Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Guide Pdf Geography Chapter 6 Industries Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Important Questions, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 6 Industries
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Industries Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer.
1. Silk weaving and household industries come under the category of ………………….
a) Small scale industry
b) Large scale industry
c) Marine based industry
d) Capital intensive industry
Answer:
a) Small scale industry
2. On the basis of ownership the industry can be divided into ……………… types
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
Answer:
c) 4
3. Amul dairy industry is the best example of ……………….. sector.
a) Private
b) Public
c) Co-operative sector
d) Joint sector
Answer:
c) Co-operative sector
![]()
4. Iron and Steel and Cement Industries are examples of ………………….. industries.
a) Agro-based
b) Mineral-based
c) Forest-based
d) Marine based
Answer:
b) Mineral-based
5. Tertiary activity is divided into ……………….. types
a) 4
b) 3
c) 2
d) 5
Answer:
c) 2
II. Fill in the blank.
1. Banking is a ……………. economic activity.
Answer:
Tertiary
2. Tertiary activity is divided into ……………. and ……………..
Answer:
Quaternary, Quinary
![]()
3. Government decision-making process comes under the ……………… category of tertiary economic activity.
Answer:
Quinary
4. Raw material based perspective Cotton Textile industry is a ………………. industry.
Answer:
Agro-based
5. Capital required for establishing a large scale industry is more than ………………..
Answer:
One Crore
III. Match the following.
| 1. Judicial sector | a) Private Sector |
| 2. TV telecasts | b) Non Geographical factor |
| 3. Geographical factor | c) Quaternary activity |
| 4. Capital | d) Raw materials |
| 5. BajajiAuto | e) Quinary activity |
Answer:
| 1. Judicial sector | e) Quinary activity |
| 2. TV telecasts | c) Quaternary activity |
| 3. Geographical factor | d) Raw materials |
| 4. Capital | b) Non Geographical factor |
| 5. Bajaj Auto | a) Private Sector |
IV. Distinguish the following.
1. Secondary economic activity and tertiary economic activity.
| Secondary economic activity | Tertiary economic Activity |
| It changes raw materials into usable products through processing and manufacturing | It provided essential services and support industries to function. |
| Eg: Bakery | Eg: Education |
2. Agro-based and marine-based industries.
| Agro-based industry | Marine based industry |
| Industries which use plant and animal-based products as raw materials. | Industries which use products from the sea and oceans as raw materials. |
| Eg: Cotton textile | Eg: Seafood processing |
3. Large scale industries and small scale industries.
| Large Scale Industries | Small Scale Industries |
| The Capital required for the establishment of an industry is more than one crore | The Capital required for the establishment of an industry is less than one crore |
| Eg: Iron and Steel | Eg: Silk wearing |
V. Answer briefly.
1. Define the industry.
Answer:
The industry is a process by which the raw materials are changed into finished products.
2. What is meant by economic activity?
Answer:
Any action that involves the production, distribution, consumption, or service is an economic activity.
![]()
3. Name the major economic activities.
Answer:
The major economic activities are:
- Primary Economic Activities (e.g., Raw cotton production)
- Secondary Economic Activities (e.g., Spinning mill)
- Tertiary Economic Activities (e.g., Trade, Transport)
4. What are the secondary economic activities? Give some examples.
Answer:
The activity which changes raw materials into usable products through processing and manufacturing
eg: Bakery, factory.
5. What is the Quinary activity? Elucidate with an example.
Answer:
- Quinary economic activities refer to the high-level decision making processes by executives in industries, business, education, and government.
- This sector includes top executives or officials in the fields of science and technology, universities health care, etc.
- In our house, our parents make decisions by themselves in some situations.
- Similarly, the Council of Ministers takes decisions to introduce various people welfare schemes in the state.
- These two are examples of quinary activities.
![]()
6. Name the factors responsible for the location of industries.
Answer:
Raw material, Labour, Capital, Market, Power, Land, Transport
7. Write a short note on the following
Answer:
1. Large scale Industries:
The capital required for the establishment of an industry is more than one crore the industry is called a large scale industry.
Eg: Iron & steel, Oil refineries, Cement and Textile industries, etc.
2. Small scale industries:
The capital required for the establishment of an industry is less than one crore, the industry is called a small scale industry.
Eg: Silk weaving and household industries.
