so low that many farmers became bankrupt and lost their farms. Livestock was the main source of cash. Com was used to feed Cattle and Pigs. But nothing could help them.
Banking Sector: Confidence in the economy was shattered, Wall street and the banks were no longer seen as reliable. Many refused to put money into stocks. The Federal Reserve did not give aid to banks and small banks collapsed.
Industrial sector: As the country’s economy worsened, local industries affected badly. Production went down. Factories closed. Workers remain unemployed. Almost 15 million people were out of work.
Political Sector: The depression affected politics badly people started disliking Herbert Hoover, the president and his type of laissez faire economics. People voted for Franklin Roosevelt. There was dangerous high U.S debt.
Question 2.
A group project work on Vietnam War is desirable. An album or pictures, portraying the air attacks of the US on Vietnam and the brave resistance put up by the Vietnamese may be prepared.
Answer:
Vietnam war: During the 1950’s and 1960’s the United states fought war to stop communism. Vietnam was a French colony since 1880. They fought for independence and won in 1954. The country was split into North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The United states helped south Vietnam with men and materials. The North Vietnam could control South Vietnam.
In 1969, Richard Nixon, became the president of Vietnam. He started bringing more soldiers into force U.S also increased bombing of North Vietnam. Later, in 1973, they agreed to a cease fire. North, South Vietnamese and U.S.A agreed to stop the war. U.S.A returned home. But communism was not stopped in Vietnam.
![]()
Timeline:
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science The World Between Two World Wars Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The …………… change the political conditions in several countries.
(a) Fascism
(b) Nazism
(c) Depression
(d) Oligarchy
Answer:
(c) Depression
Question 2.
The Greatest craze in America was
(a) Trade
(b) Gambling
(c) Share market
Answer:
(c) Share market
Question 3.
HO-Chi-Minh was greatly influenced by the …………… ideas, that he made him to return to Indo China.
(a) Mas-Tse-Tung
(b) Hitler
(c) Bismarck
(d) Tonking
Answer:
(a) Mas-Tse-Tung
Question 4.
The founder of the fascist party was
(a) Adolf Hitler
(b) Benito Mussolini
(c) Stalin
Answer:
(b) Benito Mussolini
Question 5
…………… became the first Caribbean country to throw off slavery and French Colonial control.
(a) Haiti
(b) Mayapan
(c) Portugal
(d) Lisbon
Answer:
(a) Haiti
Question 6
The great relief was provided to the workers by
(a) ILO
(b) Factory Act
(c) Charter of Labour
Answer:
(c) Charter of Labour
![]()
Question 7.
The stock market crash took place in New York in the year:
(a) 1940
(b) 1939
(c) 1929
(d) 1909
Answer:
(c) 1929
Question 8
The Allied armies occupied the resources rich
(a) Rhineland
(b) Green land
(c) Sudentenland
Answer:
(a) Rhineland
Question 9.
In 1923, Hitler attempted to capture power in
(a) Munich
(b) Bavaria
(c) Leipzig
(d) Weimar
Answer:
(b) Bavaria
Question 10.
For some time Hitler was a
(a) Painter
(b) Teacher
(c) Tailor
Answer:
(a) Painter
Question 11.
About six million jews in Europe were killed and the Nazis termed it as:
(a) The final solution
(b) Concentraion camps
(c) Security
(d) Foreign policy
Answer:
(a) The final solution
Question 12.
The Allies were strengthened by the entry of
(a) Austria
(b) America
(c) Poland
Answer:
(b) America
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks
- The unjust nature of the treaty of ………….. led to the rise of fascism in Italy and Germany.
- Hitler developed violent political base against …………..
- The Nazi state of Hitler was called as …………..
- The Social Democratic party played a major role in the formation of the ………….. republic.
- ………….. in his early days, worked as a cook in a London hotel and later lead a war against USA.
- The two independent Boer states were Transvaal and the …………..
- The Act of ………….. made it impossible for the blacks to acquire land in most of their country.
- The voting right to Blacks was abolished in the …………..
- The decrease in the value of a Country’s currency is called as …………..
- Countries in the ………….. agreed to convert paper money into fixed amount of gold.
- The secret police of Hitler was formed and run by …………..
- Mein Kampf means …………..
- A Spaniard named ………….. collapsed the Aztec empire.