VI. Write in detail.
1. Classify and explain the industries based on the source of raw materials.
Answer:
Industries are classified on various bases in the following ways. On the basis of raw materials.
1. Agro Based Industries:
- These industries use plant and animal-based products as their raw materials.
- Example; Food Processing, Vegetable Oil, Cotton Textile, Dairy Products, etc.
2. Mineral-Based Industries:
- These are the industries that use mineral ores as their raw materials.
- Iron made from iron ore is the product of a mineral-based industry. Cement, Machine Tools, etc. are the other examples of mineral-based industries.
3. Marine Based Industries:
- These industries use products from the sea and oceans as raw materials.
- Example; Processed Sea Food, Fish Oil manufacturing units, etc.
4. Forest-Based Industries:
- These industries use forest products as raw materials.
- Example; Pulp and Paper, Furniture and Some Pharmaceuticals industries, etc.
![]()
2. Explain the Geographical factors which affect the location of industries?
Answer:
The geographical factors which affect the location of industries
Raw material:
Materials cannot be transported for long distances, so industries are located near the raw material availability.
Power:
Power is the basic for the industry so it’s generated from conventional sources which should be located near the industries.
Labour:
Availability of cheap and skilled labour is more important.
Transport:
Availability of easy transportation always influences the industry location.
Storage and warehousing:
Finished products should be stored at a suitable storage or warehouse till the goods are taken to the market.
Topography:
The selected site should be flat; which is supported by different transport
Climate:
- Extreme climate condition is not suitable for successful industrial growth. Water Resources:
- Many industries are established near rivers, canals, and lakes for proper functioning.
3. Classify the industries through a flow chart.
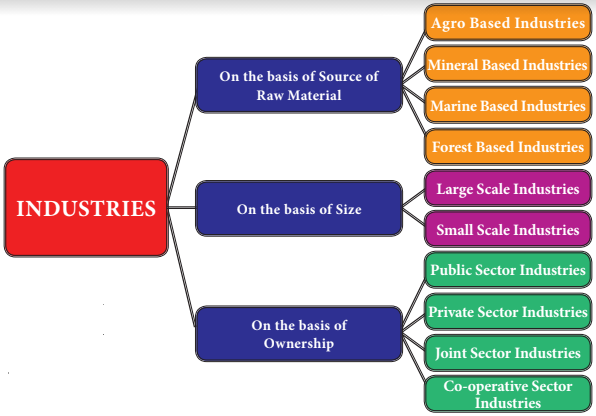
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Industries Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer.
1. Industries are ………………. Economic Activities.
a) Primary
b) Secondary
c) Tertiary
d) Quaternary
Answer:
b) Secondary
![]()
2. …………………… is mostly generated from conventional Sources like mineral oil and water.
a) Thermal Power
b) Water Resources
c) Power
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Power
3. Service sector contributing around …………………… of the Indian Gross Domestic Product.
a) 63%
b) 53%
c) 55%
d) 73%
Answer:
b) 53%
4. …………………… is served by different modes of Transport.
a) Labour
b) Power
c) Topography
d) Climate
Answer:
c) Topography
![]()
5. The factors affecting the location of Industries are …………………….
a) Raw materials
b) Land
c) Water
d) all of these
Answer:
d) all of these
6. …………………… Sector is owned and operated by individuals.
a) Public
b) Private
c) both
d) none
Answer:
b) Private
7. Example for Mineral Based Industries is …………………….
a) Vegetable oil
b) Machine Tools
c) Cotton industry
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Machine Tools
8. Example for Forest-Based Industries is ……………………
a) Paper Industry
b) Processed Seafood
c) Cotton Industry
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Paper Industry
![]()
9. …………………… is a Private Sector Industry.
a) BHEL
b) HAC
c) SAIC
d) Reliance
Answer:
d) Reliance
10. …………………… is a Joint Sector Industry.
a) Amul
b) BHEL
c) Bajaj Auto
d) Maruti Udyog
Answer:
d) Maruti Udyog
II. Fill in blanks.
1. Many …………….. are not fit for human consumption.
Answer:
raw materials
2. The economic strength of a country is always measured by the development of ………….
Answer:
manufacturing industries
![]()
3. …………….. is one of the largest sectors of India.