- ………….. declared Brazil’s independence from Portugal.
- The doctrine of ………….. amended by Roosevelt authorised US intervention in Latin America.
Answers:
- Versailles
- Jews
- Third Reich
- Weimar
- Ho-Chi-Minh
- Orange Free States
- 1913
- Cape province
- devaluation
- gold standard
- Himmler
- My struggle
- Herman cortes
- Pedro I
- 1904
![]()
III. Choose the correct statement
Question 1.
(i) The depression changed the political conditions in several countries.
(ii) Mussolini was an elementary school master initially and later became a political journalist with socialistic ideas.
(iii) During World War I, Hitler served the Italian army.
(iv) With the fall of Mussolini, the social democratic party was revived.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) Only (Hi) is correct
(c) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (ii) and (iv) are correct
Answer:
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
Question 2.
(i) Decolonisation process was quickened during the Inter-war period in India.
(ii) The Munroe Doctrine prevented Colonisation of Latin American countries by European powers.
(iii) The economic slump originated in USA in 1929 affected all the countries of
(iv) British setup the Union of South Africa, which was racist in nature.
(a) (ii) and (iv) are correct
(b) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv) are correct
(c) (in) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i) and (ii) are correct
Answer:
(b) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv) are correct
Question 3.
(i) in 1930, Civil disobedience Movement evoked tremendous response in rural India.
(ii) The decision of Britain to involve Indians in the Second World War was a welcoming effect from the Congress Ministry.
(iii) The Ottawa Submit of 1931, helped the colonies to give preference to non-imperial goods.
(iv) Decolonisation process started in India with the introduction of Swadeshi movement in 1905.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
(c) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i) and (iv) are correct
Answer:
(d) (i) and (iv) are correct
![]()
Question 4.
(i) The American and French Revolutions provided inspirations to the Latin Americans.
(ii) Latin American nationalists fought not only with Spain and Portugal but also among each other.
(iii) U.S.A protected the South American republics from Europe.
(iv) U.S.A rejected its right to intervene in Cuban internal affairs.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
(c) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i) aid (iv) are correct
Answer:
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
IV. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Assertion (A): After World War I, there was worldwide credit contraction and break down of the International system of exchange.
Reason (R): Many countries left the gold standard and followed devaluation of the currency.
(a) Both A and R are correct.
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation.
(c) Both A and R are wrong.
(d) R is correct but it has no relevance to A.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct.
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A): In 1990, the ban on ANC was lifted and Mandela was freed.
Reason (R): Apartheid is based on the belief that the political equality of white and black in South Africa would mean Black rule.
(a) Both A and R are correct.
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation.
(c) Both A and R are wrong.
(d) R is correct but it has no relevance to A.
Answer:
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation.
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Jews were removed from Government positions, deprived of citizenship and their establishments were attacked.
Reason (R): Hitler had developed violent political biases against Jews.
(a) Both A and R are correct.
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation.
(c) Both A and R are wrong. ”
(d) R is correct but it has no relevance to A.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct.
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Britain transmitted the effects of depression to its colonies. Reason (R): The great depression of 1929 favoured Britain trade and business.
(a) Both A and R are correct.
(b) A is correct but R is not fhe correct explanation.
(c) Both A and R are wrong.
(d) R is correct but it has no relevance to A.
Answer:
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation.
![]()
Question 5.
Assertion (A): Aztecs form Mexico conquered Maya country and ruled for nearly 200 years.
Reason (R): Spaniards, especially Hernan Cortes and Pizarro helped Aztecs to conquer Maya country.
(a) Both A and R are correct.
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation.
(c) Both A and R are wrong.
(d) R is correct but it has no relevance to A.
Answer:
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation.
V. Match the Followings
Question 1.
Match the Column I with Column II.
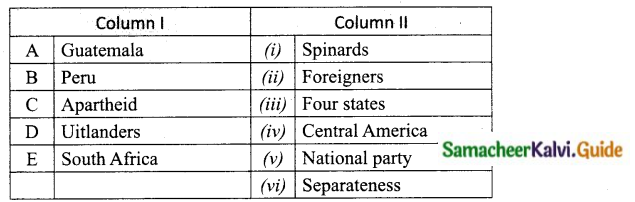
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (i)
C. (vi)
D. (ii)
E. (iii)
![]()
Question 2.