Answer:
Service Sector
4. The Service sector is the …………….. of the Indian economy.
Answer:
Backbone
5. …………….. is base and essential to run the entire industry.
Answer:
Power
6. …………….. climate is ideal for the cotton textile industry.
Answer:
Cool – humid
7. …………….. is not suitable for successful industrial growth.
Answer:
Extreme Climate
![]()
8. …………….. investment is needed for the establishment of industries.
Answer:
Capital
9. Detroit city in …………….. is known as the world’s traditional automotive centre.
Answer:
Michigan in the USA
10. …………….. is known as Detroit of India.
Answer:
Chennai
11. Creation and transfer of information is …………….. activity.
Answer:
quaternary
12. …………….. is an Example of Marine Based Industries.
Answer:
Fish oil manufacturing units
![]()
13. BHEL ……………..
Answer:
Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd
14. HAL ……………..
Answer:
Hindusthan Aeronautics Limited
15. SAIL ……………..
Answer:
Steel Authority of India
III. Match the following.
| 1. Primary economic activity | a) transportation |
| 2. Secondary economic activity | b) Science and technology |
| 3. Tertiary economic activity | c) Forestry |
| 4. Quaternary economic activity | d) flour into bread |
| 5. Quinary economic activity | e) television |
Answer:
| 1. Primary economic activity | c) Forestry |
| 2. Secondary economic activity | d) flour into bread |
| 3. Tertiary economic activity | a) transportation |
| 4. Quaternary economic activity | e) television |
| 5. Quinary economic activity | b) Science and technology |
IV. Distinguish the following.
1. Primary economic activity and Secondary economic activity.
| Primary economic activity | Secondary economic activity |
| 1. These are the economic activities which have been originated in the very beginning. | Secondary activities are those that change raw materials into usable products through processing and manufacturing. |
| 2. It includes activities such as forestry, grazing, hunting, food gathering, fishing, agriculture, mining, and quarrying. | Bakeries that make flour into bread and factories that change metals and plastics into vehicles are examples of secondary activities. |
2. Private Sector Industries and Public Sector Industries.
| Private Sector Industries | Public Sector Industries |
| These types of industries are owned and operated by individuals or a group of individuals. | These types of industries are owned and operated by the Government. |
| Eg: Bajaj Auto, Reliance, etc. | HAL, BHEL, SAIL are examples of Public sector industries. |
V. Answer briefly.
1. What is Primary economic activity?
Answer:
The activities which have been originated in the very beginning.
![]()
2. What do you know about the service sector?
Answer:
It is one of the largest sectors of India and its the backbone of the Indian economy.
3. What are the non-geographical factors responsible for the location of industries?
Answer:
Capital, Availability of Loans, Government policies or regulation.
4. How are industries classified on the basis of raw materials.
Answer:
- Agro-based industries,
- Mineral-based industries,
- Marine – based industries and
- Forest-based industries.
5. Give a short note on forest-based industries.
Answer:
The industries which use forest products as their raw materials.
6. How does climate become a factor responsible for a location for industries?
Answer:
Extreme Climatic condition is not suitable for the successful industrial growth few industries require specific climate.
7. What is co-operative sector industries.
Answer:
Industries of this kind are owned and operated by the producers or suppliers of raw materials of workers or both.
VI. Write in detail.
1. Classify and explain the industries based on the source of raw materials.
Answer:
On the basis of ownership, industries are
Private Sector Industries:
- Owned and operated by individuals or groups
- BajajAuto.
Public Sector Industries:
- Owned and operated by the Government.
- BHEL, SAIL.
Joint Sector Industries:
- Owned and operated jointly by the government and Individuals groups.
- Indian Synthetic Rubber Ltd.
Co-operative Sector Industries:
- Owned and operated by the producers.
- AMUL.
![]()
2. State the major and fundamental economic activities.
Answer:
Primary Economic Activity:
- Originated from the forest.
- Hunting, Grecizing.
Secondary Economic Activity:
- Changes raw material into usable products through processing and manufacturing.
- Bakery industries.
Tertiary Economic Activity:
- Provides essential services and support industries to function.
- Education, medical.
Quaternary Economic Activity:
- Creation and transfer of information, including research and training.
- Program telecasted in T.V.
Quinary Economic Activity:
- High-level decision-making process by executives.
- Top executives, Judiciary.