Match the Column I with Column II.
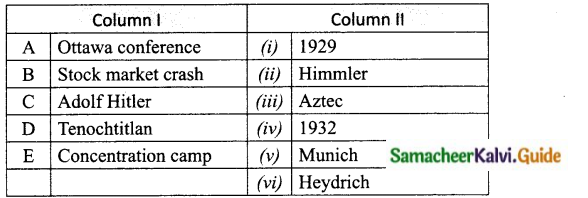
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (i)
C. (v)
D. (iii)
E. (vi)
VI. Answer briefly
Question 1.
Why did Fascism emerged in Italy and Germany?
Answer:
- The first world war gravely weakened the European powers. The trade and financial imbalances left by the war created instabilities throughout the world.
- The conflict between the working and ruling classes that controlled the government became intense. As a result of this Fascism emerged in Italy and Germany.
Question 2.
How did FDR tackle economic depression?
Answer:
- The policy formulated to tackle the economic depression by FDR was known as New Deal.
- It includes Relief, Recovery and Reforms.
![]()
Question 3.
What do you mean by Gold Standard?
Answer:
It is a monetary system where a country’s currency value is directly linked to gold. Countries in the Gold standard agreed to convert paper money into a fixed amount of gold.
Question 4.
What are the four pillars of fascism?
Answer:
- Charismatic Leadership
- Single party rule under a dictator
- Terror
- Economic control
Question 5.
Who were called as Boers?
Answer:
The descendants of original Dutch settlers of South Africa, also known as Afrikaners were called Boers. Their language is Afrikaans. The Boers hated those people whom they referred to as Uitlanders (foreigners).
Question 6.
How did Mussolini seize power?
Answer:
- On October 30, 1922, the fascists organized a march to Rome and showed their strength.
- The Government surrendered and the emperor Victor Emanuel III invited Mussolini to form the Government.
- The fascists seized power without bloodshed under the leadership of Mussolini.
Question 7.
What is meant by Good Neighbour policy.
Answer:
It was the policy of USA after 1933, put forward by Franklin Roosevelt, the president of America. According to the policy, USA would not intervene in the internal affairs of any state and would give economic and technical . assistance to Latin America.
![]()
Question 8.
How did Mussolini put an end to the conflict between the pope and King?
Answer:
- In 1929, Mussolini signed the Latern Treaty with the Pope.
- By this treaty Mussolini recognized the papacy of the Pope in the Vatican city and the Pope recognized the sovereigty of the King in Rome.
- Thus the 60 years conflict between Papacy and the Italian Government came to an end.
Question 9.
Define Oligarchy.
Answer:
Oligarchy can be defined as a small group of people having control of a country.
VII. Answer the questions given under each caption
Question 1.
Fascist Party
(a) Who was the founder of the Fascist party?
Answer:
Benito Mussolini
(b) Write the slogans of Mussolini.
Answer:
“Believe, Obey, Fight” and “The More Force, The More Honour”.
(c) What were the aims of Fascism?
Answer:
- Exaltation of the state.
- Protection of private property.
- Spirited foreign policy.
(d) What was the motto of Fascism?
Answer:
- Everything within the state.
- Nothing against the state.
- Nothing outside the state.
Question 2.
Mussolini
(a) When did Mussolini joined the Fascist party?
Answer:
When the fascist party was founded in 1919, he immediately joined the . fascist party.
(b) What did Mussolini organise?
Answer:
Mussolini organise the Fascist March on Rome and showed his force and strength in October 1922.
(c) How was he called?
Answer:
He was called as Duce (the leader) by his followers.
(d) What was made the religion of Italy?
Answer:
The Roman Catholic faith was made the religion of Italy.
![]()
Question 3.
Hitler’s Aggressive policy
(a) Why did Hitler conquer territories?
Answer:
Hitler conquered territories to accommodate the growing population and to accumulate resources.
(b) How did he violated the Lacarno treaty of 1925?
Answer:
In 1936, he reoccupied Rhine Land by violating the Lacamo treaty of 1925.
(c) What did he demanded from Poland?
Answer:
Hitler demanded the right to construct a military road connecting East Prussia with Germany through Poland and also the surrender of Danzig.
(d) When did he declared war on Poland?
Answer:
Hitler declared war on Poland on 1st September 1939.
![]()
Question 4.
Social Democratic Party
(a) When and where was the social Democratic party founded?
Answer:
Social Democratic party was founded on 23rd May 1863 in Leipzig by Ferdinand Lassalle.
(b) Why did Bismarck out lawed this party from 1878 to 1890?
Answer:
The German superior group of people considered the very existence of the party is a threat to the Security and stability of the newly formed Reich. .
(c) What happened to the social democrats when the party was outlawed?
Answer:
The social democrats were arrested and sent to concentration camps.
(d) When was the party revived?
Answer:
With the fall of Hitler, in 1945 the social Democratic party was revived.
![]()
Question 5.
Boer War
(a) Who were called as Boers?
Answer:
The descendants of original Dutch settlers of South Africa, were called as Boers.
(b) With whom did the Boers fought with?
Answer:
Boers fought with British and the last started for three years 1899-1902. British won finally.
(c) What were the states annexed by the British?
Answer:
The British annexed the two Boer states, the Transvaal and Orange free state,
(d) What happened to the two states of Boers and two colonies of British?
Answer:
The four states formed into a union of South Africa in May 1910.
VIII. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Narrate the emergence of Mussolini and his triumph.
Answer:
- After the treaty of Versailes, in 1919, Italian socialists proclaimed that they follow communism in Russia (Bolsheviks)
- As a powerful speaker, he supported the use of violence and broke with socialists when they opposed Italy’s entry into the war.
- In 1919, when Fascist party was founded, he joined it.
- Fascist raised in strength with support of ex-soldiers, Industrialists and youth.
- In 1922, he led a march to Rome and showed the king, his force and strength.
- Impressed by that, the king invited Mussolini to form the government.
- He advocated dictatorship, and radical authority called as Fascism.
- In 1924 elections, Fascist secured 65% of votes.
- When the fairness of the elections were questioned by Matteotti, a socialist leader, he was murdered and opposition party was banned.
- Assuming the title of Duce in 1926, he became the dictator.
- In 1929, he signed the Lateran treaty with pope and won over the Roman Catholic church by transferring the Vatican city as an Independent state.
- He passed law forbidding strikes and locks outs.
- In 1938, parliament was abolished and was replaced by a body representing the fascist party.
![]()
Question 2.
How did Hitler establish Nazi rule in Germany?
Answer:
Adolf Hitler:
He was born in 1889 in Austria. His father was a customs officer. He lost his parents from his earlyhood. So he went to Vienna for job and was a painter for sometime. During the First World War, he joined the army and fought bravely for which he was awarded the Iron cross.
Rise of Nazis party:
After the war, Hitler did not get any job. So he organized a group of men called the National socialists in 1919, which became the Nazist party.
Beer Hall Revolution:
- In 1923, he made attempt to capture power. It was known as “Beer Hall Revolution”. But he failed in his attempt.
- He was arrested for high treason and sentenced to five years imprisonment.
- While he was in prison he wrote a book called “Mein Kampf” (My struggle), which became the Bible of the Nazis.
Capture of power:
Under the inspiring leadership of Hitler, the Nazi party grew in power and number.
- In the election of 1932, the Nazi party became the 2nd largest group in the German parliament.
- In 1933, the Nazists became the largest party in the German parliament and Hitler became the Chancellor and Hindenburg as president.
- On the death of President Hindenburg, he made himself as President and Chancellor.
- He abolished the Weimar Republic and himself became a dictator.
Question 3.
How did the Munroe Doctrine protected the South American Republics?
Answer:
- When European kings wanted to help the king of Spain to crush the revolutionaries in the South America Colonies, America Interfered.
- The President of the USA, Munroe declared that if Europeans interfered anywhere in America, North or South, it is equal to wage a war against the United states.
- The threat of the president of USA frightened the European powers.
- By this, in 1830, the whole of South America was free from European domination.
- In 1898, after defeating the Spanish, USA occupied Cuba and Puerto Rico.
- USA retained its right to intervene in Cuban internal affairs.
- Later Roosevelt made an important amendment to the Munroe doctrine in 1904. It authorized U.S, Intervention in Latin America.
- Thus, the Munroe Doctrine protected the American continent from European affairs.